| Battle of Lissa | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Third Italian War of Independence | |||||||
 The Sea Battle of Lissa, Carl Frederik Sørensen | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
26 ships: 4 ironclads 3 armoured frigates 1 ship of the line 5 screw frigates 1 screw corvette 2 screw gunboats 6 gunboats 1 screw tender 3 steamships |
32 ships: 9 ironclads 1 armoured frigate 2 armoured corvettes 7 screw frigates 1 screw corvette 2 paddle corvettes 1 sloop 3 gunboats 2 avisos 4 merchantmen | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 176 killed and wounded[1] |
660 killed and wounded[1] 2 ironclads sunk | ||||||
 Location within Croatia | |||||||
The Battle of Lissa (or Battle of Vis) (Croatian: Bitka kod Visa) took place on 20 July 1866 in the Adriatic Sea near the Dalmatian island of Vis (Italian: Lissa) and was a significant victory for an Austrian Empire force over a numerically superior Italian force. It was the first major sea battle between ironclads and one of the last to involve deliberate ramming. The Italian navy fired roughly 1450 shots during the engagement but failed to sink any Austrian ship and lost two ironclads.
One of the main reasons for this poor performance was internal rivalry between the Italian fleet commanders: for example, Italian Vice Admiral Albini, with his ships, did not engage the enemy during the battle.[2] The engagement was made up of several small battles: the main battle was between seven Austrian and twelve Italian ironclads and showed the ability of Austrian Admiral Wilhelm von Tegetthoff to divide his more numerous opponents and then destroy the isolated ironclads.
Background
The battle occurred as part of the Third War of Italian Independence in which Italy allied with Prussia in the course of its conflict against Austria. The major Italian objective was to capture Venice and at least part of its surrounds from Austria. The fleets were composed of a mix of unarmoured sailing ships with steam engines, and armoured ironclads also combining sails and steam engines. The Italian fleet of 12 ironclads and 17 unarmoured ships outnumbered the Austrian fleet of 7 and 11 respectively. The Austrians were also severely outmatched in rifled guns (276 to 121) and total weight of metal (53,236 tons to 23,538 tons).[3] A single turret ship took part in the action — the Italian Affondatore. Piedmontese Count Carlo di Persano commanded the Italian fleet, while the Austrian fleet was commanded by Konteradmiral Wilhelm von Tegetthoff. The fort on the island of Lissa was under the command of Oberst David Urs de Margina, an ethnic Romanian from Transylvania. The Italian fleet under Persano was divided into three divisions: Persano commanded the main battle force with 9 ironclads; his deputy, Albini, commanded a "support" division (engaged mainly in landings); and Admiral Giovanni Vacca commanded a third "reserve" division with minor wooden ships. The attacking Austrian fleet was also split into three divisions. The 1st Division consisted of the armoured ships, while the 2nd consisted of the powerful but obsolete unarmoured wooden ship of the line Kaiser and 5 frigates. The 3rd Division consisted of the smaller screw gunboats and armed merchantmen. The armed merchant cruiser Stadion was ahead of the fleet acting as a scout.
