In molecular biology, endonucleases are enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a polynucleotide chain (namely DNA or RNA). Some, such as deoxyribonuclease I, cut DNA relatively nonspecifically (without regard to sequence), while many, typically called restriction endonucleases or restriction enzymes, cleave only at very specific nucleotide sequences. Endonucleases differ from exonucleases, which cleave the ends of recognition sequences instead of the middle (endo) portion. Some enzymes known as "exo-endonucleases", however, are not limited to either nuclease function, displaying qualities that are both endo- and exo-like.[1] Evidence suggests that endonuclease activity experiences a lag compared to exonuclease activity.[2]
Restriction enzymes are endonucleases from eubacteria and archaea that recognize a specific DNA sequence.[3] The nucleotide sequence recognized for cleavage by a restriction enzyme is called the restriction site. Typically, a restriction site will be a palindromic sequence about four to six nucleotides long. Most restriction endonucleases cleave the DNA strand unevenly, leaving complementary single-stranded ends. These ends can reconnect through hybridization and are termed "sticky ends". Once paired, the phosphodiester bonds of the fragments can be joined by DNA ligase. There are hundreds of restriction endonucleases known, each attacking a different restriction site. The DNA fragments cleaved by the same endonuclease can be joined regardless of the origin of the DNA. Such DNA is called recombinant DNA; DNA formed by the joining of genes into new combinations.[4] Restriction endonucleases (restriction enzymes) are divided into three categories, Type I, Type II, and Type III, according to their mechanism of action. These enzymes are often used in genetic engineering to make recombinant DNA for introduction into bacterial, plant, or animal cells, as well as in synthetic biology.[5] One of the more famous endonucleases is Cas9.
Categories
Ultimately, there are three categories of restriction endonucleases that relatively contribute to the cleavage of specific sequences. The types I and III are large multisubunit complexes that include both the endonucleases and methylase activities. Type I can cleave at random sites of about 1000 base pairs or more from the recognition sequence and it requires ATP as source of energy. Type II behaves slightly differently and was first isolated by Hamilton Smith in 1970. They are simpler versions of the endonucleases and require no ATP in their degradation processes. Some examples of type II restriction endonucleases include BamHI, EcoRI, EcoRV, HindIII, and HaeIII. Type III, however, cleaves the DNA at about 25 base pairs from the recognition sequence and also requires ATP in the process.[4]
Notations
The commonly used notation for restriction endonucleases[6] is of the form "VwxyZ", where "Vwx" are, in italics, the first letter of the genus and the first two letters of the species where this restriction endonuclease may be found, for example, Escherichia coli, Eco, and Haemophilus influenzae, Hin. This is followed by the optional, non-italicized symbol "y", which indicates the type or strain identification, for example, EcoR for E. coli strains bearing the drug resistance transfer factor RTF-1,[6] EcoB for E. coli strain B,[7] and Hind for H. influenzae strain d.[6] Finally, when a particular type or strain has several different restriction endonucleases, these are identified by Roman numerals, thus, the restriction endonucleases from H. influenzae strain d are named HindI, HindII, HindIII, etc. Another example: "HaeII" and "HaeIII" refer to bacterium Haemophilus aegyptius (strain not specified), restriction endonucleases number II and number III, respectively.[4]: 64–64 The restriction enzymes used in molecular biology usually recognize short target sequences of about 4 – 8 base pairs. For instance, the EcoRI enzyme recognizes and cleaves the sequence 5' – GAATTC – 3'.[8]

Restriction endonucleases come in several types. A restriction endonuclease typically requires a recognition site and a cleavage pattern (typically of nucleotide bases: A, C, G, T). If the recognition site is outside the region of the cleavage pattern, then the restriction endonuclease is referred to as Type I. If the recognition sequence overlaps with the cleavage sequence, then the restriction endonuclease restriction enzyme is Type II.
