| Canary Wharf | |
|---|---|
| Central business district | |
From top, left to right: Canary Wharf skyline; Canary Wharf DLR station; Canary Wharf tube station; Canada Square; Cabot Square; Crossrail Place; West India Quay | |
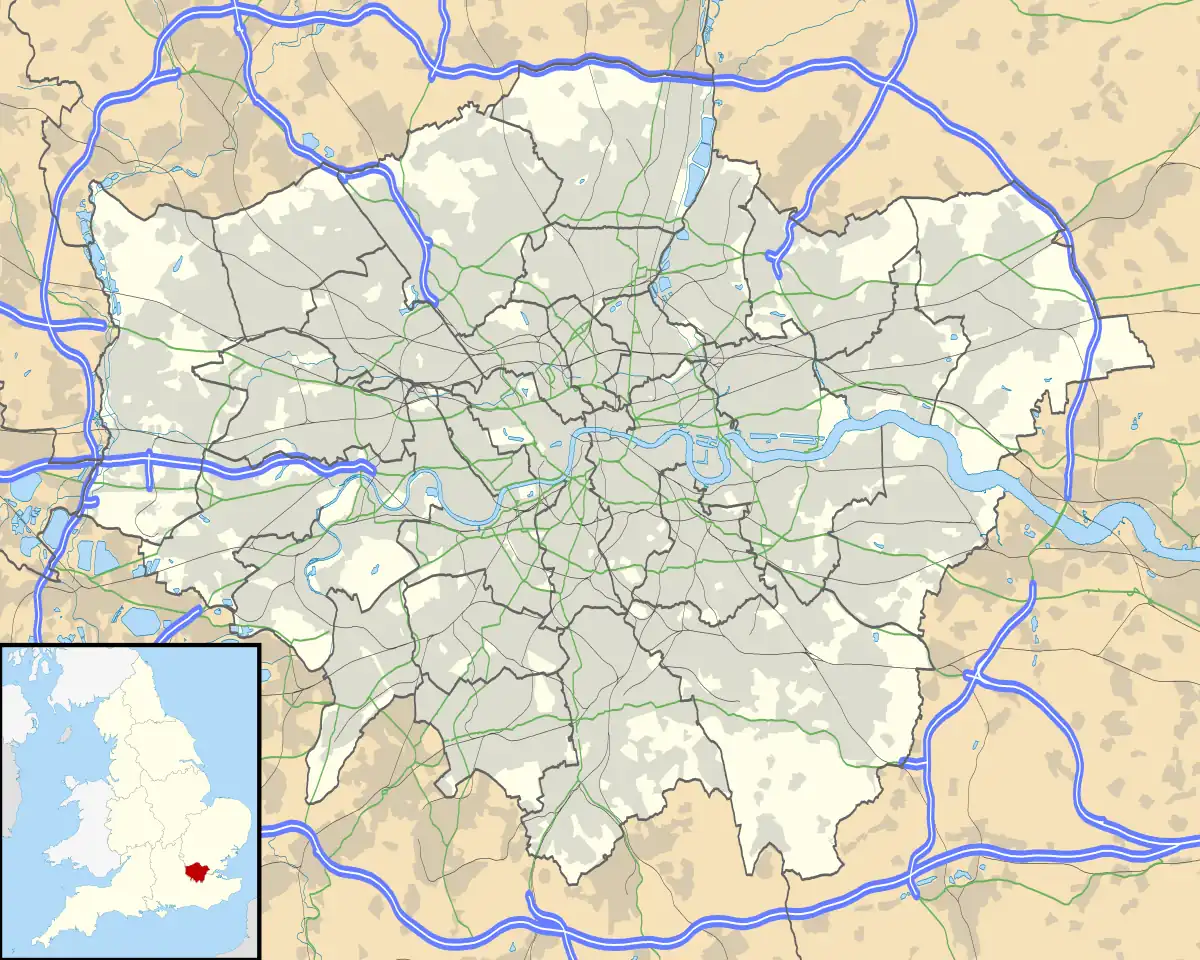 Canary Wharf Location within Greater London | |
| Population | 68,700 (Millwall, Blackwall and Cubitt Town, East India and Lansbury and Limehouse wards 2011 Census) |
| OS grid reference | TQ375802 |
| London borough | |
| Ceremonial county | Greater London |
| Region | |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | LONDON |
| Postcode district | E14 |
| Police | Metropolitan |
| Fire | London |
| Ambulance | London |
| UK Parliament | |
| London Assembly | |
Canary Wharf is an area of East London, England, located near the Isle of Dogs in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. Canary Wharf is defined by the Greater London Authority as being part of London's central business district, alongside Central London.[1] Alongside the City of London, it constitutes one of the main financial centres in the United Kingdom and the world,[2] containing many high-rise buildings including the third-tallest in the UK, One Canada Square,[3] which opened on 26 August 1991.[4]
Developed on the site of the former West India Docks, Canary Wharf contains around 16,000,000 sq ft (1,500,000 m2) of office and retail space. It has many open areas, including Canada Square, Cabot Square and Westferry Circus. Together with Heron Quays and Wood Wharf, it forms the Canary Wharf Estate, around 97 acres (39 ha) in area.
History

.jpg.webp)

Canary Wharf is located on the West India Docks on the Isle of Dogs.
West India Dock Company
From 1802 to the late 1980s, what would become the Canary Wharf Estate was a part of the Isle of Dogs (Millwall), Limehouse, and Poplar and was one of the busiest docks in the world. West India Docks was primarily developed by Robert Milligan (c. 1746–1809) who set up the West India Dock Company.
Port of London Authority
The Port of London Authority was established in 1909 and took control of West India Dock. The enterprise of Sir Alfred Lewis Jones, a Welsh shipping magnate who was a prominent figure in the Canary Islands, led to a constant stream of ships arriving into London’s South Quay Dock and the naming of Canary Wharf, after the ships' origin.[5] It was named after No. 32 berth of the West Wood Quay of the Import Dock. This was built in 1936 for Fruit Lines Ltd, a subsidiary of Fred Olsen Lines for the Mediterranean and Canary Islands fruit trade. It is located on the Isle of Dogs, the quay and warehouse were given the name Canary Wharf.[6]
London Docklands Development Corporation
After the 1960s, when cargo became containerized, port industry began to decline, leading to all the docks being closed by 1980.[7][8] After the docks closed in 1980, the British Government adopted policies to stimulate redevelopment of the area, including the creation of the London Docklands Development Corporation (LDDC) in 1981 and the granting of Urban Enterprise Zone status to the Isle of Dogs in 1982.[8]
The Canary Wharf of today began when Michael von Clemm, former chairman of Credit Suisse First Boston (CSFB), came up with the idea to convert Canary Wharf into a back office. Further discussions with G Ware Travelstead led to proposals for a new business district and included the LDDC developing an inexpensive light metro scheme, the Docklands Light Railway, to make use of a large amount of redundant railway infrastructure and to improve access.
The project was sold to the Canadian company Olympia & York[9] and construction began in 1988, master-planned by Skidmore, Owings & Merrill with Yorke Rosenberg Mardall as their UK advisors, and subsequently by Koetter Kim. The first buildings were completed in 1991, including One Canada Square, which became the UK's tallest building at the time and a symbol of the regeneration of Docklands. By the time it opened, the London commercial property market had collapsed, and Olympia and York Canary Wharf Limited filed for bankruptcy in May 1992.
Initially, the City of London saw Canary Wharf as an existential threat. It modified its planning laws to expand the provision of new offices in the City of London, for example, creating offices above railway stations (Blackfriars) and roads (Alban Gate). The resulting oversupply of office space contributed to the failure of the Canary Wharf project.