The three Austrian divisions were formed up into three consecutive arrowhead or "V" formations; the armoured 1st division under Tegetthoff was in the vanguard, the weaker gunboats and paddle steamers of the 3rd division to the rear, while the powerful but unarmoured vessels of Kommodor Petz's 2nd division were in the centre. The Austrian plan, due to their weaker firepower, was to close quickly into a melée, and to use close range fire and ramming to sink a small portion of the Italian fleet, thereby breaking the Italian will to fight. The Italians, despite their numerical superiority, were not prepared for battle. They were busy preparing for landings on the island of Vis (Lissa) when the news that the Austrian fleet was at sea and seeking battle reached them. Persano cancelled the landings, ordered the fleet into line abreast but having second thoughts, cancelled that order (creating confusion among the Italian commanders) and ordered the fleet into three divisions in a line ahead formation, the same formation as at battles in the age of sail. The 1st division in the vanguard consisted of Principe di Carignano, Castelfidardo and Ancona under Admiral Vacca, Captain 1st Class Faà di Bruno's 2nd division in the centre consisted of Re d'Italia, Palestro and San Martino, and the 3rd division to the rear had the Re di Portogallo, Regina Maria Pia and, at the extreme rear, Varese under Captain Augusto Riboty. In total, the Italians had 11 ironclads in the battle line. The other (wooden) ships were dispersed into the battleline. The exception was Affondatore, which was on the far side of the 2nd squadron and out of the battleline. Persano may have intended this to be an uncommitted reserve. Before the battle Persano caused more confusion by deciding to transfer his flag to the Affondatore and the 2nd and 3rd Divisions slowed to allow Re d'Italia to lower her boats. However the signal to slow down never reached the 1st Division and they continued to steam on, allowing a gap to open in the Italian battle line. To compound the error Persano never signaled the change of flag, and throughout the action the Italians continued to look to the old flagship Re d'Italia for orders rather than Affondatore.
Battle

In the Austrian fleet there was enthusiasm but also fear, because the Italian fleet was bigger: 12 ironclads and 19 wooden ships with 641 guns, while the Austrians had only 7 ironclads and 20 wooden ships with 532 guns.... When the engagement began, the Italian division led by Vacca was on a long circuit of the north of Lissa, and so was at first away from the battle. And it is curious that the Albini ships with their 398 guns, though ordered by Persano to do so, did not fire a single shot all through the battle.[4]
Having ignored warnings from his pickets of suspicious ships in sight, Persano had effectively allowed the Austrians to ambush his force while it was still forming. Tegetthoff, seeing a gap opening between the 1st and 2nd Divisions, forced his fleet into it and concentrated on raking the Italians and ramming. This meant that he allowed his T to be crossed. While the Austrians were approaching, Vacca's 1st Italian Division threw a heavy weight of fire at them. The Austrians could only reply with their chase guns. Because Persano was in the process of transferring his flag, no general order was given. The 2nd and 3rd Divisions did not join in and the Austrians crossed the killing area, suffering some serious damage but no ships were lost. Drache on the extreme right (starboard) wing of the Austrian 1st Division was hit 17 times by heavy shells, losing her mainmast and temporarily losing propulsion. Her captain, Heinrich von Moll,[5] was decapitated by a heavy shell, but his subordinate, Karl Weyprecht, brought the ship back into the fight. By 10:43 am the Austrians had brought the Italian vanguard to close action. Habsburg, Salamander and Kaiser Max on the Austrian left wing had engaged the Italian 1st Division, while the right wing of Don Juan d'Austria, Drache and Prinz Eugen engaged the Italian 2nd Division. Persano, now on the most powerful warship in either fleet, Affondatore, stayed clear of the engagement.[6]
With the confusion in the Italian vanguard, Kommodor von Petz took the opportunity to take his 2nd Division to the Italian rear and fall on their 3rd Division. The unarmoured wooden ships of the Austrian 2nd Division were facing modern ironclads armed with heavy guns, yet despite suffering heavy fire they held together. The screw frigate Novara was hit 47 times, and her captain, Erik af Klint, was killed. Erzherzog Friedrich was hit by a heavy shell below the waterline but still remained afloat, while Schwarzenberg was disabled by heavy Italian fire and set adrift. Seeing things going badly, Persano decided to ram the unarmoured screw battleship Kaiser rather than one of the armoured ships engaged with the Italian 2nd Division much nearer him. However, Kaiser managed to dodge Affondatore. Taking heart from his admiral, the captain of Re di Portogallo laid heavy fire on Kaiser with his rifled guns. At the last moment, von Petz turned into the ram, conducting a counter ram. The impact tore off Kaiser's stem and bowsprit, leaving her figurehead embedded in Re di Portogallo. The Italian used the opportunity to rake Kaiser with fire, putting her mainmast and funnel into the sea. The smoke was so great that as they backed off for another ram they lost sight of each other and ended the duel. At roughly the same time, Tegetthoff threw his flagship Erzherzog Ferdinand Max (commanded by Maximilian Daublebsky von Sterneck) at first at the former Italian flagship, Re d'Italia, and then at Palestro. In both cases he scored only glancing blows, but these caused serious damage, especially to Palestro, which was dismasted and set afire.