Further discussion
Restriction endonucleases may be found that cleave standard dsDNA (double-stranded DNA), or ssDNA (single-stranded DNA), or even RNA. This discussion is restricted to dsDNA; however, the discussion can be extended to the following:
- Standard dsDNA
- Non-standard DNA
- Holliday junctions
- Triple-stranded DNA, quadruple-stranded DNA (G-quadruplex)
- Double-stranded hybrids of DNA and RNA (one strand is DNA, the other strand is RNA)[4]: 72–73
- Synthetic or artificial DNA (for example, containing bases other than A, C, G, T, refer to the work of Eric T. Kool). Research with synthetic codons, refer to the research by S. Benner, and enlarging the amino acid set in polypeptides, thus enlarging the proteome or proteomics, see the research by P. Schultz.[4]: chapter 3
In addition, research is now underway to construct synthetic or artificial restriction endonucleases, especially with recognition sites that are unique within a genome.
Restriction endonucleases or restriction enzymes typically cleave in two ways: blunt-ended or sticky-ended patterns. An example of a Type I restriction endonuclease.[4]: 64
Furthermore, there exist DNA/RNA non-specific endonucleases, such as those that are found in Serratia marcescens, which act on dsDNA, ssDNA, and RNA.
DNA repair
Endonucleases play a role in DNA repair. AP endonuclease, specifically, catalyzes the incision of DNA exclusively at AP sites, and therefore prepares DNA for subsequent excision, repair synthesis and DNA ligation. For example, when depurination occurs, this lesion leaves a deoxyribose sugar with a missing base.[9] The AP endonuclease recognizes this sugar and essentially cuts the DNA at this site and then allows for DNA repair to continue.[10] E. coli cells contain two AP endonucleases: endonuclease IV (endoIV) and exonuclease III (exoIII) while in eukaryotes, there is only one AP endonuclease.[11]
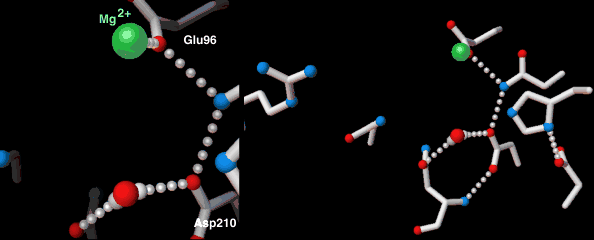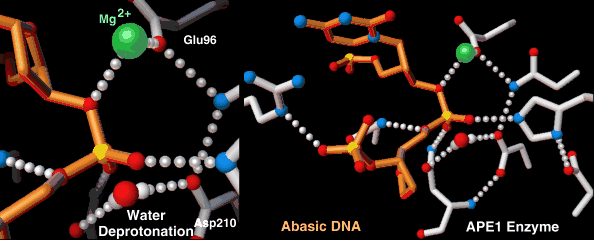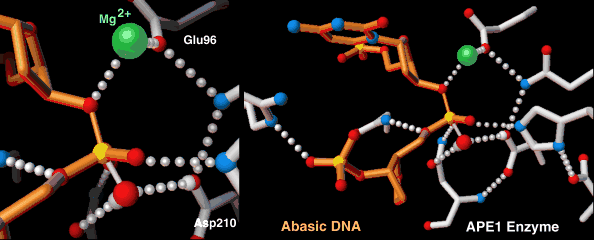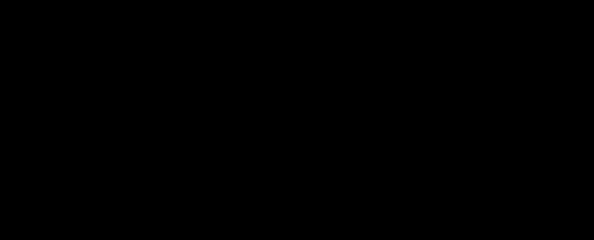
DNA crosslink repair
Repair of DNA in which the two complementary strands are joined by an interstrand covalent crosslink requires multiple incisions in order to disengage the strands and remove the damage. Incisions are required on both sides of the crosslink and on both strands of the duplex DNA. In mouse embryonic stem cells, an intermediate stage of crosslink repair involves production of double-strand breaks.[12] MUS81/EME1 is a structure specific endonuclease involved in converting interstrand crosslinks to double-strand breaks in a DNA replication-dependent manner.[12] After introduction of a double-strand break, further steps are required to complete the repair process. If a crosslink is not properly repaired it can block DNA replication.
