Casomorphin is an opioid peptide (protein fragment) derived from the digestion of the milk protein casein.[1]
Health
Digestive enzymes can break casein down into peptides that have some biological activity in cells and in laboratory animals though conclusive causal effects on humans have not been established.[1]
Although research has shown high rates of use of complementary and alternative therapies for children with autism, including gluten and/or casein exclusion diets, as of 2008 there was a lack of evidence that these diets had any effect.[2]
If opioid peptides breach the intestinal barrier, typically linked to permeability and constrained biosynthesis of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4), they can attach to opioid receptors. Elucidation requires a systemic framework that acknowledges that public-health effects of food-derived opioids are complex with varying genetic susceptibility and confounding factors, together with system-wide interactions and feedbacks.[3]
List of known casomorphins (non-exhaustive)
β-Casomorphins 1–3
- Structure: H-Tyr-Pro-Phe-OH
- Chemical formula: C23H27N3O5
- Molecular weight: 425.48 g/mol
Bovine β-casomorphins 1–4
- Structure: H-Tyr-Pro-Phe-Pro-OH
- Chemical formula: C28H35N4O6
- Molecular weight: 522.61 g/mol
Bovine β-casomorphin 1–4, amide
- Structure: H-Tyr-Pro-Phe-Pro-NH2
- Chemical formula: C28H35N5O5
- Molecular weight: 521.6 g/mol
Also known as morphiceptin
Bovine β-casomorphin 5
- Structure: H-Tyr-Pro-Phe-Pro-Gly-OH
- Chemical formula: C30H37N5O7
- Molecular weight: 594.66 g/mol
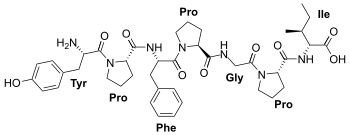
Bovine β-casomorphin 7
- Structure: H-Tyr-Pro-Phe-Pro-Gly-Pro-Ile-OH
- Chemical formula: C41H55N7O9
- Molecular weight: 789.9 g/mol
Bovine β-casomorphin 8
- Structure: H-Tyr-Pro-Phe-Pro-Gly-Pro-Ile-Pro-OH
- Chemical formula: C46H62N8O10
- Molecular weight: 887.00 g/mol
(Note: There is also a form of bovine β-casomorphin 8 that has histidine instead of proline in position 8, depending on whether it is derived from A1 (His) or A2 (Pro) beta-casein.)
References
- 1 2 European Food Safety Authority. 1 February 2009 Review of the potential health impact of β-casomorphins and related peptides
- ↑ Millward, C; Ferriter, M; Calver, S; Connell-Jones, G (2008). "Gluten- and casein-free diets for autistic spectrum disorder". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD003498. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003498.pub3. PMC 4164915. PMID 18425890.
- ↑ Keith, Bernard Woodford (2021). "Casomorphins and Gliadorphins Have Diverse Systemic Effects Spanning Gut, Brain and Internal Organs". Int J Environ Res Public Health. 18 (15): 7911. doi:10.3390/ijerph18157911. PMC 8345738. PMID 34360205.