Canary Wharf Group
In October 1995, an international consortium that included investors such as Alwaleed, bought control for $1.2 billion. Paul Reichmann, of Olympia & York, was named chairman, and Canary Wharf went public in 1999.[10] The new company was called Canary Wharf Limited, and later became Canary Wharf Group.
In 1997, some residents living on the Isle of Dogs launched a lawsuit against Canary Wharf Ltd for private nuisance because the tower interfered with TV signals. The residents lost the case.[11]
Recovery in the property market generally, coupled with continuing demand for large floorplate Grade A office space, slowly improved the level of interest. A critical event in the recovery was the much-delayed start of work on the Jubilee Line Extension, which the government wanted ready for the Millennium celebrations.
In March 2004, Canary Wharf Group plc. was taken over by a consortium of investors, backed by its largest shareholder Glick Family Investments[12] and led by Morgan Stanley using a vehicle named Songbird Estates plc.
Tallest buildings


In addition to being a leading global financial district in the United Kingdom, Canary Wharf is famous for a cluster of the tallest modern commercial complexes and residential high-rise buildings.[13] Building from scratch in early 1990s, the district is home to the first tallest iconic skyscraper, One Canada Square, in the United Kingdom. In twenty years, Charf Wharf’s new rapid grown skyscraper cluster has dramatically transformed the skyline of London with modern architectures.[14][15]
- As of 2023, Canary Wharf has five out of the top ten tallest buildings in the United Kingdom.[16]
- One Canada Square (235 m) and Landmark Pinnacle (233 m) are the third and fourth tallest buildings in the United Kingdom. The seventh to ninth tallest buildings in the United Kingdom are: Newfoundland (220 m), South Quay Plaza (215 m), and One Park Drive (205 m).[17]
- The 75-storey Landmark Pinnacle is the tallest residential tower in the United Kingdom and the whole of western Europe.[18]
- Newfoundland is the tallest build-to-rent building in the United Kingdom.[19]
- Novotel London Canary Wharf is the tallest all-hotel building in the United Kingdom, and the tallest Novotel in the world.[20]
- One Canada Square, at 235 metres (771 ft), achieved a 21-year record of the tallest building in the United Kingdom from 1991 to 2012. With its distinctive pyramid pinnacle, the building is recognised as a London landmark, and has been featured in many films and television shows.[17][21]
This table lists completed buildings in Canary Wharf that are at least 100 metres tall.
| Ranking by height | Image | Name | Height | Floors | Completion date | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metres | Feet | ||||||
| 1 |  | One Canada Square | 235 | 771 | 50 | 1991 | The third-tallest completed building in the United Kingdom, the tallest being The Shard. Designed by Cesar Pelli, it was the tallest building in the United Kingdom upon completion in 1991. Multi-tenanted; occupiers include BNY Mellon, the CFA Institute, Clearstream, European Energy Exchange, Euler Hermes, the International Sugar Organization, Mahindra Satyam, MetLife, Moody's Analytics and Reach.[22] |
| 2 |  | Landmark Pinnacle | 233 | 764 | 75 | 2020 | Residential tower. The tallest residential tower in the United Kingdom and the whole of western Europe.[18] Awarded the Premier Guarantee Awards for Quality Recognition in 2021 and 2022, as well as the Excellence Award in 2021.[23] Winner of the Best Luxury High Rise Living category at the 2023 Luxury Lifestyle Awards.[24] |
| 3 |  | Newfoundland | 220 | 722 | 60 | 2019 | The first residential building ever built on the Canary Wharf private estate, which makes it stand out among the financial centers buildings.[25] Known as "the diamond tower" due to its distinctive diamond-pattern steel exoskeleton design.[26] Winner of the Residential High Rise Development at 2021 International Property Awards.[27] Awarded Best Exterior Design (Silver) and Best Build to Rent Project (Bronze) at 2021 WhatHouse? Awards.[28] |
| 4 | .jpg.webp) | South Quay Plaza (Phase 1, Hampton Court) | 215 | 705 | 68 | 2020 | Residential tower. Also known as Valiant Tower[29] Winner of the Best Garden/Landscaping Design at the British Home Awards 2022.[30] |
| 5 |  | One Park Drive | 205 | 673 | 57 | 2019 | Residential tower. Wood Wharf’s flagship residential building. In 2021, won two British Homes Awards,[31] and two Golds at the WhatHouse? Awards.[32] In 2023, the penthouse at One Park Drive was named the Best Apartment at the Evening Standard New Homes Awards,[33] and won gold in the Best Interior Design category in WhatHouse? Awards.[34] |
| 6 |  | 8 Canada Square | 200 | 655 | 42 | 2002 | The joint eleventh-tallest completed building in the United Kingdom. Occupied by HSBC as its global headquarters.[35] |
| 7 |  | 25 Canada Square | 200 | 655 | 42 | 2001 | The joint eleventh-tallest completed building in the United Kingdom. 25 Canada Square and 33 Canada Square together form a single complex known as the Citigroup Centre. Primarily occupied by Citigroup as its EMEA headquarters.[36] Other tenants include Gain Capital, 3i Infotech, Crossrail, Instinet, Munich Re, MWB Group, FIS, Interoute, NYK and Wells Fargo. |
| 8 |  | Wardian London (East Tower) | 187 | 614 | 55 | 2019 | Residential tower. Awarded the Silver Award for Best Luxury Development in 2023.[37] |
| 9 |  | Amory Tower (The Madison) | 182 | 597 | 53 | 2019 | Residential tower. Winner of Tall Building Award in 2022.[38] |
| 10 |  | Wardian London (West Tower) | 168 | 552 | 50 | 2019 | Residential tower. (see Wardian East Tower) |
| 11 |  | One Churchill Place | 156 | 513 | 32 | 2005 | Occupied by Barclays as its global headquarters.[39] Currently the eighth-tallest building in the United Kingdom, it was originally planned to be 50 storeys in height, but was scaled down to 31 after the 11 September attacks. |
| 12= |  | 40 Bank Street | 153 | 502 | 33 | 2003 | Multi-tenanted; occupiers include Allen & Overy, ANZ Bank, China Construction Bank, Duff & Phelps, Saxo Bank, and Skadden, Arps, Slate, Meagher & Flom.[22] |
| 12= |  | 25 Bank Street | 153 | 502 | 33 | 2003 | Occupied by JPMorgan Chase as its European headquarters since 2012.[40] |
| 14 |  | 10 Upper Bank Street | 151 | 495 | 32 | 2003 | Occupied by Clifford Chance as its global headquarters.[41] Other occupiers include FTSE Group, Infosys, Mastercard, Deutsche Bank, and Total.[22] |
| 15 |  | 10 Park Drive Wood Wharf | 150 | 492 | 43 | 2019 | Residential tower.[42] The first new residential development to be built in Wood Wharf.[43] Awarded a Gold award for Best Apartment Scheme at the 40th annual WhatHouse? Awards.[44] |
| 16 |  | Arena Tower (Baltimore Tower) | 149 | 489 | 45 | 2017 | Residential tower. Winner of the Best Residential High Rise Award at the International Property Awards.[45] |
| 17 |  | Pan Peninsula (East Tower) | 147 | 484 | 48 | 2008 | Residential tower. Pan Peninsula was arguably the first “Ultra Luxury” development in Canary Wharf.[46] |
