| Guichen Bay | |
|---|---|
 The Robe Obelisk | |
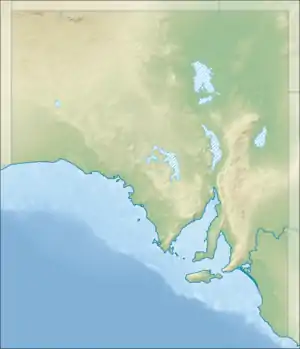 Guichen Bay Location in South Australia | |
| Location | Limestone Coast, South Australia |
| Coordinates | 37°7′14″S 139°45′58″E / 37.12056°S 139.76611°E[1] |
| Type | Bay |
| Basin countries | Australia |
| Max. length | 6 km (3.7 mi)[2] |
| Max. width | 3.4 km (2.1 mi)[2] |
| Max. depth | 11.3 m (37 ft)[2] |
| Settlements | Robe |
Guichen Bay, (locally /ˈɡiːʃən/ GHEE-shən, French: Baie de Guichen) is a bay located on the south-east coast of the Australian state of South Australia about 115 kilometres (71 miles) northwest of the regional city of Mount Gambier and about 270 kilometres (170 miles) south-southeast of the state capital of Adelaide. It was named in 1802 by the Baudin expedition of 1800-03 after Luc Urbain de Bouëxic, comte de Guichen. The town of Robe is located at the southern end of the bay.
Extent and description


Guichen Bay lies between Cape Thomas at its northern extremity and Cape Dombey at its southern extremity on the south-east coast of South Australia. The east side of the bay which runs for a distance of about 6 nautical miles (11 km; 6.9 mi) to the south of Cape Thomas is formed by a sandy beach known as Long Beach. The bay’s south shore consists of ‘rocky points and sandy bays’ with ‘drying rocks extend a short distance offshore’. Within the bay, the water depth ranges from 9.1 m (30 ft) to 11 m (36 ft) over a large part of the bay.[3] A rocky point known as Boatswain Point projects south for a distance of about 0.75 nautical miles (1.39 km; 0.86 mi) to the east southeast of Cape Thomas while at the south end of the bay, there is a rocky point known as Robe Point.[2][4]
A number of navigation aids are located around Cape Dombey at the bay’s south end. These consist of a lighthouse known as the Robe Lighthouse on Cape Dombey, a flashing light located near Commodore Point on the ocean coastline to the immediate south of Cape Dombey, and two lights within the bay - a light marking the end of the breakwater at the entrance of the Lake Butler marina in Robe and a flashing light near Robe Point. Prior to the erection of the Robe Lighthouse in 1972, the sole navigational aid available for navigating in Robe was a Daymark in the form of an obelisk painted with red and white bands which is known as the Robe Obelisk.[4][5][6]
History
The Bungandidj people were living in the Robe region prior to the arrival of Europeans.
The bay was first charted in 1802 by Baudin and Péron of the Baudin expedition. Baudin named the bay Ances des Albatross, but this was revised after his death, in Freycinet's publication, to Guichen Bay to honour French war hero Luc Urbain de Bouëxic, comte de Guichen.[7]
In the 1830s, Bungandidj woman "Black Maggie" was the first indigenous inhabitant encountered by European men, probably whalers, sealers or sailors visiting the area several years before the South Australian province was proclaimed or settled by Europeans.[8]
Ports and other settlements
Robe is the sole settlement and port in Guichen Bay. Its infrastructure consists of a jetty and a marina complete with a protective breakwater.[4][6]
Protected areas
The following protected areas respectively include and adjoin the bay’s extent: the Upper South East Marine Park and the Guichen Bay Conservation Park.[9][10]
Citations and references
Citations
- ↑ "Guichen Bay". Gazetteer of Australia online. Geoscience Australia, Australian Government.
- 1 2 3 4 DMH, 1985, chart 5
- ↑ Sailing Directions (Enroute), Pub. 175: North, West, and South Coasts of Australia (PDF). Sailing Directions. United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. 2017. p. 229.
- 1 2 3 BIA, 2005, page 181
- ↑ "The Robe Lighthouse". Lighthouses of Australia Inc. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- 1 2 "Lake Butler Marina". District Council of Robe. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ↑ "Property Location Browser (search for 'Guichen Bay')". Department of Transport Planning and Infrastructure. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ↑ "Robes History" (PDF).
- ↑ "MARINE PARK 18, Upper South East" (PDF). Department of Environment, Water and Natural Resources. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ↑ NPWS, 1994, page 4
References
- Boating Industry Association of South Australia (BIA); South Australia. Department for Environment and Heritage (2005), South Australia's waters an atlas & guide, Boating Industry Association of South Australia, ISBN 978-1-86254-680-6
- South Australia. Department of Marine and Harbors (DMH) (1985), The Waters of South Australia a series of charts, sailing notes and coastal photographs, Dept. of Marine and Harbors, South Australia, ISBN 978-0-7243-7603-2
- National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS) (1994). Small Coastal Parks of the South East Management Plan (PDF). National Parks and Wildlife Service, Department of Environment and Planning, South Australia. ISBN 978-0-7308-4651-2. Retrieved 29 July 2014.