Pfullendorf | |
|---|---|
 Center of the town with the Church of Saint James | |
 Coat of arms | |
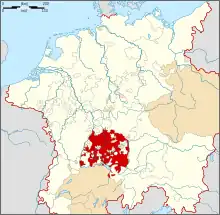
Location of Pfullendorf within Sigmaringen district  | |
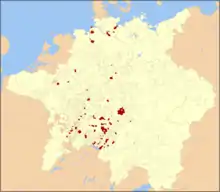
 Pfullendorf  Pfullendorf | |
| Coordinates: 47°55′27″N 9°15′24″E / 47.92417°N 9.25667°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Baden-Württemberg |
| District | Sigmaringen |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2022–30) | Ralph Gerster[1] (CDU) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 90.56 km2 (34.97 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 654 m (2,146 ft) |
| Population (2021-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 13,501 |
| • Density | 150/km2 (390/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 88630 |
| Dialling codes | 07552 |
| Vehicle registration | SIG |
| Website | www.pfullendorf.de |
Pfullendorf is a small town of about 13,000 inhabitants located 25 km (16 mi) north of Lake Constance in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It was a Free Imperial City of the Holy Roman Empire for nearly 600 years.
The town is in the district of Sigmaringen south of the Danube valley and therefore on the continental divide between the watersheds of the Rhine and the Danube. The area is known as the Linzgau.
History


Early history
Pfullendorf was founded by the Alamanni tribe during their third wave of settlement and might have been named after a clan chief named Pfullo. According to another theory, it was named Dorf am Phoul (Pfuol), meaning village on the Phoul.
The area around Lake Constance, particularly the Linzgau, Hegau and Vorarlberg, came progressively under the rule of the counts of Pfullendorf from the 8th century onward. The earliest documented bearer of that name was Count Ludwig von Pfullendorf, who is referred to as the ruler of the county of Hegau from 1067 to 1116. Presumably, Pfullendorf expanded due to its proximity to the counts' castle. Count Rudolf, a partisan of the future Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa, was able to expand his family's possessions and they eventually owned fiefs from the Danube to the Grisons. Following the death of his son Berthold in 1167, Count Rudolf named the Emperor as his heir and then moved to the Holy Land where he died in 1181.
Free Imperial City
Imperial City of Pfullendorf Reichsstadt Pfullendorf | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1220–1803 | |||||||||
| Status | Free Imperial City of the Holy Roman Empire | ||||||||
| Capital | Pfullendorf | ||||||||
| Government | Republic | ||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||
| June 2 1220 | |||||||||
• Establishment of guild constitution | 1383 | ||||||||
| 1415 | |||||||||
| 1803 | |||||||||
| |||||||||

In June 1220, Emperor Frederick II elevated Pfullendorf to the status of Imperial City. However, the prince-bishops of Constance, as the biggest landowners in the Linzgau and patrons of several religious institutions such as Holy Spirit Hospital in Pfullendorf, continued to exert significant political influence over the whole area. At the Council of Constance (1415), King Sigismund granted Blutgerichtsbarkeit ("Blood justice" or the right to pronounce sentences of death or mutilation) to the town, a status that confirmed the city as being answerable to God and to the Emperor only.
Starting in 1383, Pfullendorf ruled itself according to a constitution that gave decisive powers to the town guilds and provided for the annual election of the mayor. A 50-member “High Council” also elected annually, was vested with executive authority alongside a 17-member “Small Council” chaired by the mayor. With brief interruptions, this guild-based constitution remained in force until 1803 and was to serve as a model for other cities.
Pfullendorf became a member of the powerful Swabian League in 1488 and took part in the war of 1492 against Duke Albrecht of Bavaria. The city was assigned to contribute 4 footmen, 6 horsemen, 4 wagons and 8 tents for the campaign.
Like a few other small Free Imperial Cities in the vicinity of Lake Constance, Pfullendorf was comparatively untouched by the turmoil that engulfed Germany during the Protestant Reformation and it was to be one of the 12 Free Imperial Cities, out of 50, that was to be officially classified as Catholic at the Peace of Westphalia, that also explicitly stated for the first time that Free Imperial Cities enjoyed the same degree of independence (Imperial immediacy) as the other Imperial Estates.
End of the Free Imperial City of Pfullendorf


Like most of the other 50 Free Imperial Cities, Pfullendorf lost its freedom in the course of the mediatisation of 1803 and was annexed to the Margraviate of Baden.
The old hospital building in the center of town was sold and in 1845 (it now houses the restaurant Deutscher Kaiser) and a new hospital opened on the site of a former monastery near the Upper Gate. The city was connected to the railway network in 1873-75.
Pfullendorf remained an administrative center in the upper Linzgau until 1936. It then became part of the district of Überlingen, and has been a part of the district of Sigmaringen since 1973. During the administrative reforms that occurred from 1972 to 1976, the neighboring villages of Aach-Linz, Denkingen, Gaisweiler, Tautenbronn, Großstadelhofen, Mottschieß, Otterswang, and Zell-Schwäblishausen became part of Pfullendorf.
Culture
The German Army's Special Operations Training Centre (German: Ausbildungszentrum für spezielle Operationen) is located in Pfullendorf, as was the NATO International Long Range Reconnaissance Patrol School following its move from Weingarten to its closure in 1999. In 2001 the United States Army took command of the I-LRRP School in Pfullendorf and the name was changed to the International Special Training Centre (ISTC). ISTC is the International Wing (I-Wing) of the German Ausbildungszentrum Special Operations.
Twin towns
- Allschwil in Switzerland since April 13, 1984
- Saint-Jean-de-Braye in France since May 1, 1987
Notable Pfullendorfers
- Roderich Kiesewetter, politician
- Daniel Schuhmacher, DSDS winner for Season 6.
- Sinan Gümüş, Galatasaray, professional football player.
References
- ↑ Bürgermeisterwahl Pfullendorf 2022, Staatsanzeiger.
- ↑ "Bevölkerung nach Nationalität und Geschlecht am 31. Dezember 2021" [Population by nationality and sex as of December 31, 2021] (CSV) (in German). Statistisches Landesamt Baden-Württemberg. June 2022.