| 18 |  | Maine Tower (Harbour Central Block D) | 144 | 472 | 42 | 2018 | Residential tower. The center piece of Harbour Central development containing 7 buildings.[47][48] Also see Harbour Central Block C (Sirocco Tower). |
| 19 | .jpg.webp) | One & Five Bank Street | 143 | 469 | 28 | 2019 | Commercial tower.[49] Bounded by water on two sides, this building marks the entrance to the Canary Wharf Estate.[50] Achieved a BREEAM Outstanding rating, making it one of the most sustainable buildings of its type in London.[51] European Bank for Reconstruction and Development relocated its headquarters to Five Bank Street in 2022.[52] |
| 20 |  | 24 Marsh Wall (Landmark East Tower) | 140 | 458 | 44 | 2010 | Residential tower |
| 21= |  | 40 Marsh Wall (Novotel London Canary Wharf) | 128 | 420 | 39 | 2017 | Hotel operating as 'Novotel Canary Wharf' |
| 21= |  | 10 George Street Wood Wharf | 128 | 420 | 35 | 2018 | Residential tower. It is the first of three “Build to Rent” properties commissioned by the rental arm of the Canary Wharf group, known as Vertus.[53] Won Gold for the Best build-to-rent (BtR) Project at 2020 What House? Awards.[54] |
| 23 |  | Harbour Central Block C (Sirocco Tower)[55] | 125 | 409 | 36 | 2018 | Residential tower. Sirocco tower waw the first built out of the 7 buildings planned on the Harbour Central site.[47] Also see Maine Tower. |
| 24 |  | Pan Peninsula (West Tower) | 122 | 400 | 39 | 2008 | Residential tower. (see Pan Peninsula East Tower) |
| 25 |  | 25 Churchill Place | 118[56] | 387 | 24 | 2014 | The building housed the European Medicines Agency from early 2014 until March 2019 when they relocated to Amsterdam[57] and Ernst & Young from 2015. |
| 26 |  | Dollar Bay Tower | 109 | 358 | 31 | 2016 | Residential tower. Has won numerous housing and architectural awards, including: The Best New Iconic Scheme, and The Mayors award for Environmental Excellence, at the London Planning Awards in 2018.[58] |
| 27 |  | 1 West India Quay | 108 | 354 | 36 | 2004 | Floors 1–12 are occupied by a Marriott Hotel.[59] Floors 13–33 house 158 apartments. |
| 28 |  | 33 Canada Square | 105 | 344 | 18 | 1999 | 33 Canada Square and 25 Canada Square together form a single complex, see above for details. |
Listed Buildings


As at 12 February 2023, there are 16 listed buildings in Canary Wharf of which 2 are Grade I and 14 in Grade II.[60]
- Grade I Listed Buildings
- Quay Walls, Copings and Buttresses to Import Dock and Export Dock: The original West India Docks consists of three docks. The Import Dock, the earliest, was opened in 1800–02, and followed to south by the Export Dock of 1803–06.[61][62]
- Warehouses and General Offices at Western End of North Quay: originally a range of nine warehouses was built 1800–04 at the western end of North Quay, West India Dock Road. Only two warehouses survived the bombing raid in World War II.[63][64]
These docks with Nos 1 and 2 warehouses are now the only surviving examples of the first intensive period of London Docklands construction: 1800–10.
- Grade II Listed Buildings
Most of the Grade II Listed buildings in Canary Wharf sit to the north-west of West India Dock North, and are located within the West India Dock Conservation Area.[65] In addition to architectural values, “these buildings and structures are of significance due to their association with the development of the docks and the community that grew up around them”.[66]
| Photograph | Building Name | Construction Date | Location (E14) | Listing Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 10 and 12, Garford Street E14 [67] | 1800s, early | Garford Street | 27 September 1973 | Early 19th century pairs of stock brick houses. These cottages were originally built for the officers and sergeants who supervised the Docks. |
 | 14, Garford Street E14 [68] | 1800s, early | Garford Street | 27 September 1973 | Early 19th century stock brick house. |
 | 16 and 18, Garford Street E14 [69] | 1800s, early | Garford Street | 27 September 1973 | Early 19th century pairs of stock brick houses. |
 | Entrance Gates to West India Docks[70] | 1800s, early | West India Dock Road | 19 July 1950 | 2 rusticated Portland stone piers with a capping of 4 dwarf pediments and acroteria. |
 | Former West Entrance Gate to West India Docks with Curved Walling and Bollards [71] | 1900s, early | Westferry Road | 1 July 1983 | Stock brick curved wing walls and Portland stone gatepiers. Modern brick wall blocks entrance. Two cast-iron obelisk pattern bollards with the inscription WIDC (West India Dock Company). |
 | Railings to West of Main Gate at West India Docks[72] | 1800s, early | West India Dock Road | 30 September 1981 | Cast iron railings approximately 70 yards in length. |
 | Former Excise Office [73] | 1807 | West India Dock Road | 30 September 1981 | Also known as Dockmaster's House, by the architect and engineer Thomas Morris. |
 | Railings and Gatepiers to Former Excise Office [74] | 1807 | West India Dock Road | 30 September 1981 | Contemporary iron railings with six rusticated stucco gatepiers on street front. The stucco decoration of the piers elaborated mid 19th century. |
 | Quadrangle Stores at West India Dock[75] | 1825 | West India Dock Road | 30 September 1981 | Also known as Cannon Workshops, by engineer John Rennie the Younger. A rare survival of an early purpose built illustrative of the workings of the Docks Company. |
 | Salvation Army Hostel [76] | 1905 | Garford Street | 27 September 1973 | Neo Georgian style building by architectural partnership Niven and Wigglesworth. Also known as: 20 Garford Street. |
 | West India Dock Former Guard House [77] | 1803 | West India Dock Road | 27 September 1973 | A one storey, small circular building designed by architect George Gwilt. It originally formed one of a pair built by Docks Company as a lock-up and armoury. |
.jpg.webp) | Former West Entrance Lock to South Dock, West India Docks[78] | 1803-05 | Westferry Road | 1 July 1983 | By civil engineer William Jessop, built as the west entrance lock to the City Canal, later taken into the West India Docks system. |
| Fitch and Sons Works [79] | 1870-80 | Westferry Road | 1 July 1983 | A good example of the smaller warehouses in the historical West India Docks, with built in retail outlet on ground floor, a now rare feature. | |
 | Cascades[80] | 1987-88 | Westferry Road | 18 April 2018 | A 20-storey residential tower by CZWG.
|
Corporations and agencies
Canary Wharf contains around 16,000,000 sq ft (1,500,000 m2) of office and retail space, of which around 7,900,000 sq ft (730,000 m2) (about 49%) is owned by Canary Wharf Group.[82] Around 105,000 people work in Canary Wharf,[83] and it is home to the world or European headquarters of numerous major banks, professional services firms, and media organisations, including Barclays, Citigroup, Clifford Chance, Credit Suisse, Ernst & Young, Fitch Ratings, HSBC, Infosys, JPMorgan Chase, KPMG, MetLife, Moody's, Morgan Stanley, Royal Bank of Canada, Deutsche Bank, S&P Global, Skadden, Arps, Slate, Meagher & Flom, State Street, The Economist Group and Thomson Reuters.[84] Until 2018, Canary Wharf also hosted two European Union agencies, European Medicines Agency[85] and European Banking Authority,[86] that moved to Amsterdam and Paris respectively due to Brexit.
