| Swabian Circle Schwäbischer Reichskreis | |
|---|---|
| |
| 1500–1808 | |
 Coat of arms
| |
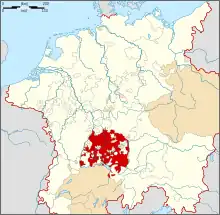 The Swabian Circle as at the beginning of the 16th century within the Holy Roman Empire | |
| Capital | Ulm |
| Area | |
• 1801 | 34,314 km2 (13,249 sq mi) |
| Government | |
| Circle Colonel | |
• 1531-1537 | Wolfgang von Montfort |
• 1556-1562 | Wilhelm von Eberstein |
• 1563, 1564-1568 | Christoph |
• 1569-1591 | Louis III |
• 1622-1628 | John Frederick |
| Legislature | Circle Diet |
| Historical era | Early modern period |
• Established | 1500 |
• Peace of Westphalia | 1648 |
| 1806 | |
• Disestablished | 1808 |
| Today part of | Austria Germany Liechtenstein Switzerland |
The Circle of Swabia or Swabian Circle (German: Schwäbischer Reichskreis or Schwäbischer Kreis) was an Imperial Circle of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1500 on the territory of the former German stem-duchy of Swabia. However, it did not include the Habsburg home territories of Swabian Austria, the member states of the Swiss Confederacy nor the lands of the Alsace region west of the Rhine, which belonged to the Upper Rhenish Circle. The Swabian League of 1488, a predecessor organization, disbanded in the course of the Protestant Reformation and the Thirty Years War later in the 16th century.
Administration
The directors of the Swabian Circle were the Bishop of Constance (replaced by the margrave of Baden after the 1803 Reichsdeputationshauptschluss) and the Duke of Württemberg; meetings of the circle's diet were usually held at the Imperial city of Ulm. Though it was shattered into a multitude of mainly very small states, the circle had an effective government, which, in view of the eastward expansion of France, from 1694 on even maintained its own army based at the Kehl fortress.
As of 1792 the Swabian Circle consisted of 88 territories, of which only the Duchy (later Kingdom) of Württemberg, the Margraviate ( later Grand Duchy ) of Baden and the Bishopric of Augsburg were of any significance. The Reichsdeputationshauptschluss reduced the number to 41 and the 1806 Rheinbundakte to seven (including the territories that had fallen to Bavaria).
Composition
The circle was made up of the following states:
| Name | Type of entity | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Imperial City | 35th Swabian City, Reichsfreiheit granted by Emperor Charles IV of Luxembourg in 1360. | |
| Prince-Bishopric | Established in the 11th century, from the 15th century residence at Dillingen with the 25th seat to the Reichstag. | |
| Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Rudolph of Habsburg in 1276, 2nd Swabian City. | |
| Margraviate | Established in 1112, partitioned into Baden-Durlach and Baden-Baden from 1535 to 1771. | |
| Margraviate | Subdivision of Baden from 1535, residence at Rastatt from 1705, to Baden-Durlach in 1771. 58th seat to the Reichstag. | |
| Margraviate | Subdivision of Baden from 1535, residence at Karlsruhe from 1715. 60th seat to the Reichstag. | |
| Margraviate | Markgräflerland territory, inherited by Baden in 1503. 62nd seat to the Reichstag. | |
| Baindt | Imperial Abbey | 21st Swabian Prelature, gained Reichsfreiheit in 1376. |
| Imperial City | 17th Swabian City, Reichsfreiheit granted by Rudolph of Habsburg in 1281. | |
| Lordship | Acquired by St. Blaise's Abbey in 1609 to gain Reichsfreiheit. | |
| Imperial City | Since 1241. | |
| Imperial Abbey | Established in 819 by Louis the Pious; 11th Prelatess of the Rhine and 2nd Swabian Countess. | |
| Imperial City | Since the 13th century; 36th Swabian City. | |
| Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Rudolph of Habsburg in 1275. | |