Thymine dimer repair
Exposure of bacteriophage (phage) T4 to ultraviolet irradiation induces thymine dimers in the phage DNA. The phage T4 denV gene encodes endonuclease V that catalyzes the initial steps in the repair of these UV-induced thymine dimers.[13] Endonuclease V first cleaves the glycosylic bond on the 5’ side of a pyrimidine dimer and then catalyzes cleavage of the DNA phospodiester bond that originally linked the two nucleotides of the dimer. Subsequent steps in the repair process involve removal of the dimer remnants and repair synthesis to fill in the resulting single-strand gap using the undamaged strand as template.
Common endonucleases
Below are tables of common prokaryotic and eukaryotic endonucleases.[14]
| Prokaryotic Enzyme | Source | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| RecBCD enonuclease | E. coli | Partially ATP dependent; also an exonuclease; functions in recombination and repair |
| T7 endonuclease (P00641) | phage T7 (gene 3) | Essential for replication; preference for single stranded over double stranded DNA |
| T4 endonuclease II (P07059) | phage T4 (denA) | Splits -TpC- sequence to yield 5'-dCMP- terminated oligonucleotides; chain length of product varies with conditions |
| Bal 31 endonuclease | P. espejiana | Also an exonuclease; nibbles away 3' and 5' ends of duplex DNA. A mixture of at least two nucleases, fast and slow.[15] |
| Endonuclease I (endo I; P25736) | E. coli (endA) | Periplasmic location; average chain length of product is 7; inhibited by tRNA; produces double stranded DNA break; produces nick when complexed with tRNA; endo I mutants grow normally |
| Micrococcal nuclease (P00644) | Staphylococcus | Produces 3'-P termini; requires Ca2+; also acts on RNA; prefers single stranded DNA and AT-rich regions |
| Endonuclease II (endo VI, exo III; P09030) | E. coli (xthA) | Cleavage next to AP site; also a 3'-->5' exonuclease; phosphomonoesterase on 3'-P termini |
| Eukaryotic Enzyme | Source | Comments |
| Neurospora endonuclease[16] | Neurospora crassa, mitochondria | Also acts on RNA. |
| S1 nuclease (P24021) | Aspergillus oryzae | Also acts on RNA |
| P1-nuclease (P24289) | Penicillium citrinum | Also acts on RNA |
| Mung bean nuclease I | mung bean sprouts | Also acts on RNA |
| Ustilago nuclease (Dnase I)[17] | Ustilago maydis | Also acts on RNA |
| Dnase I (P00639) | Bovine pancreas | Average chain length of product is 4; produces double strand break in presence of Mn2+ |
| AP endonuclease | Nucleus, mitochondria | Involved in DNA Base Excision Repair pathway |
| Endo R[18] | HeLa cells | Specific for GC sites |
Mutations
Xeroderma pigmentosa is a rare, autosomal recessive disease caused by a defective UV-specific endonuclease. Patients with mutations are unable to repair DNA damage caused by sunlight.[19]
Sickle Cell anemia is a disease caused by a point mutation. The sequence altered by the mutation eliminates the recognition site for the restriction endonuclease MstII that recognizes the nucleotide sequence.[20]
tRNA splicing endonuclease mutations cause pontocerebellar hypoplasia. Pontocerebellar hypoplasias (PCH) represent a group of neurodegenerative autosomal recessive disorders that is caused by mutations in three of the four different subunits of the tRNA-splicing endonuclease complex.[21]
See also
References
- ↑ "Properties of Exonucleases and Endonucleases". New England BioLabs. 2017. Retrieved May 21, 2017.
- ↑ Slor, Hanoch (April 14, 1975). "Differentiation between exonucleases and endonucleases and between haplotomic and diplotomic endonucleases using 3-h-dna-coated wells of plastic depression plates as substrate". Nucleic Acids Research. 2 (6): 897–903. doi:10.1093/nar/2.6.897. PMC 343476. PMID 167356.
- ↑ Stephen T. Kilpatrick; Jocelyn E. Krebs; Lewin, Benjamin; Goldstein, Elliott (2011). Lewin's genes X. Boston: Jones and Bartlett. ISBN 978-0-7637-6632-0.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cox M, Nelson DR, Lehninger AL (2005). Lehninger principles of biochemistry. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman. pp. 952. ISBN 978-0-7167-4339-2.