Leisure
- Marina
West India Quays and Poplar Dock are two marinas that are used as moorings for barges and private leisure river craft and is owned by the Canal & River Trust.[87][88]
- Library
A local public library, called Idea Store Canary Wharf, is in Churchill Place shopping mall and run by Tower Hamlets Council which opened on Thursday 16 March 2006 as part of the Idea Store project[89] and is the borough fourth Idea Store.[90]
- Cinema
Canary Wharf hosts two multiplexes (cinemas), one on West India Quay run by Cineworld.[91][92] and another at Crossrail Place called Everyman Cinema.[93]
Squares and Public Areas
- Canada Square
Canada Square is one of the central squares at Canary Wharf. It is a large open space with grass, except during the winter when it is converted into an ice rink. The square is named after Canada, because the original developers of modern Canary Wharf, Olympia & York, wanted to reflect their heritage. Underneath the square is Canada Place shopping mall.
- Westferry Circus
Westferry Circus is on the west side of Canary Wharf. It is a garden at ground level, and below is a roundabout allowing traffic to flow through. The garden is enclosed by bespoke hand-crafted ornamental railings and entrance gates by artist Giuseppe Lund. The area has a long history, dating back to 1812, when the Poplar and Greenwich Roads Company operated a horse ferry between Greenwich and the Isle of Dogs. It operated on the West Ferry and East Ferry Roads, which the names survived. Westferry Circus was chosen as the name for the roundabout and park by virtue of its proximity to Westferry Road.
- Cabot Square
Cabot Square is one of the biggest squares at Canary Wharf, with a large fountain at the centre. The inner perimeter has additional fountains covered by trees. The square has large circular glass ventilation holes to allow gases to escape from the underground car park. The square is named after John Cabot and his son Sebastian, who were Italian explorers who settled in England in 1484.
- Churchill Place
Churchill Place is an area on the east side of Canary Wharf. It is named after Winston Churchill.
- Columbus Courtyard
A small square on the west side of Canary Wharf named after Christopher Columbus. The first phase of Canary Wharf was completed in 1992, 500 years after Columbus arrived in America.
- Chancellor Passage
A passageway south of Cabot Square. Named after Richard Chancellor who sailed with Sir John Willoughby from Greenwich on their voyage through the White Sea to Moscow.
- Wren Landing
Small area north of Cabot Square. Leads to North Dock footbridge towards Port East. Named after British architect Christopher Wren.
- Montgomery Square
Located at the east end of Jubilee Park, Montgomery Square is a buzzy outdoor spot that’s made for socialising. With a regular roster of events from street food markets, beach volleyball tournaments,[94] padel tennis competition,[95] to free minigolf course,[96] there’s always something happening in this convivial open space.[97]
Parks and Green Spaces
Canary Wharf Group is enthusiastic about adding more green spaces and gardens to the dense urban environment. A total of 20 acres of landscaped parks, gardens and verdant squares complete with 1,000 trees, 4,000 shrubs and 70,000 seasonal plants are added each year.[97] Visitors are welcome to explore these parks and green spaces, which are ideal places for relaxation, social gatherings, performances, viewing outdoor public art, as well as hosting outdoor events and festivities.[98]
- Jubilee Park

Jubilee Park is a 10,000m² roof garden located above Jubilee Place, a shopping mall, and Canary Wharf Jubilee Station, an underground railway station.[99] The park, opened on 2002, was named in honour of the Golden Jubilee of Elizabeth II.[100] Jubilee Park is a serene oasis located in the heart of the financial district of Canary Wharf, surrounded by towering commercial buildings. The park’s central feature is a raised serpentine water channel with rough stone walls. The curvilinear design of the water channel provides a striking contrast to the scale and straightness of the surrounding buildings, creating a sense of harmony between nature and architecture.[101] The park is an ideal spot for a peaceful lunch break or a moment of relaxation amidst the hustle and bustle of the city. In 2023, Jubilee Park won the prestigious Green Flag Award, which recognizes Jubilee Park as one of the country’s best parks in the United Kingdom[102]
- Crossrail Place Roof Garden
A 4,160m² roof garden, one of London's largest, houses on the top of seven-storey Crossrail Place structure, which contains the Elizabeth line Canary Wharf station. Opened to public in 2015, it lies almost exactly on the Meridian line splitting eastern and western hemispheres. The plants originating from the eastern hemisphere are planted to the East of the Meridian line in the garden, with those from the Western hemisphere on the opposite side.[103][104] The design and development of Crossrail Place Roof Garden was honored by winning numerous prestigious international and United Kingdom awards.[105] Selected notable awards include: “Best Urban Regeneration Project” at 2016 MIPIM awards in France,[106] the first prize for the best “Innovative Design of a Contemporary Garden” at the 2017 European Garden Awards in Berlin,[107] and a Highly Commended accolade at the 2016 Landscape Institute Awards in the category ‘Design for a Small-Scale Development’.[108]
- Harbour Quay Garden
A newly opened garden, located at the strand of Wood Wharf, features a boardwalk for waterside wandering. The garden also offers plenty of family-friendly picnic spots and outdoor fitness equipment on the green lawn, where visitors can relax, view outdoor public art, and watch the water. Just around the corner, it has access to a new garden square, Harbord Square Park.[109]
- Harbord Square Park
Harbord Square Park, the newest garden square in Wood Wharf, continues the great London tradition of garden squares. It is open 24/7 and offers green space available for mindfulness activities and to support nearby residents’ general wellbeing.[110]
Shopping Center
Canary Wharf shopping center, ranked as one of the best in London,[111] has five interconnected shopping malls: Canada Place, Cabot Place, Jubilee Place, Crossrail Place and Churchill Place. The malls provide over 102,193m² (1.1 million sq ft) of retail space, more than 310 shops from beauty, fashion, lifestyle, luxurious brands, health, and homeware, as well as 70 cafés, bars, and restaurants, 8 grocery stores, 5 health clubs and 1 cinema.[112] There are also numerous bars, restaurants, and food halls at street level, alongside plenty of outdoor seating enabling visitors to see the stunning wharf and riverside views.
Local government elections
Every four years, residents of Canary Wharf ward elect two councillors to represent them on Tower Hamlets Council.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspire | Maium Talukdar | 1,164 | 18.06 | +5.51 | |
| Aspire | Saled Ahmed | 1,023 | 15.88 | ||
| Independent | Andrew Wood † | 993 | 15.41 | -0.42 | |
| Labour Co-op | Adam Allnutt | 885 | 13.73 | ||
| Labour Co-op | Shajia Sultana | 846 | 13.13 | ||
| Conservative | Francis Germaine-Powell | 492 | 7.64 | ||
| Conservative | Samia Hersey | 408 | 6.33 | ||
| Liberal Democrats | Morgan Jones | 363 | 5.63 | ||
| Liberal Democrats | Mohammed Hannan | 270 | 4.19 | ||
| Total votes | 6,444 | ||||
| Rejected ballots | 26 | ||||
| Registered electors | 11,389 | ||||
| Turnout | 3,676 | 32.28 | -1.61 | ||
| Aspire gain from Conservative | Swing | ||||
| Aspire gain from Labour | Swing | ||||
† Andrew Wood was elected for the Conservative Party in 2018, but resigned to sit as an Independent in 2020.[114]
Transport
Canary Wharf is served by London-wide, regional, national and international transport connections.
Rail
Canary Wharf is in London fare zone 2, and several stations can be found throughout the estate.