| Prince-Bishopric | Established about 585, Reichsfreiheit confirmed by Frederick I Barbarossa in 1155, residence at Meersburg from 1526, 23th seat to the Reichstag. | |
| Imperial City | Since 1351. | |
| County | Line extinct in 1660, inherited by Baden, 10th vote in the Swabian bench. | |
| Lordship | Held by Thurn und Taxis from 1726. | |
| Lordship | Held by the Counts of Abensberg from 1661. | |
| Elchingen | Imperial Abbey | Established about 1120, gained Reichsfreiheit in 1485. |
| Prince-Provostry | Established in 1460 as successor of Ellwangen Imperial Abbey, 57th seat to the Reichstag | |
| Imperial City | Since 1229. | |
| Freiherren | Acquired the former County of Kirchberg and Weißenhorn in 1507, ennobled by Maximilian I in 1511, hereditary Imperial counts from 1530. | |
| Princely county | Various territories, established from the bequest of Berthold V of Zähringen in 1218, Fürstenberg-Baar since 1441; Principality in 1664 with the 90th seat to the Reichstag | |
| County | Subdivision from 1559, again partitioned in 1614. | |
| County | Subdivision of Fürstenberg-Blumberg from 1614, became main in 1716, inherited by Fürstenberg-Fürstenberg in 1744. | |
| County | Subdivision of Fürstenberg-Blumberg from 1614, became main in 1744. | |
| County | Subdivision from 1559, raised to Principality and main in 1664, extinct in 1716. | |
| Imperial Abbey | Established about 730 by Saint Pirmin, granted to Prince-Bishopric of Bamberg by Henry II in 1007. | |
| Imperial City | Since 1360. | |
| Imperial City | Since 1391. | |
| Lordship | Acquired by Baden in 1507. | |
| Abbacy | 19th Swabian Prelature established in 1237, Reichsfreiheit granted by Emperor Sigismund in 1437. | |
| Lordship | Territory around Hausen Castle, near Beuron. Acquired by Fugger in 1682 following extinction of the line of Lords; to Castell in 1735. | |
| Imperial Abbey | 18th Swabian Prelature established in 1231, gained Reichsfreiheit about 1428. | |
| Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Charles IV in 1371. | |
| County | 1st Swabian County, held by the Counts of Fürstenberg from 1535. | |
| County | Member of the Counts of Swabia, to Bavaria. | |
| County | Reichsfreiheit granted by Ferdinand I in 1560, acquired by Habsburg in 1765. | |
| County | 948AD to 1634AD then to the House of Kronberg, then held by the House of Leyen from 1697, Imperial Counts from 1711, Principality of Leyen in 1806. | |
| Lordship | Established in 1415, with Stühlingen acquired by Pappenheim in 1582, to Fürstenberg-Stühlingen in 1639. | |
| County | County of Zollern established in the 11th century, partitioned in 1576. | |
| County | Subdivision of Hohenzollern from 1576, raised to principality in 1623. | |
| County | Former Lordship of Haigerloch, subdivision of Hohenzollern from 1576, inherited by Hohenzollen-Sigmaringen in 1767. | |
| County | Subdivision of Hohenzollern from 1576, raised to principality in 1623. | |
| Imperial Abbey | Established in 1186, gained Reichsfreiheit in 1694. | |
| Imperial City | 25th Swabian City from 1365. | |
| Lordship | Territory around Justingen Castle near Schelklingen, acquired by Württemberg in 1751. | |
| Imperial Abbey | Established in 1133, Imperial abbey since 1346. | |
| Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Rudolph of Habsburg in 1286. | |
| Prince-Abbey | Established in 752, Reichsfreiheit granted by Henry IV in 1062, 55th seat to the Reichstag. | |
| Imperial City | 20th Swabian City, Reichsfreiheit granted by Rudolph of Habsburg in 1289. | |
| Lordship | Territory around Wolfach, held by Fürstenberg since 1291. | |
