| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 75 seats in the House of Representatives 38 seats were needed for a majority in the House 18 (of the 36) seats in the Senate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Registered | 2,835,327 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 1,934,478 (78.30%)[lower-alpha 1] ( | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
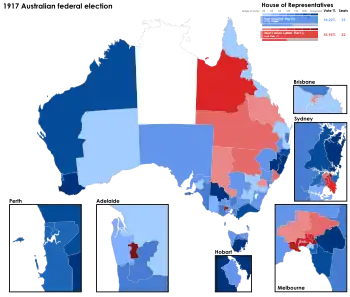 Results by division for the House of Representatives, shaded by winning party's margin of victory. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1917 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 5 May 1917. All 75 seats in the House of Representatives and 18 of the 36 seats in the Senate were up for election. The incumbent Nationalist Party, led by Prime Minister Billy Hughes, defeated the opposition Labor Party led by Frank Tudor in a landslide.
Hughes, at the time a member of the ALP, had become prime minister when Andrew Fisher retired in 1915. The Australian Labor Party split of 1916 over the conscription issue had led Hughes and 24 other pro-conscription Labor MPs to split off as the National Labor Party, which was able to form a minority government supported by the Commonwealth Liberal Party under Joseph Cook. Later that year, National Labor and the Liberals merged to form the Nationalist Party, with Hughes as leader and Cook as deputy leader. The election was fought in the aftermath of the 1916 plebiscite on conscription, which had been narrowly defeated. The Nationalists won a decisive victory, securing the largest majority government since Federation. The ALP suffered a large electoral swing against it, losing almost seven percentage points of its vote share compared with 1914. The swing was magnified by the large number of former Labor MPs who followed Hughes out of the party. This election would be the last federal election using the first past the post election system as Australia switched to the preferential voting system in 1919.
This is the first of two elections (the other in 1922 also with Hughes as the incumbent Prime Minister), in which the incumbent Prime Minister, Hughes, had successfully transferred to another seat.
At this election, Hughes had abandoned West Sydney, which he won with 75.3% of the vote as the Labor candidate at the previous election in 1914, and moved to Bendigo instead, winning it as the Nationalist candidate: unlike 1922, Hughes made his seat transfer in 1917 by defeating that seat’s incumbent member, Alfred Hampson, for re-election, the only time that an incumbent Prime Minister has defeated another MP for his seat.
Except for the 1917 and 1922 elections, all other elections have seen the incumbent Prime Minister recontest the seat that they held prior to the election.
Results
House of Representatives
| Party | Votes | % | Swing | Seats | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nationalist | 1,021,138 | 54.22 | +7.01 | 53 | +21 | |
| Labor | 827,541 | 43.94 | –6.96 | 22 | –20 | |
| Independents | 34,755 | 1.85 | −0.05 | 0 | –1 | |
| Total | 1,883,434 | 75 | ||||
| Nationalist | Win | 53 | +21 | |||
| Labor | 22 | −20 | ||||
- Notes
- Ten members were elected unopposed – seven Nationalist and three Labor.
- The changes recorded for the Nationalist Party are with regard to the Commonwealth Liberal Party's performance in 1914.
Senate
| Party | Votes | % | Swing | Seats won | Seats held | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nationalist | 3,516,354 | 55.37 | +7.60 | 18 | 24 | +18 | |
| Labor | 2,776,648 | 43.72 | −8.42 | 0 | 12 | −18 | |
| Socialist Labor | 32,692 | 0.51 | +0.51 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Independents | 24,676 | 0.39 | +0.39 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 6,350,370 | 18 | 36 | ||||
- Notes
- The changes recorded for the Nationalist Party are with regard to the Commonwealth Liberal Party's performance in 1914.
Seats changing hands
- Members listed in italics did not contest their seat at this election.
Post-election pendulum
| Non-government seats | |||
| Australian Labor Party | |||
| Marginal | |||
| Macquarie (NSW) | Samuel Nicholls | ALP | 00.0 |
| Brisbane (Qld) | William Finlayson | ALP | 00.0 |
| Maribyrnong (Vic) | James Fenton | ALP | 02.2 |
| Capricornia (Qld) | William Higgs | ALP | 02.3 |
| Barrier (NSW) | Michael Considine | ALP | 02.5 vs IND |
| Darling (NSW) | Arthur Blakeley | ALP | 03.3 |
| Hunter (NSW) | Matthew Charlton | ALP | 03.4 |
| Dalley (NSW) | William Mahony | ALP | 04.0 |
| Bourke (Vic) | Frank Anstey | ALP | 04.5 |
| Maranoa (Qld) | Jim Page | ALP | 04.8 |
| Fairly safe | |||
| Newcastle (NSW) | David Watkins | ALP | 08.0 |
| Safe | |||
| Melbourne (Vic) | William Maloney | ALP | 10.3 |
| Batman (Vic) | Frank Brennan | ALP | 10.9 |
| Kennedy (Qld) | Charles McDonald | ALP | 12.8 |
| South Sydney (NSW) | Edward Riley | ALP | 13.3 |
| Cook (NSW) | James Catts | ALP | 14.4 |
| Melbourne Ports (Vic) | James Mathews | ALP | 16.3 |
| West Sydney (NSW) | Con Wallace | ALP | 16.5 |
| Very safe | |||
| Yarra (Vic) | Frank Tudor | ALP | 21.3 |
| Adelaide (SA) | George Edwin Yates | ALP | unopposed |
| Ballaarat (Vic) | Charles McGrath | ALP | unopposed |
| East Sydney (NSW) | John West | ALP | unopposed |
See also
Notes
- ↑ Turnout in contested seats
References
External links
- University of WA election results in Australia since 1890