- The Docklands Light Railway (DLR) calls at Canary Wharf, Heron Quays and West India Quay stations. The line opened in 1987.[115]
- DLR trains link Canary Wharf northbound to Bank in the City of London, via Shadwell. Northbound trains also travel to Stratford via Poplar and Bow Church. Southbound trains terminate south of the River Thames in Lewisham, calling at Greenwich en route.[115]
- London Underground Jubilee line services call at Canary Wharf station. Eastbound trains travel to Stratford via North Greenwich, Canning Town and West Ham. Westbound trains link Canary Wharf to the West End and key London interchanges including London Bridge, Waterloo and Baker Street. Trains towards Central London eventually terminate in North West London.[116]
- The Elizabeth line (constructed by the Crossrail project) calls at Canary Wharf station. The line provides the area with a frequent, direct connection to the City of London and the West End. Westbound trains serve Central London and key interchanges at Liverpool Street and Paddington. Elizabeth line trains also serve Heathrow Airport and Reading, Berkshire to the west. Eastbound services terminate at Abbey Wood.[117]
Stations in Canary Wharf only offer direct connections to London and Berkshire destinations. Regional and national National Rail connections can be found elsewhere in London, including at Liverpool Street, Lewisham, London Bridge, Stratford, Stratford International and Waterloo.[116]
Road

Major roads near Canary Wharf include:
- A12 - begins in nearby Blackwall and carries traffic northeast towards Stratford, the M11 (for Stansted Airport
 ), and destinations in Essex and East Anglia.
), and destinations in Essex and East Anglia. - A13 (East India Dock Road) - westbound to Limehouse and the City of London (Aldgate); eastbound towards Barking, the M25 and Southend (
 ).
). - A102 (Blackwall Tunnel) - begins in nearby Blackwall and carries traffic southbound to Greenwich, the A2 and the A20 for destinations in Kent.
- A1020 (Lower Lea Crossing) - carries traffic eastbound to London City Airport (
 ).
). - A1203 (Limehouse Link) - carries traffic eastbound to Shadwell and the City of London (Tower Hill).
- A1205 (Burdett Road) - carries traffic northbound to Mile End and Hackney.
- A1206 (Westferry Circus/Prestons Road) - loops around the western, southern and eastern edges of the Isle of Dogs. Links to the A1261.
- A1261 (Aspen Way) - westbound to the A13 for Limehouse and the city; eastbound to the A1020 for City Airport (
 ) and the A13 towards Barking.
) and the A13 towards Barking.
Air pollution

Transport for London (TfL) and the London Borough of Tower Hamlets monitor the air quality around Canary Wharf.
In 2017, an automatic monitoring station in Blackwall found that local air quality failed to meet UK National Air Quality Objectives, recording an annual average Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) concentration of 56 μg/m3 (micrograms per cubic metre). The National Objective is set by the government at 40 μg/m3.
Alternative stations nearer Canary Wharf recorded cleaner air. Monitors at the Limehouse Link/Westferry Road junction and on Prestons Road recorded a 2017 annual average NO2 concentration of 40 μg/m3, which Tower Hamlets argue fails to meet the UK National Objective.[118]
Buses
London Buses routes 135, 277, D3, D7, D8, N277 and N550 call at bus stops near Canary Wharf. Bus 135 links Canary Wharf directly to Liverpool Street in the City of London, and bus D8 to Stratford.[119]
Riverboat
Several Riverboat services call at Canary Wharf Pier, including:
- RB1 - eastbound to North Greenwich and Woolwich Arsenal Pier; westbound to Tower, London Bridge City, Bankside, Blackfriars, Embankment, the London Eye and Westminster.
- RB1X - eastbound to North Greenwich and Royal Wharf Pier; westbound to Tower, London Bridge City, Bankside, Embankment, the London Eye and Westminster (limited service to Battersea Power Station).
- RB4 - the Canary Wharf – Rotherhithe Ferry crosses the Thames to Nelson Dock.
- RB6 - limited eastbound service towards Putney.
Tower, London Bridge City and Blackfriars are in the City of London. Oyster Cards are valid for travel on TfL-coordinated riverboat services.[120]
Airports
London City Airport is three miles from Canary Wharf. Over 4.8 million passengers passed through City Airport in 2018. The airport serves domestic and international destinations, including New York.[121][122]
London City Airport is on the DLR. Passengers from Canary Wharf can change trains at Poplar for services to the Airport.[115]
Cycling
The Canary Wharf Group, London Borough of Tower Hamlets and Transport for London (TfL) provide cycling infrastructure in and around Canary Wharf. Several leisure and commuter routes pass through or near the estate, including:

- National Cycle Route 1 (NCR 1) - a leisure cycle route from Dover, Kent to Shetland, Scotland. The route is indirect, running through London on low-traffic paths. In North London, the route runs from the Greenwich Foot Tunnel to Enfield Lock via Canary Wharf, Mile End and Tottenham. The route runs to the west of Canary Wharf, parallel to the River Thames.[123]
- EuroVelo 2 ("The Capitals Route") - an international leisure cycle route from Moscow, Russia to Galway, Ireland. In North London, EV2 follows the route of NCR 1.[124]
- National Cycle Route 13 (NCR 13) - a leisure cycle route from the City to Fakenham, Norfolk. The route is indirect, running through East London on low-traffic paths. The route leaves London near Rainham.[125]
- Cycle Superhighway 3 (CS3) - a commuter cycle route from Barking to West London. The route runs east–west through nearby Poplar on low-traffic or residential streets. The route is signposted and unbroken.[126]
- East of Poplar, the route to Barking predominantly runs on traffic-free cycle track.
- West of Limehouse, the route runs on low-traffic or traffic-free paths to Shadwell. The route is signposted and unbroken. After Shadwell, the route becomes a traffic-free cycle track which provides Canary Wharf with a direct link to Tower Hill, Blackfriars, Westminster, Buckingham Palace, Hyde Park Corner and Lancaster Gate.
- Cycleway from Hackney to the Isle of Dogs - proposed cycle link which would link Canary Wharf directly to Mile End on traffic-free cycle track.[127]
- Limehouse Cut towpath - shared-use path from nearby Limehouse to Stratford. The route is traffic-free.[128]
- Regent's Canal towpath - shared-use path from nearby Limehouse to Angel. The route is traffic-free and passes through Mile End, Haggerston, and Islington.[128]
Culture
Opened in a Grade I listed Georgian warehouse by Queen Elizabeth II in June 2003, the Museum of London Docklands is one of the main attractions in the area.[129] It is dedicated to the history of London’s river, port, and people from Roman settlement to the present day. The museum offers a range of activities for children and families, including interactive displays and immersive activities.[130]
Canary Wharf has been reported since 2017 as part of the Pokémon Go augmented reality game to being the home for the most wanted Pokémon gyms in London including Canary Wharf DLR station and Montgomery Square.[131]
Canary Wharf Group published an official Pokémon map for PokéStop's and Pokémon Gyms, the managing director for retail Camille Waxer said in 2016 that Pokémon Go has serious potential to attract new audiences to the area, particularly food and drink outlets are seeing an increase in footfall.[132]
Canary Wharf features in both the Doctor Who and Torchwood franchises as the fictional base of the Torchwood Institute, an organisation created by Queen Victoria to combat extraterrestrial threats. Canary Wharf features heavily as the staging post for the 2007 Cyberman invasion of Earth and is heavily damaged during a resulting battle between the Cybermen and the Daleks.
Thom Yorke of Radiohead, during their concert Live at the Astoria in May 1994,[133] explained their song Fake Plastic Trees is about Canary Wharf.