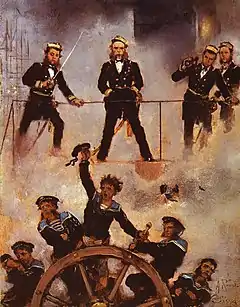
Palestro's captain, Cappellini, pulled his ship out of the line. His crew refused to abandon their captain and Palestro finally blew up and sank at 2.30pm, with only 19 survivors out of a complement of 230. Meanwhile, Erzherzog Ferdinand Max was circling Faà di Bruno's Re d'Italia, pouring on fire before surging forward and achieving a good impact with her ram, aided by the Italian having reversed in a poorly thought-out attempt to avoid crossing the Austrian's bows at the crucial moment. This put an 18 ft (5.5 m) hole below Re d'Italia's waterline, and she struck her colours and sank two minutes later. According to legend, her captain shot himself after giving the order to strike the colours.[7] As Erzherzog Ferdinand Max limped away, damaged after conducting three ramming attacks, Ancona closed on her attempting to ram. The Italian gunners got a full broadside off at point blank range, but while they had remembered the gunpowder, in the excitement they had forgotten to load the shot. After his encounter with Re di Portogallo earlier in the battle and having fought his way clear of Maria Pia, Kommodor von Petz's Kaiser found itself at close range with Affondatore.
Despite being a perfect target for a ram, Kaiser survived when Persano ordered Affondatore to turn away.[8] Tegetthoff's victory was saluted by his mariners – mainly Croats and Venetians, from Venetia, Istria and Dalmatia – with the traditional Venetian cry of victory: "Viva San Marco!" ("Hurrah with Saint Mark!").[9] By 15:00, Tegetthoff had led his fleet into the harbour of Lissa, where the damaged Kaiser had already arrived, undisturbed by the Italian ships; despite Persano's orders to engage the Austrian vessels, both Albini and Vacca ignored the orders, as the latter candidly testified at Persano's trial.[10] With his ships low on fuel and ammunition, and his crews spent, Persano led his fleet back towards his home port of Ancona. Kaiser's encounter with Affondatore was the last major action of the battle. With two armoured ships sunk, the Italians withdrew, although there would be some exchange of long range fire for several hours.
Aftermath
In Italy, Persano announced a victory, causing much initial celebration until the real outcome of the battle was publicized. The outrage over the loss of two ironclads was huge and Persano after the battle was judged by the Italian Senate, condemned for incompetence and stripped of his rank, but Admiral Albini was merely relieved of command, and Admiral Vacca had to retire soon after for age limits.[11][12] Tegetthoff returned home a hero, was promoted Vizeadmiral, and is considered one of the greatest naval commanders in Austrian history. The Italian defeat was overshadowed by the crushing Prussian victory over the Austrian Army at Königgrätz. Austria, humbled by Prussia and bullied by Napoleon III of France, agreed to cede Venetia to Italy despite the overall failure of the Italian war effort. Tegetthoff's efforts were instrumental in preventing the Italians from annexing some of the Dalmatian islands, which were once part of the Republic of Venice.
