This is a list of currently active separatist movements in Oceania. Separatism includes autonomism and secessionism.
Criteria
What is and is not considered an autonomist or secessionist movement is sometimes contentious. Entries on this list must meet three criteria:
- They are active movements with active members.
- They are seeking greater autonomy or self-determination for a geographic region (as opposed to personal autonomy).
- They are citizens/people of the conflict area and do not come from another country.
Under each region listed is one or more of the following:
- De facto state (de facto entity): for unrecognized regions with de facto autonomy.
- Proposed state: proposed name for a seceding sovereign state.
- Proposed autonomous area: for movements towards greater autonomy for an area but not outright secession.
- De facto autonomous government: for governments with de facto autonomous control over a region.
- Government-in-exile: for a government based outside of the region in question, with or without control.
- Political party (or parties): for political parties involved in a political system to push for autonomy or secession.
- Militant organisation(s): for armed organisations.
- Advocacy group(s): for non-belligerent, non-politically participatory entities.
- Ethnic/ethno-religious/racial/regional/religious group(s).
Australia
- Proposed states or autonomous areas: The Aboriginal Tent Embassy has demanded that the government give Aboriginals control of the
 Northern Territory as a state along with various other claimed areas by different advocacy groups.
Northern Territory as a state along with various other claimed areas by different advocacy groups.
- Advocacy groups: Aboriginal Tent Embassy,
 Murrawarri Republic, Sovereign Union of First Nations and Peoples in Australia[1] Tasmanian Aboriginal Centre, Aboriginal Provisional Government, Yuggera Ugarapul Tribal People's,[2][3][4][5]
Murrawarri Republic, Sovereign Union of First Nations and Peoples in Australia[1] Tasmanian Aboriginal Centre, Aboriginal Provisional Government, Yuggera Ugarapul Tribal People's,[2][3][4][5]  Sovereign Yidindji Government,[6] ,
Sovereign Yidindji Government,[6] , Euahlayi People's Republic,[7][8]
Euahlayi People's Republic,[7][8]  Torres Strait Islands,
Torres Strait Islands,  Republic of Mbarbaram,
Republic of Mbarbaram, Wiradjuri Central West Republic, Mirrabooka Sovereign United Nations, Djurin Republic and various others
Wiradjuri Central West Republic, Mirrabooka Sovereign United Nations, Djurin Republic and various others - Political parties: Indigenous-Aboriginal Party of Australia
- Advocacy groups: Aboriginal Tent Embassy,
- Proposed: Norfolk Island as an autonomous region of Australia or free association with New Zealand[9]
- Advocacy groups: Norfolk Island Party[10]
- Proposed state or autonomous area: Western Australia
- Political party: WAxit Party,[11] Western Australia Party
- Proposed: Statehood for Northern Territory within Australia
- Political party: Country Liberal Party
Chile
France
- Proposed state or autonomous region:
 Tahiti or Kingdom of Tahiti
Tahiti or Kingdom of Tahiti
- Political party (secessionist): Tavini Huiraatira
- Political parties (autonomist): A here ia Porinetia, ʻĀmuitahiraʻa o te Nūnaʻa Māʻohi, Ia Ora te Nuna'a, Tāpura Huiraʻatira, No Oe E Te Nunaa
- Ethnic groups: Kanaks, Caldoche
- Proposed state:
 New Caledonia or Kanaky
New Caledonia or Kanaky
Indonesia
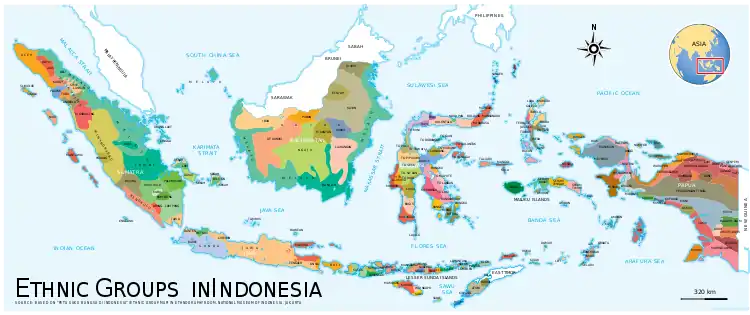
The map of native ethnic groups in Indonesia, foreign ethnic groups such as Chinese, Arab, and Indian are not shown, but usually inhabit urban areas.