- ↑ Simon M (2010). Emergent computation: Emphasizing Bioinformatics. New York: Springer. p. 437. ISBN 978-1441919632.
- 1 2 3 Smith, HO; Nathans, D (15 December 1973). "A suggested nomenclature for bacterial host modification and restriction systems and their enzymes". Journal of Molecular Biology. 81 (3): 419–23. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(73)90152-6. PMID 4588280.
- ↑ Rubin, RA; Modrich, P (25 October 1977). "EcoRI methylase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 252 (20): 7265–72. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)66964-4. PMID 332688.
- ↑ Losick R, Watson JD, Baker TA, Bell S, Gann S, Levine MW (2008). Molecular biology of the gene. San Francisco: Pearson/Benjamin Cummings. ISBN 978-0-8053-9592-1.
- ↑ Ellenberger T, Friedberg EC, Walker GS, Wolfram S, Wood RJ, Schultz R (2006). DNA repair and mutagenesis. Washington, D.C: ASM Press. ISBN 978-1-55581-319-2.
- ↑ Alberts B (2002). Molecular biology of the cell. New York: Garland Science. ISBN 978-0-8153-3218-3.
- ↑ Nishino T, Morikawa K (December 2002). "Structure and function of nucleases in DNA repair: shape, grip and blade of the DNA scissors". Oncogene. 21 (58): 9022–32. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206135. PMID 12483517.
- 1 2 Hanada, K.; Budzowska, M.; Modesti, M.; Maas, A.; Wyman, C.; Essers, J.; Kanaar, R. (2006). "The structure-specific endonuclease Mus81-Eme1 promotes conversion of interstrand DNA crosslinks into double-strands breaks". The EMBO Journal. 25 (20): 4921–4932. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601344. PMC 1618088. PMID 17036055.
- ↑ Bernstein, C. (1981). "Deoxyribonucleic acid repair in bacteriophage". Microbiological Reviews. 45 (1): 72–98. doi:10.1128/mr.45.1.72-98.1981. PMC 281499. PMID 6261109.
- ↑ Tania A. Baker; Kornberg, Arthur (2005). DNA replication. University Science. ISBN 978-1-891389-44-3.
- ↑ Wei, CF; Alianell, GA; Bencen, GH; Gray HB, Jr (25 November 1983). "Isolation and comparison of two molecular species of the BAL 31 nuclease from Alteromonas espejiana with distinct kinetic properties". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 258 (22): 13506–12. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)43942-1. PMID 6643438.
- ↑ Linn, S; Lehman, IR (10 June 1966). "An endonuclease from mitochondria of Neurospora crassa". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 241 (11): 2694–9. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)96595-6. PMID 4287861.
- ↑ Holloman, WK; Holliday, R (10 December 1973). "Studies on a nuclease from Ustilago maydis. I. Purification, properties, and implication in recombination of the enzyme". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 248 (23): 8107–13. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)43199-2. PMID 4201782.
- ↑ Gottlieb, J; Muzyczka, N (5 July 1990). "Purification and characterization of HeLa endonuclease R. A G-specific mammalian endonuclease". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 265 (19): 10836–41. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)38522-9. PMID 2358441.
- ↑ Medical Biochemistry at a Glance. New York: Wiley. 2012. ISBN 978-0-470-65451-4.
- ↑ Ferrier DR, Champe PC, Harvey RP (2008). Biochemistry. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-6960-0.
- ↑ Budde BS, Namavar Y, Barth PG, Poll-The BT, Nürnberg G, Becker C, van Ruissen F, Weterman MA, Fluiter K, te Beek ET, Aronica E, van der Knaap MS, Höhne W, Toliat MR, Crow YJ, Steinling M, Voit T, Roelenso F, Brussel W, Brockmann K, Kyllerman M, Boltshauser E, Hammersen G, Willemsen M, Basel-Vanagaite L, Krägeloh-Mann I, de Vries LS, Sztriha L, Muntoni F, Ferrie CD, Battini R, Hennekam RC, Grillo E, Beemer FA, Stoets LM, Wollnik B, Nürnberg P, Baas F (September 2008). "tRNA splicing endonuclease mutations cause pontocerebellar hypoplasia". Nat. Genet. 40 (9): 1113–8. doi:10.1038/ng.204. PMID 18711368. S2CID 205345070.