| Landgraviate | Held by the Counts of Sulz since 1410, acquired by the House of Schwarzenberg in 1698. | |
| County | Territory around Guggenhausen, acquired the Imperial county of Rothenfels in 1565, Freiherren from 1621 as 8th Swabian County, partitioned in 1622. | |
| Lordship | Subdivision of Königsegg from 1622, Imperial county from 1629, main Königsegg from 1666. | |
| Lordship | Subdivision of Königsegg from 1622, Imperial county from 1629. | |
| Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Adolf of Nassau in 1293. | |
| Imperial Abbey | Established about 822, gained Reichsfreiheit in 1466 then ceded to the city. | |
| Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Rudolph of Habsburg in 1275, 15th Swabian city. | |
| Commandery | An administrative grouping of lands held by the Teutonic Order since 1272. | |
| Imperial Abbey | Established about 776, gained Reichsfreiheit in 1500. | |
| Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Rudolph of Habsburg in 1286. | |
| Lordship | Held by the Counts of Zimmern since 1354, fell to the House of Helfenstein in 1594, Fürstenberg-Messkirch from 1627. | |
| Lordship | Held by the House of Frundsberg since 1467, fell to the Duchy of Bavaria in 1586, held by John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough as Prince of Mindelheim from 1705 to 1714. | |
| Princely County | To the dukes of Württemberg with the 80th seat to the Reichstag | |
| Imperial Abbey | Established in 1095, Reichsfreiheit contested by the House of Oettingen-Wallerstein, confirmed by the Reichskammergericht in 1764. | |
| Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Frederick II of Hohenstaufen in 1215. | |
| Imperial Abbey | Established about 1090, gained Reichsfreiheit in 1495. | |
| County | Partitioned in 1522. | |
| County | Subdivision of Oettingen from 1522, raised to principality in 1674, extinct in 1731. | |
| County | Subdivision of Oettingen from 1522, raised to principality in 1774. | |
| County | Subdivision of Oettingen-Wallerberg from 1623, raised to principality in 1734. | |
| Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Frederick II of Hohenstaufen in 1240. | |
| Imperial Abbey | Established in 983 by Saint Gebhard of Constance, Reichsfreiheit granted by Frederick II of Hohenstaufen. | |
| Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Frederick II of Hohenstaufen in 1220. | |
| Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Rudolph of Habsburg in 1278. | |
| Imperial City | From about 1240. | |
| Imperial Abbey | Established in 1126, gained Reichsfreiheit in 1482. | |
| Imperial Abbey | Established in 1126, gained Reichsfreiheit in 1376. | |
| County | Territory around Immenstadt held by the Counts of Montfort since 1332, acquired by Königsegg in 1565. | |
| Imperial Abbey | 20th Swabian Prelature established in 1224, Reichsfreiheit granted by Frederick II of Hohenstaufen in 1237. | |
| Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Sigismund of Luxembourg in 1434, associate of the Swiss Confederacy 1519–1689. | |
| Imperial abbey | Established about 1134, Reichsfreiheit granted by Conrad III of Hohenstaufen in 1142. | |
| Imperial Abbey | Established by Rot an der Rot Abbey in 1183, gained Reichsfreiheit about 1440. | |
| Imperial City | Since about 1250. | |
| Imperial City | Since 1280. | |
| Lordship | Territory in the Kraichgau, held by the successors of Imperial Knight Franz von Sickingen, Freiherren from 1606, Imperial counts from 1790. | |
| Imperial Abbey | 22nd Swabian Prelature established about 1258 by the Counts of Dillingen, gained Reichsfreiheit against Ulm in 1773. | |
| Imperial Abbey | 23rd Swabian Prelature established in 1096, gained Reichsfreiheit in 1781. | |