Events and Festivals
Winter Lights Festival

Incepted in 2014, the Canary Wharf Winter Lights Festival turns on January of the year.[134] Public are free to visit a range of outdoor light art and interactive installations created by artists from around the world. The festival has awarded the Best Creative Lighting Event award by the [d]arc awards in 2017 and 2019.[135][136] The 2023 Canary Wharf Winter Lights Festival is described as the largest light art festival in London.[137][138]
WaterAid Dragon Boat Race
It is an annual fundraising event organized by WaterAid, an international charity, in collaboration with the Canary Wharf Group. The funds raised through this event are used to combat the escalating water crisis that leaves people globally unable to access clean water and without a basic toilet. The Dragon Boat Race, based on a Chinese tradition dating back over 2,000 years, takes place in South Dock of Canary Wharf on summer, and is open to corporate teams of between 11 and 17 participants. In 2022, 15 teams participated the race, and the event raised £26,000.[139] With 19 teams taking place in the 2023 race, the raised funds was increased to £31,744.[140]
Festival14
Hosted by the Canary Wharf Group, the festival was a four-day event from Thursday 21st to Sunday 24 July 2022.[141] It hosted over 60 live acts including music, theatre, dance, poetry, comedy, family funs and children’s activities throughout the estate. The majority of acts were free to attend, and the event transformed the Estate’s numerous parks, plazas, and open spaces as they hosted a stunning line-up of artists and performers from across the world.[142] The second year of Festival14 is extended to a five day event from Wednesday 26th to Sunday 30 July 2023.[143][144]
Open Water Swimming
Canary Wharf has partnered with Love Open Water to launch its first outdoor swimming since summer 2022. The venue, located in the 220-year-old Middle Dock, offers 600 square meters of open water swimming. Residents, workers and visitors can enjoy a unique experience of outdoor swimming in the heart of the London commercial district whilst taking in the stunning views of the iconic One Canada Square and Newfoundland residential skycrapper.[145][146]
Outdoor Public Art

The Canary Wharf Art Trail is the largest outdoor public art collection in London.[148][149] People are free to visit more than 100 pieces of stand-alone sculptures, integrated architectural works, and outdoor art exhibiting outside buildings around the Canary Wharf area.[150] Two printed maps are regularly updated by the Canary Wharf Group for visitors to discover and identify artworks permanently on display all over the estate.
- Canary Wharf Art Map: over 100 pieces of artworks, with a brief description, are numbered sequentially as to their exhibition locations at Canary Wharf.[151]
- Children's Art Trail: a smaller trail of 12 sculptures and artworks for children.[152]
The Canary Wharf website provides information about Raise Your Art Rate, an ongoing event that allows visitors to explore the outdoor public art collection while exercising. The event offers 1, 3, and 5 km walking, jogging or running routes that traverse the artworks. The routes are tailored to showcase the over 100 artworks on display throughout the estate. The event is free and open to all visitors.[153]
Media
The East London Advertiser (formerly The Docklands & East London Advertiser) is a local newspaper printing weekly and also online.
Wharf life is a fortnightly publication of 15,000 copies for Canary Wharf, Docklands and east London. An E-edition is also available.[154]
See also
References
- ↑ Greater London Authority 2008, p. 6.
- ↑ Greater London Authority 2008, p. 4.
- ↑ "United Kingdom Skyscraper Diagram". skyscraperpage.com. Retrieved 26 August 2021.
- ↑ A. Beaumont (2015). Contemporary British Fiction and the Cultural Politics of Disenfranchisement: Freedom and the City (illustrated ed.). Springer. p. 40. ISBN 9781137393722.
- ↑ Clarke, Ross (13 September 2018). "The peculiar tale of how London's Canary Wharf got its name". BBC. Retrieved 3 June 2023.
- ↑ The West India Docks: The buildings: warehouses, Survey of London: volumes 43 and 44: Poplar, Blackwall and Isle of Dogs (1994), pp. 284–300 Archived 29 August 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 22 July 2008
- ↑ West India Docks (1803–1980) Archived 3 February 2008 at the Wayback Machine (Port Cities) accessed 22 July 2008
- 1 2 "History". Canary Wharf Group. Archived from the original on 23 June 2006. Retrieved 11 November 2010.
- ↑ "The Development of Transport in London Docklands – Part I: The Chronological Story". LDDC history. 17 July 1987. A New Era: the Coming of Canary Wharf. Archived from the original on 26 April 2012. Retrieved 12 January 2009.
- ↑ Khan, Riz (2005). Alwaleed, Businessman Billionaire Prince. New York: HarperCollins. pp. 120–121. ISBN 9780060850302.
- ↑ The court found against the appellants (Hunter and others) as private nuisance legislation generally concerns "emanations" from land, not interference with such emanations. "Hunter and Others v. Canary Wharf Ltd./Hunter and Others v. London Docklands Corporation" Archived 10 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine House of Lords Session 1996–97. Retrieved on 23 March 2009.
- ↑ "Glick family in late move over Canary Wharf battle". The Independent. 2 January 2011. Archived from the original on 2 January 2011.
- ↑ Canary Wharf vs City of London January 5, 2023 Canary Development. 5 January 2023. Retrieved 23 December 2023.
- ↑ Canary Wharf Group transforms London's skyline with modern architecture. Mia Daughenbaugh and David Bell South China Morning Post. 16 June 2014. Retrieved 17 December 2023.
- ↑ Dramatic pictures show just how much London's Canary Wharf has changed in 20 years. Rory Bennett MyLondon. 2 February 2023. Retrieved 17 December 2023.
- ↑ The 100 Tallest Completed buildings in United Kingdom in 2023 Council on Tall Building and Urban Habitat. 12 December 2023. Retrieved 12 December 2023.
- 1 2 Top 10 Tallest Buildings in the UK as of 2023 CivilNotePpt. Retrieved 13 February 2023.
- 1 2 Landmark Pinnacle — Chalegrove Properties Canary Development. 4 January 2021. Retrieved 13 February 2023.
- ↑ Vertus launches highest BTR apartments in the UK at Newfoundland Nick Biring. 24 October 2022. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ↑ How tall is Canary Wharf? Canary Development. 12 January 2021. Retrieved 13 February 2023
- ↑ One Canada Square Canary Development, 9 March 2021. Retrieved 13 February 2023.
- 1 2 3 "Who's Here". Canary Wharf Group plc. Archived from the original on 19 April 2001. Retrieved 13 November 2010.
- ↑ Premier Guarantee Awards for ‘Landmark Pinnacle’ Premier Guarantee. Retrieved 16 December 2023.
- ↑ Winner: Best Luxury High Rise Living for ‘Landmark Pinnacle’ – 2023 Luxury Lifestyle Awards Chalegrove Properties Limited. 5 May 2023. Retrieved 16 December 2023.
- ↑ Newfoundland Quay — Canary Wharf Canary Development. 26 October 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ↑ Horden Cherry Lee creates Canary Wharf skyscraper wrapped in diamond-shaped exoskeleton.Tom Ravenscroft. 27 January 2022. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ↑ Our Project Story, Newfoundland. A diamond in The Smoke Hoare Lea. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ↑ Newfoundland wins two WhatHouse? awards – 26.11.21 Canary Wharf Group plc. 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 December 2023.
- ↑ South Quay Plaza — Berkeley Homes Canary Development. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ↑ South Quay Plaza has won Best Garden/Landscaping Design at the British Home Awards 2022 HTA Design LLP. 3 October 2022. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ↑ One Park Drive wins two British Homes Awards 2021 – 23.11.21 Canary Wharf Group plc. 23 November 2021. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ↑ Canary Wharf Group’s One Park Drive wins two Golds at the WhatHouse? Awards – 26.11.21 Canary Wharf Group plc. 26 November 2021. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ↑ One Park Drive’s penthouse wins prestigious Evening Standard New Homes Award – 02.10.23 Press Office, Canary Wharf Group. 2 October 2023. Retrieved 17 December 2023.
- ↑ CWG Wins Two Awards at the WhatHouse? Awards 2023 – 20.11.23 Canary Wharf Group plc. 20 November 2023. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ↑ "Contact us". HSBC Holdings plc. Archived from the original on 4 December 2010. Retrieved 13 November 2010.