- Ethnic group: Moluccans
- Proposed state:
 South Moluccas
South Moluccas
- Government-in-exile: Republik Maluku Selatan (member of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization)
- Advocacy group: Maluku Sovereignty Front
- Ethnic group: Papuans
- Proposed state:
 West Papua or unification with
West Papua or unification with  Papua New Guinea[18]
Papua New Guinea[18]
- Government-in-exile: Republic of West Papua (member of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization)
- Militant organisation: Free Papua Movement, West Papua National Liberation Army
- Advocacy group: United Liberation Movement for West Papua
New Zealand
- People: South Islanders
- Proposed state or autonomus area:
 South Island, New Munster Province or New Munster Republic
South Island, New Munster Province or New Munster Republic - political party: South Island Independence Movement[19]
- pressure group: South Island First[20]
- Proposed state or autonomus area:
- ethnic group: Māori people
- proposed: Independence or autonomy for the Māori people
- political party: Te Pāti Māori[22]
- movement: Māori protest movement
Papua New Guinea
![]() Autonomous Region of Bougainville
Autonomous Region of Bougainville
- Proposed state:
 Bougainville
Bougainville
- Political parties: Bougainville Independence Movement, Bougainville Labour Party, Bougainville People's Congress,New Bougainville Party,Bougainville Islands Unity Party
Solomon Islands
United States
- Ethnic group: Native Hawaiians, Haoles
- Proposed: Creating Native Hawaiian nations within the state of Hawaii equal to Native American nations, Independence under free association with the USA, or complete independence from the USA
- Pressure groups: Nation of Hawaiʻi (organization), Office of Hawaiian Affairs, Ka Lāhui Hawaiʻi
- Political party: Aloha ʻĀina Party
![]() Guam and
Guam and ![]() Northern Mariana Islands[28]
Northern Mariana Islands[28]
- ethnic group: Chamorro people
Vanuatu
- Ethnic group: Ni-Vanuatu
- Proposed autonomous area:
 Vemerana
Vemerana
- Political party: Nagriamel
See also
References
- ↑ "Sovereign Union - First Nations Asserting Sovereignty | Asserting Australia's First Nations Sovereignty into Governance". nationalunitygovernment.org. Retrieved 2023-04-22.
- ↑ "The Murrawarri Republic declaration". Sovereign Union - First Nations Asserting Sovereignty. 2 April 2013. Retrieved 2 March 2023.
- ↑ Geia, Jeremy (12 May 2013). "Murrawarri people take sovereignty campaign to UN". SBS News. SBS. Retrieved 2 March 2023.
- ↑ "Murrawarri people: The Queen Recognises Murrawarri Republic". Sovereign Union - First Nations Asserting Sovereignty. 10 May 2013. Retrieved 2 March 2023.
- ↑ Neubauer, Ian Lloyd (30 May 2013). "Australia's Aborigines Launch a Bold Legal Push for Independence". world.time.com. TIME. Retrieved 2 March 2023.
- ↑ Howden, Saffron (2 November 2015). "Murrumu Walubara Yidindji renounces citizenship to reclaim Australia". The Age. Retrieved 2 March 2023.
- ↑ "ACQUIESCENCE TO THE VOICE THREATENS FIRST NATIONS CONTINUING SOVEREIGNTY". Tribune International (Australia). 2023-01-26. Retrieved 2023-05-29.
- ↑ BushTelegraph, Workers (2013-10-29). "Euahlayi Peoples Republic appoint their Provisional Executive Council of State". Workers BushTelegraph. Retrieved 2023-05-29.
- ↑ "Norfolk Island: Why residents want to ditch Australia for New Zealand". 30 October 2019.
- ↑ "Sense of turmoil prompts birth of Norfolk Island Party". Radio New Zealand. 7 October 2021.
- ↑ (13 March 2021). The objective of the WAxit Party is to improve the fortunes of Western Australia citizens, business and industry by achieving autonomy and independence through secession from the Federation. WAxit.org. Retrieved 25 August 2022
- ↑ "Victorian Independence Movement". vicindependence.com. Retrieved 2022-12-25.
- ↑ "March of the penguin: the forces behind the secessionist Victorian Independence Movement". the Guardian. 2022-06-30. Retrieved 2022-12-25.
- ↑ "Native Village News". Nativevillage.org. Archived from the original on October 24, 2007.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ↑ "easterisland - www". Hectortobar.com. 2004-01-28. Archived from the original on 2017-04-06. Retrieved 2010-07-28.
- ↑ Leyral, Mike (1 May 2023). "French Polynesia: Independentists' victory is first step toward a self-determination referendum". lemonde.fr. Le Monde. Retrieved 30 August 2023.
- ↑ Westnage, Justin (9 May 2023). "With independence off the table for now, what's next for New Caledonia's push for self-determination?". The Conversation. Retrieved 30 August 2023.
- ↑ "Free Papua Movement (OPM)". Retrieved 30 August 2022.
- ↑ "'It will happen' - South Island Independence Movement vows to break away".
- ↑ "SOUTH ISLAND FIRST".
- ↑ "John Tamihere | Why Is Our Desire For Self-Governance Viewed As Separatism?".
- ↑ "National leader Christopher Luxon has expanded on why he believes National can't work with Te Pāti Māori, saying the latter is "separatist" and "radical"".
- ↑ "Solomons province pushes for independence in 'China switch' fallout". Reuters. 2020-09-02. Retrieved 2020-09-06.
- ↑ "Explainer: -What is behind unrest in the Solomon Islands?". Reuters.
- ↑ "While US celebrates its independence, Hawaiians still wait for theirs".
- ↑ "Why Hawaiian sovereignty has undeniable context for the Maui fires". NBC News.
- ↑ "What Is the Hawai'i Sovereignty Movement?".
- ↑ "Vision for an Independent Guåhan: We Are Stronger Than We Think".
- ↑ "Counter China by Making Guam a State".
- ↑ "Guam's Continuing Quest for Self-Governance".
- ↑ Gilbert, Haidee Eugenio. "'Right to self-determination': Guam appeals political status case to US Supreme Court". Pacific Daily News.
- ↑ Leon-Guerrero, Ken. "Letter: Guam just isn't ready for self-determination". Pacific Daily News.
- ↑ "UNPO: Guam Prepares for Largest March for Self-Determination on September 2nd 2019". unpo.org.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
.svg.png.webp)
_(Polynesia_centered).svg.png.webp)

.svg.png.webp)
_(US50)_(-grid).svg.png.webp)
.svg.png.webp)