The importance of ramming in the battle led to naval designers, over the next 50 years, equipping future warships (especially battleships and cruisers) with ram bows. That aggravated a number of incidents of ships being sunk by their squadron-mates in accidental collisions. Ramming never featured as a viable battle tactic again. The fixation on ramming may also have inhibited the development of gunnery. Modern commentators now take the view that Lissa occurred during a period of weapons development when armour was considerably stronger than the guns available to defeat it. This was compounded, on the Italian side, by poor gunnery and, on the Austrian side, by the fact that a number of their ships (including Ferdinand Max) had been forced to go into battle without their full armament owing to the Prussian embargo. Kaiser, remarkably, reported herself fit for action the morning after the battle. Her feat, an unarmored wooden ship willingly engaging four ironclads at short range, appears to be unprecedented and was never repeated.
Order of battle
Vessels are ranked by fighting power (most powerful first).
Austrian Empire
1st Division – Armoured ships
- Erzherzog Ferdinand Max (fleet flag, 2nd class armoured frigate, launched 1865, 5130t, 16-48pdr SB, 4-8pdr SB, 2-3pdr SB. 123 mm iron belt over the battery, 12.5kts)
- Habsburg (launched 1865, as Erzherzog Ferdinand Max)
- Kaiser Max (3rd class armoured frigate, launched 1862, 3588t, 16-48pdr SB, 1-12pdr SB, 1-6pdr SB, 15-24pdr ML rifles. 110 mm iron belt, 11.4kts)
- Don Juan d'Austria (launched 1862, as Kaiser Max)
- Prinz Eugen (launched 1862, as Kaiser Max)
- Drache (armoured corvette, launched 1861, 2750t, 10-48pdr SB, 18-24pdr MLR, 1-8pdr SB, 1-4pdr SB landing gun, 115 mm iron belt, 11kts)
- Salamander (launched 1861, as Drache)
2nd Division – Wooden steam warships
_-_NH_87011.jpg.webp)
- Kaiser (squadron flag, 2-decker screw ship of the line, launched 1858,[13] 5811t, 2-24pdr ML rifles, 16-40pdr SB, 74-30pdr SB, wooden and unarmoured, 11.5kts)
- Novara (screw frigate, launched 1850, 2615t, 4-60pdr shell, 28-30pdr SB, 2-24pdr BL rifles, 1-12pdr landing gun, 1-6pdr landing gun, 12kts)
- Schwarzenberg (screw frigate, launched 1853, 2614t, 6-60pdr Paixhans shell guns, 26-30pdr Type 2 ML, 14-30pdr Type 4 ML, 4-24pdr BL rifles, 11kts)
- Radetzky (screw frigate, launched 1854, 2234t, 6-60pdr Paixhans shell guns, 40-24pdr SB, 4-24pdr BL rifles, 9kts)
- Donau (launched 1856, 2165t, otherwise as Radetzky)
- Adria (launched 1856, 2165t, otherwise as Radetzky)
- Erzherzog Friedrich (screw corvette, launched 1857, 1697t, 4-60pdr Paixhans shell guns, 16-30pdr SB, 2-24pdr BL rifles, 9kts)
3rd Division – Minor craft
- Narenta (screw gunboat, 2-48pdr SB, 2-24pdr BL rifles)
- Kerka (as Narenta)
- Hum (2nd class gunboat, 2-48pdr SB, 2-24pdr BL rifles, 11?kts)
- Vellebich (as Hum)
- Dalmat (as Hum)
- Seehund (2nd class gunboat, 2-48pdr SB, 2-24pdr BL rifles, 11kts)
- Wal (as Seehund)
- Streiter (as Seehund)
- Reka (as Seehund)
- Andreas Hofer (screw tender, 3-30pdr SB)
- Kaiserin Elisabeth (sidewheeler steamer (radaviso), launched 1854, 4-12pdr SB)
- Greif (sidewheel steamer, 2-12pdr SB)
- Stadion (unarmed merchant steamer. Employed as a scout and was in the vanguard)