- ↑ "£16bn cross-London project to take four floors in Canary Wharf tower". Property Week. 6 June 2008. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 13 November 2010.
- ↑ Ballymore honoured at the 2023 What House? Awards in London Ballymore news. Retrieved 17 December 2023.
- ↑ Billings Design Associates News 2022 Billings Design Associates. Retrieved 17 December 2023.
- ↑ "Corporate enquiries". Barclays. Archived from the original on 29 March 2010. Retrieved 13 November 2010.
- ↑ Canary Wharf Group plc – Estate Map Archived 1 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine. Canarywharf.com (13 May 2010). Retrieved on 12 July 2013.
- ↑ "United Kingdom". Clifford Chance. Archived from the original on 15 August 2010. Retrieved 13 November 2010.
- ↑ "10 Park Drive (A3)". Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- ↑ 10 Park Drive — Canary Wharf Group Canary Development. 4 January 2021. Retrieved 5 December 2023.
- ↑ [ https://group.canarywharf.com/press-release/canary-wharf-groups-10-park-drive-wins-gold-award-at-whathouse-awards-071220/ Canary Wharf Group’s 10 Park Drive Wins Gold Award at WhatHouse? Awards – 07.12.20]Press Office, Canary Wharf Group. 7 December 2020. Retrieved 17 December 2023.
- ↑ Baltimore Tower-Galliard Canary Development. 4 January 2021. Retrieved 17 December 2023.
- ↑ Pan Peninsula – Ballymore Canary Development. 4 January 2021. Retrieved 5 December 2023.
- 1 2 Sailmakers – Harbour Central Canary Development. 25 January 2022. Retrieved 18 December 2023.
- ↑ Maine Tower – Harbour Central Canary Development. 16 March 2021. Retrieved 18 December 2023.
- ↑ 1 Bank Street, London Council on Tall Building and Urban Habitat. Retrieved 18 December 2023.
- ↑ One & Five Bank Street London’s built environment community. 6 November 2020. Retrieved 18 December 2023.
- ↑ One & Five Bank Street: BREEAM Outstanding Buildington. 21 May 2016. Retrieved 18 December 2023.
- ↑ EBRD headquarters European Bank for Reconstruction and Development. Retrieved 18 December 2023.
- ↑ Vertus – 10 George Street Canary Development. 4 January 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ↑ Vertus’ 10 George Street Awarded Gold at What House? Awards – 07.12.20 Canary Wharf Group plc. 7 December 2020. Retrieved 27 December 2023.
- ↑ Sirocco Tower, London Council on Tall Building and Urban Habitat. Retrieved 20 December 2023.
- ↑ 25 Churchill Place, London Council on Tall Building and Urban Habitat. Retrieved 19 December 2023.
- ↑ "Brexit: the United Kingdom's withdrawal from the European Union | European Medicines Agency". 17 September 2018. Archived from the original on 25 August 2020. Retrieved 26 August 2020.
- ↑ Dollar Bay — Mount Anvil Canary Development. 16 March 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ↑ "Contact Us". Marriott International, Inc. Archived from the original on 11 March 2011. Retrieved 8 March 2011.
- ↑ Listed Buildings in Canary Wharf Ward, Tower Hamlets British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 12 February 2023.
- ↑ Quay Walls, Copings and Butresses to Import Dock and Export Dock, A Grade I Listed Building in Canary Wharf, London British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 12 February 2023.
- ↑ Import Dock And Export Dock / Quay Walls, Copings And Butresses To Import Dock And Export Dock Historic England. Retrieved 12 February 2023.
- ↑ Warehouses and General Offices at Western End of North Quay, A Grade I Listed Building in Canary Wharf, London British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 12 February 2023.
- ↑ Warehouses and General Offices at Western End of North Quay Historic England. Retrieved 12 February 2023.
- ↑ West India Dock Conservation Area London Borough of Tower Hamlets. 7 March 2007. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ North Quay Heritage Assessment by Peter Stewart Consultancy Canary Wharf Group Plc. July 2020. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ 10 and 12, Garford Street E14, A Grade II Listed Building in Canary Wharf, London British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ 14, Garford Street E14, A Grade II Listed Building in Canary Wharf, London British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ 16 and 18, Garford Street E14, A Grade II Listed Building in Canary Wharf, London British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ Entrance Gates to West India Docks, A Grade II Listed Building in Canary Wharf, London British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ Former West Entrance Gate to West India Docks with Curved Walling and Bollards, A Grade II Listed Building in Canary Wharf, London British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ Railings to West of Main Gate at West India Dock, A Grade II Listed Building in Canary Wharf, London British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ Former Excise Office, A Grade II Listed Building in Canary Wharf, London British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ Railings and Gatepiers to Former Excise Office, A Grade II Listed Building in Canary Wharf, London British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ Quadrangle Stores at West India Dock, A Grade II Listed Building in Canary Wharf, London British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ Salvation Army Hostel, A Grade II Listed Building in Canary Wharf, London British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ West India Dock Former Guard House, A Grade II Listed Building in Canary Wharf, London British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ Former West Entrance Lock to South Dock, West India Docks, A Grade II Listed Building in Canary Wharf, London British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ Fitch and Sons Works, A Grade II Listed Building in Canary Wharf, London British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ Cascades, A Grade II Listed Building in Canary Wharf, London British Listed Buildings, History in Structure. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ↑ Cascades CZWG Listed Buildings. Retrieved 23 Feb 2023.
- ↑ "Higher occupancy lifts Canary Wharf's Songbird". Reuters. 22 March 2007. Archived from the original on 1 July 2019. Retrieved 11 November 2010.
- ↑ "Canary Wharf boss sees future in creative campus". Archived from the original on 13 May 2015. Retrieved 3 March 2014.
- ↑ "China to invest in Canary Wharf". China Economic Review. 31 August 2009. Retrieved 11 November 2010.
- ↑ "European Medicines Agency -". www.ema.europa.eu. Archived from the original on 26 May 2012. Retrieved 20 February 2018.
- ↑ "European Banking Authority". www.eba.europa.eu. Archived from the original on 10 March 2011. Retrieved 26 August 2021.
- ↑ "West India Docks". canalrivertrust.org.uk. Archived from the original on 13 February 2018. Retrieved 12 February 2018.
- ↑ "Poplar Dock Marina, London - BWML". Archived from the original on 6 December 2018. Retrieved 31 October 2018.
- ↑ "Idea Stores: service integration with libraries and learning". GOV.UK. Archived from the original on 10 February 2018. Retrieved 9 February 2018.
- ↑ "Idea Store - Canary Wharf". www.ideastore.co.uk. Archived from the original on 10 February 2018. Retrieved 9 February 2018.
- ↑ "Cineworld | West India Quay". Archived from the original on 12 February 2018.
- ↑ "Cinema Listings - West India Quay". www.cineworld.co.uk. Archived from the original on 12 February 2018. Retrieved 11 February 2018.
- ↑ "Cinema Listings - Everyman Cinema". www.everymancinema.com. Archived from the original on 26 August 2021. Retrieved 11 February 2018.
- ↑ Beach Volleyball Canary Wharf Group plc. Retrieved 30 December 2023.
- ↑ Padel Tennis Canary Wharf Group plc. Retrieved 30 December 2023.
- ↑ A Wonderfully Colourful (And Free!) Minigolf Course Has Landed In Canary Wharf. They're clearly not worried about errant golf balls smashing into any of Canary Wharf's many glass skyscrapers! Secret London. 22 May 2023. Retrieved 30 December 2023.