| Imperial Abbey | 6th Rhenish Prelate | |
| County | Reached Reichfreiheit in 1705 by purchasing the Lordship of Thannhausen (not to be confused with Tannhausen), split into Stadion-Thannhausen and Stadion-Warthausen in 1741. | |
| Lordship | Held by the Freiherren von Staufen (not related to the House of Hohenstaufen), extinct in 1602, then part of Further Austria, acquired by St Blaise's Abbey in 1738. | |
| Landgraviate | Held by the Counts of Lupfen since 1251, extinct in 1582, acquired by Pappenheim, to Fürstenberg-Stühlingen in 1639. | |
| Duchy | Former branch of the House of Zähringen, extinct in 1439, ducal title granted to Eberhard I of Württemberg by Maximilian I in 1495. | |
| Lordship | Held by the Counts of Monfort, fell to Further Austria in 1780. | |
| Lordship | Reichsfrei territory around Tannhausen (not to be confused with Thannhausen). | |
| Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit confirmed about 1400. | |
| Imperial City | 4th Swabian City, gained Reichsfreiheit in the 12th century. | |
| Imperial Abbey | Established about 1128, gained Reichsfreiheit in 1143. | |
| Archstewardship | Territory around Nüziders, lordship held by the Truchsess of Waldburg since 1455, Reichsfreiheit granted by Frederick III of Habsburg in 1463, line extinct in 1511. | |
| Archstewardship | Territory around Trauchburg castle near Isny, held by Waldburg since 1306, Imperial county from 1628, extinct in 1772. | |
| Archstewardship | Former County of Friedberg around Scheer castle, held by Waldburg-Sonnenburg since 1454, inherited by Waldburg-Trauchburg in 1511, to Thurn und Taxis in 1785. | |
| Archstewardship | Territory around Zeil castle near Leutkirch, held by Waldburg since 1337, acquired Wolfegg and Waldsee from Waldburg-Trauchburg in 1508, partitioned in 1589. | |
| Archstewardship | Subdivision of Waldburg-Wolfegg-Zeil from 1589, Imperial county from 1628, again partitioned in 1667, extinct in 1798. | |
| Archstewardship | Subdivision of Waldburg-Wolfegg from 1667, inherited Waldburg-Wolfegg in 1798, raised to principality in 1803. | |
| Archstewardship | Subdivision of Waldburg-Wolfegg-Zeil from 1589, Imperial county from 1628, again partitoned in 1674, inherited Waldburg-Trauchburg in 1772, raised to principality in 1803. | |
| Archstewardship | Subdivision of Waldburg-Zeil from 1674, raised to principality in 1803. | |
| Imperial City | Reichsfreiheit granted by Rudolph of Habsburg in 1286. | |
| Imperial City | Since about 1275. | |
| Imperial Abbey | Established in 1056 by Duke Welf I of Bavaria, gained Reichsfreiheit in 1274. | |
| Imperial Abbey | Established in 1145, gained Reichsfreiheit about 1257. | |
| Prince-Provostry | Established in 1130. | |
| Lordship | Held by the House of Helfenstein, partitioned between Fürstenberg and the Duchy of Bavaria in 1627. | |
| Imperial City | Since about 1300. | |
| Duchy | County of Wirtemberg established in the 12th century, raised to duchy in 1495 by Maximilian I, 52th seat to the Reichstag. | |
| Imperial City | Since the 14th century. | |
| Imperial Abbey | Established in 1089, gained Reichsfreiheit from Württemberg in 1750. |
References
- Imperial Circles in the 16th Century Historical Maps of Germany
- https://web.archive.org/web/20110718204310/http://maja.bsz-bw.de/kloester-bw/klostertexte.php?kreis=&bistum=&alle=&ungeteilt=&art=&orden=&orte=1&buchstabe=G&nr=619&thema=Geschichte The History Of Gutenzell (German Version)
- https://www.baden-wuerttemberg.de/en/our-state/state-history/ The History Of Baden-Wuttemburg
External links
 Media related to Swabian Circle at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Swabian Circle at Wikimedia Commons
-en.png.webp)