Kingdom of Italy
.jpg.webp)
Armoured ships
- Affondatore (fleet flag, ironclad turret ram, launched 1865, 4006t, 2-9in 300pdr Armstrong SB (2x1), 5in iron on belt and turrets, 12kts)
- Re d'Italia (squadron flag, 2nd class armoured frigate {broadside ironclad}, launched 1863, 5610t, 6-72pdr SB shell, 32–164 mm breechloading rifles, 4.5in iron belt, 10.5kts)
- Re di Portogallo (launched 1863, as Re d'Italia)
- Regina Maria Pia (2nd class armoured frigate {broadside ironclad}, launched 1863, 4201t, 4-72pdr SB shell, 22–164 mm breechloading rifles, 4.3in iron belt, 12kts)
- San Martino (launched 1863, as Regina Maria Pia)
- Castelfidardo (launched 1863, as Regina Maria Pia)
- Ancona (launched 1864, as Regina Maria Pia)
- Principe di Carignano (3rd class armoured frigate {broadside ironclad}, launched 1865, 3446t, 10-72pdr 8in SB shell, 12–164 mm breechloading rifles, 4.75in iron belt, 10kts)
- Formidabile (broadside ironclad, launched 1861, 2682t, 4-72pdr SB shell, 16–164 mm (5.5 in) breechloading rifles, 4.3in iron belt, 10kts (19 km/h))
- Terribile (launched 1861, as Formidabile)
- Palestro (armoured corvette {coast defence ironclad}, launched 1865, 2165t, 4–200 mm muzzleloading rifles, 1–165 mm muzzleloading rifle, 4.5in iron belt, 8kts)
- Varese (launched 1865, as Palestro)
Wooden steam warships
- Gaeta (ex-Neapolitan screw frigate, launched 1861, 3917t, 8–160 mm ML rifles, 12-108pdr shell, 34-72pdr shell)
- Maria Adelaide (ex-Sardinian screw frigate, launched 1859, 3429t, 10–160 mm ML rifles, 22-108pdr shell, 19 small guns) (Squadron Flag)
- Duca di Genova (ex-Sardinian screw frigate, launched 1860, 3459t, 8–160 mm ML rifles, 10-108pdr shell, 32-72pdr shell)
- Garibaldi (ex-Neapolitan screw frigate Borbone, launched 1860, 3390t, 8–160 mm ML rifles, 12-108pdr shell, 34-72pdr shell)
- Principe Umberto (ex-Sardinian screw frigate, launched 1861, 3446t, 8–160 mm ML rifles, 10-108pdr shell, 32-72pdr shell, 4 small guns)
- Carlo Alberto (ex-Sardinian screw frigate, launched 1853, 3231t, 8–160 mm ML rifles, 10-108pdr shell, 32-72pdr shell guns, 7 small guns)
- Vittorio Emanuele (ex-Sardinian screw frigate, launched 1856, 3201t, 8–160 mm ML rifles, 10-108 and 32-72pdr shell guns, 7 small guns)
- San Giovanni (ex-Sardinian screw corvette, launched 1861, 1752t, 8–160 mm ML rifles, 14-72 pounder shell, 12 small guns)
- Governolo (ex-Sardinian sidewheel paddle corvette, launched 1849, 2243t, 10-108pdr shell, 2 small guns)
- Guiscardo (ex-Neapolitan sidewheel paddle corvette, launched 1843, 1343t, 2–160 mm ML rifles, 4-72pdr shell)
Minor ships
- Giglio (ex-Tuscan sloop, launched 1846, 246t, 2 SB of unknown type)
- Cristoforo Colombo (gunboat, 4-30pdr SB)
- Gottemolo (as Cristoforo Colombo)
- Unknown (as Cristoforo Colombo)
- Esploratore (sidewheel dispatch vessel, launched 1863, 981t, 2-30pdr SB, 17 knots)
- Messaggere (launched 1863, as Esploratore)
- Indipendenza (unarmed merchantman)
- Piemonte (unarmed merchantman)
- Flavio Gioia (unarmed merchantman)
- Stella d'Italia (unarmed merchantman)
Namesakes
SMS Lissa, an Austro-Hungarian broadside ironclad, was launched in 1869 and named in honor of the battle of Lissa. She was scrapped between 1893 and 1895.