- 1 2 Spring in Canary Wharf: Green Spaces and Parks Canary Wharf Group plc. 10 May 2023. Retrieved 29 December 2023.
- ↑ Open Spaces Canary Wharf Group plc. Retrieved 29 December 2023.
- ↑ Jubilee Park, Canary Wharf, The Garden Guide Gardenvisit.com. Retrieved 14 December 2023.
- ↑ Jubilee Park, Canary Wharf, London Life on Roof. Retrieved 14 December 2023.
- ↑ Jubilee Park, Canary Wharf, London Life on Roof. Retrieved 28 December 2023.
- ↑ Jubilee Park awarded the coveted Green Flag Award as it is officially recognized as one of the country’s best parks – 19.07.23 Canary Wharf Group plc. 19 July 2023. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ↑ Crossrail Place Roof Garden Canary Wharf Group. Retrieved 18 February 2023.
- ↑ The Gallery and Video | Construction of Crossrail Place roof garden, by Katherine Smale New Civil Engineer. 1 May 2015. Retrieved 15 February 2023.
- ↑ Projects / Crossrail Place Canary Wharf Foster + Partners. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ↑ Canary Wharf’s Crossrail Place gets international acclaim, picking up a gong at Mipim’s annual awards ceremony CityA.M. 20 March 2016. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ↑ Gillespies scoops first prize at the European Garden Awards for Crossrail Place Roof Garden Gillespies. 20 September 2017. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ↑ LI-commended Crossrail Place Roof Garden wins European Garden Award Landscape Institute. 23 October 2017. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ↑ Harbour Quay Canary Wharf Group plc. Retrieved 28 December 2023.
- ↑ Harbord Square Park Canary Wharf Group plc. Retrieved 28 December 2023.
- ↑ 13 Best Shopping Malls in London, London's Most Popular Malls and Department Stores Hotel.com. Retrieved 27 December 2023.
- ↑ Retail Leasing: Expand the ever-growing, vibrant lifestyle at Canary Wharf. Canary Wharf Group plc. Retrieved 27 December 2023.
- ↑ "Election results for Canary Wharf, 5 May 2022". 5 May 2022.
- ↑ King, Jon (17 February 2020). "Canary Wharf Conservative councillor quits party". East London Advertiser. Retrieved 27 September 2023.
- 1 2 3 "DLR map" (PDF). Transport for London (TfL). Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 May 2019.
- 1 2 "London's Rail & Tube services" (PDF). Transport for London (TfL). Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 April 2019.
- ↑ "Elizabeth line - December 2019" (PDF). Transport for London (TfL). Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 August 2018.
- ↑ "London Borough of Tower Hamlets Air Quality Annual Status Report for 2017" (PDF). London Borough of Tower Hamlets. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 May 2019.
- ↑ "Buses from Canary Wharf" (PDF). Transport for London (TfL). Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 May 2019.
- ↑ "London's River Services map" (PDF). Transport for London (TfL). Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 April 2019.
- ↑ "Passenger numbers at London City Airport up by 6.4 per cent in 2018". International Airport Review. 9 January 2019. Archived from the original on 28 May 2019.
- ↑ "Destinations". London City Airport. Archived from the original on 26 April 2019.
- ↑ "Route 1". Sustrans. Archived from the original on 14 April 2019.
- ↑ "Overview Route Database - EuroVelo - the European cycle route network". www.eurovelo.org. Archived from the original on 29 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- ↑ "Route 13". Sustrans. Archived from the original on 28 May 2019.
- ↑ "Barking to Tower Gateway: CS3" (PDF). Transport for London. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 April 2019.
- ↑ "Cycleway between Hackney and the Isle of Dogs" (PDF). Transport for London (TfL). Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 May 2019.
- 1 2 "Cycling | Canal & River Trust". canalrivertrust.org.uk. Archived from the original on 7 April 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- ↑ Museum of London Docklands: 'The past is problematic in this country'BBC News. 16 July 2023. Retrieved 10 January 2024.
- ↑ Families fun and learning for allMuseum of London Docklands. Retrieved 10 January 2024.
- ↑ "10 things you didn't know about Canary Wharf". SACO. Archived from the original on 6 May 2018. Retrieved 5 May 2018.
- ↑ "Canary Wharf Welcomes Pokémon Go Players With Map And Prizes". Bisnow. Archived from the original on 28 January 2021. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
- ↑ Yorke, Thom (27 May 1994). "Radiohead - Live at the Astoria (May 1994) At Home". YouTube. Archived from the original on 20 August 2021. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- ↑ Winter Lights Canary Wharf Group plc. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ↑ Canary Wharf Winter Lights Festival Scoops Best Creative Lighting Event at darc awards 2017 Canary Wharf Group plc. 12 October 2017. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ↑ Canary Wharf’s Winter Lights Festival Adds Second darc award to the Mantelpiece Canary Wharf Group plc. 15 January 2020. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ↑ Winter Lights Canary Wharf Group. Retrieved 16 February 2023.
- ↑ Canary Wharf Winter Lights festival 2023: First look at the luminous spectacle taking over E14 Evening Standard. 17 January 2023. Retrieved 16 February 2023.
- ↑ Canary Wharf businesses to ride the wave in annual Dragon Boat Race for WaterAid. Safeeyah Kazi WaterAid. 11 May 2023. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ↑ Canary Wharf businesses splash their way to £31,744 in annual Dragon Boat Race for WaterAid. Safeeyah Kazi WaterAid. 12 July 2023. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ↑ Brand New Music, Arts, Theatre and Comedy Festival Coming to Canary Wharf this July – 12.05.22 Canary Wharf Group plc. 12 May 2022. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ↑ Brand New Music, Arts, Theatre and Comedy Festival Coming to Canary Wharf this July – 12.05.22 Canarywharf.com. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ↑ Get Into the Groove: Canary Wharf’s Free Music and Culture Festival Returns This July – 25.04.23 Canary Wharf Group plc. 25 April 2022. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ↑ Festival14 Wed 26 – Sun 30 July 2023, Canary Wharf Canarywharf.com. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ↑ Open water swimming returns to Canary Wharf for second summer. The Middle Dock is open to swimmers ‘of all levels’ for £8.50 a visit The Standard. 5 June 2023. Retrieved 30 December 2023.
- ↑ Open Water Swimming, Reopening 2024 Canary Wharf Group plc. Retrieved 30 December 2023.
- ↑ Lynn Chadwick: Couple on Seat Canary Wharf Group. Retrieved 16 February 2023.
- ↑ Culture for Community-Art for Everyone Canary Wharf Group. Retrieved 16 February 2023.
- ↑ A guide to the Canary Wharf Art Trail Canary Development. 10 February 2021. Retrieved 16 February 2023.
- ↑ Art on the Estate Canary Wharf Group. Retrieved 16 February 2023.
- ↑ Canary Wharf Art Map Canary Wharf Group. Retrieved 15 February 2023.
- ↑ Children’s Art Trail Canary Wharf Group. Retrieved 15 February 2023.
- ↑ Raise Your Art RateCanary Wharf Art Trail. Canary Wharf Group plc. Retrieved 8 January 2024.
- ↑ Wharf life Wharf life. Retrieved 19 February 2023.
Further reading
- Greater London Authority (January 2008). London's Central Business District: Its global importance (PDF). p. 6. ISBN 978-1-84781-109-7. Retrieved 26 August 2021.
- Kevin D'Arcy (2012). London's 2nd City: Creating Canary Wharf. Rajah Books. ISBN 978-0955670626.
_-_geograph.org.uk_-_4676594.jpg.webp)

.jpg.webp)




.jpg.webp)