Alfredo Cappellini of Palestro was the namesake of an Italian armored gunboat launched in 1868 and an Italian monitor Alfredo Cappellini launched in 1915.
Faà di Bruno of Re d'Italia was the namesake of an Italian armored gunboat launched in 1868 and a monitor launched in 1916. During World War II, an Italian submarine with his name was sunk in 1940 near Scotland.
Augusto Riboty of Varese was the namesake of an Italian destroyer leader launched in 1916 (and which survived both world wars, finally being scrapped in 1951).
Vizeadmiral von Tegetthoff was the namesake of an Austro-Hungarian center battery ironclad launched in 1878, a class of dreadnought battleships and the lead vessel of that class, launched in 1912. Ironically, at the end of World War I, the latter ship was given to the Italian Royal Navy, which in 1924–25 scrapped the ship that bore the name of the man who had defeated it in its first battle.
Notes
- 1 2 Stevens (1942), pp. 261–62
- ↑ "The Italian "mistakes" in Lissa battle (in Italian)". lastoriamilitare.splinder.com. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ↑ Stevens (1942), p. 257
- ↑ Scotti, Giacomo. Lissa 1866. la grande battaglia per l'Adriatico First chapter: "Nella flotta austriaca non mancava l’entusiasmo ma erano presenti anche timori, la flotta italiana era più numerosa:12 corazzate e 19 unità di legno con 641 cannoni.Gli austriaci avevano solo 7 corazzate e 20 unità di legno con 532 cannoni.... La divisione Vacca intanto, ormai lontana, stava compiendo un larghissimo giro a nord che la allontanava dalla battaglia. Per quanto sollecitate dal Persano le navi di Albini invece, forti di 398 cannoni, non intervenivano"
- ↑ "BLKÖ:Moll, Heinrich Freiherr von – Wikisource". de.wikisource.org. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ↑ It has been pointed out the contradicting facts that the Affondatore was the most heavily hit Italian ship, and that even the Austrian battle report recognized that Persano exposed himself to the enemy fire (Storia Militare n. 215, Parma 2011, pp. 56–65)
- ↑ Some eyewitnesses told that the captain jumped overboard; however, he drowned, being unable to swim. Storia Militare N. 215, pp. 64–65.
- ↑ A participant to the battle explained this as being due to Affondatore's turret poorly arrayed viewports, which led Persano and her captain to give confusing orders. Storia Militare n. 215, p. 61.
- ↑ "La battaglia di Lissa". Wars. May 2011.
- ↑ Storia Militare N. 215, p. 62
- ↑ Storia Militare N. 215, pp. 63–65
- ↑ Bertoldi, Silvio. Sangue Sul Mare. (Mondadori 2006)
- ↑ "The history of Uljanik". Uljanik d.d. Retrieved 2 September 2010.
A contemporary account is available in "The Engineer"May 15, 1885. http://www.gracesguide.co.uk/images/d/d4/Er18850515.pdf
Bibliography
- Stevens, William Oliver and Allan Westcott (1942). A History of Sea Power. Doubleday.
- Sacchi, Martino. Navi e cannoni: la Marina italiana da Lissa a oggi, Giunti, Firenze 2000.
- Sandler, Stanley. "The Emergence of the Moder Capital Ship." Associated University Presses, Lexington, KY, 1979.
- Scotti, Giacomo. Lissa 1866. la grande battaglia per l'Adriatico, LINT Editoriale, Trieste 2004. ISBN 88-8190-211-7
- Martino, Ermanno. Lissa 1866: Perché?, in Storia Militare, N. 214 and N. 215, Parma 2011. ISSN 1122-5289
- Giorgierini, Giorgio. La guerra italiana sul mare, Oscar Mondadori, Milano 2002. ISBN 978-8804501503
.svg.png.webp)
_(1868-1918).svg.png.webp)
