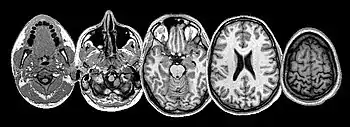
This article describes the anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, and throat.
Structure
Bones
The head rests on the top part of the vertebral column, with the skull joining at C1 (the first cervical vertebra known as the atlas). The skeletal section of the head and neck forms the top part of the axial skeleton and is made up of the skull, hyoid bone, auditory ossicles, and cervical spine.
The skull can be further subdivided into:
- the cranium (8 bones: frontal, 2-parietal, occipital, 2-temporal, sphenoid, ethmoid), and
- the facial bones (14 bones: 2-zygomatic, 2-maxillary, 2-palatine, 2-nasal, 2-lacrimal, vomer, 2-inferior conchae, mandible).
The occipital bone joins with the atlas near the foramen magnum, a large hole (foramen) at the base of the skull. The atlas joins with the occipital condyle above and the axis below. The spinal cord passes through the foramen magnum.
Muscles
| Group | Name | Nerve | Function |
| facial expression | Epicranius: Frontalis and Occipitalis | facial nerve | eyebrows and scalp |
| facial expression | Orbicularis oris | facial nerve | closes lips |
| facial expression | Zygomaticus major | facial nerve | smiling |
| facial expression | Zygomaticus minor | facial nerve | smiling |
| facial expression | Levator labii superioris | facial nerve | upper lip |
| facial expression | Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi | facial nerve | upper lip |
| facial expression | Depressor labii inferioris | facial nerve | lower lip |
| facial expression | Depressor anguli oris | facial nerve | frowning |
| facial expression | Platysma | facial nerve | frowning (during fear or shock) |
| facial expression | Buccinator | facial nerve | cheeks |
| facial expression | Mentalis | facial nerve | chin |
| facial expression | Platysma | facial nerve | frowning |
| facial expression | Risorius | facial nerve | mouth angle |
| facial expression | Orbicularis oculi | facial nerve | closes eye |
| facial expression | Nasalis | facial nerve | flare nostrils |
| facial expression | Corrugator supercilli | facial nerve | eyebrow |
| facial expression | Levator palpebrae superioris | oculomotor nerve | upper eyelid |
| chewing – lower mandible | Masseter | Trigeminal nerve | closing and protruding mandible, |
| chewing – lower mandible | Temporalis | Trigeminal nerve | elevates and controls side to side movement of mandible |
| chewing – lower mandible | Medial pterygoid | Trigeminal nerve | elevates mandible, |
| chewing – lower mandible | Lateral pterygoid | Trigeminal nerve | protracts mandible, opens mouth. |
| tongue – extrinsic | Genioglossus | hypoglossal nerve | protraction, |
| tongue – extrinsic | Styloglossus | hypoglossal nerve | elevation and retraction, |
| tongue – extrinsic | Hyoglossus | hypoglossal nerve | depresses tongue |
| tongue – extrinsic | Palatoglossus | Pharyngeal plexus, pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve | elevates tongue while swallowing |
| oral cavity floor | Digastric | Trigeminal nerve and Facial nerve | hyoid and mandible movement |
| oral cavity floor | Stylohyoid | Facial nerve | elevates hyoid |
| oral cavity floor | Mylohyoid | Trigeminal nerve | hyoid and mandible movement |
| oral cavity floor | Geniohyoid | Cervical nerve C-1 | hyoid, tongue, and mandible movement |
| move head | Sternocleidomastoid | Accessory nerve | nodding and turning |
| move head | Semispinalis | dorsal rami of cervical nerves | extends head, supports turning |
| move head | Splenius capitis | dorsal rami of middle and lower cervical nerves | extend head, supports turning |
| move head | Longissimus capitis | dorsal rami of middle and lower cervical nerves | extends head, supports turning |
| move head | Rectus capitis posterior major | Suboccipital nerve C-1 | extends head |
| move head | Rectus capitis posterior minor | Suboccipital nerve C-1 | extends head |
Skin
The head and neck is covered in skin and its appendages, termed the integumentary system. These include hair, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and sensory nerves. The skin is made up of three microscopic layers: epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. The epidermis is composed of stratified squamous epithelium and is divided into the following five sublayers or strata, listed in order from outer to inner:
- Stratum corneum,
- Stratum lucidum,
- Stratum granulosum,
- Stratum spinosum,
- Stratum germinativum also called stratum basale. The deepest layer is the miotic layer, stratum basale producing daughter cells by mitosis.
Mouth
The mouth, also called the oral cavity, is the entranceway into the digestive system containing both primary and accessory organs of digestion.
Teeth
Two rows of teeth are supported by facial bones of the skull, the maxilla above and the mandible below. Adults have 32 permanent teeth, and children have 20 deciduous teeth. There are various tooth shapes for different jobs. For example, when chewing, the upper teeth work together with the lower teeth of the same shape to bite, chew, and tear food. The names of these teeth are:
- (1) Incisors, there are eight incisors located in the front of the mouth (four on the top and four on the bottom). They have sharp, chisel-shaped crowns that cut food.
- (2) Cuspids (or canine tooth), the four cuspids are next to each incisor. Cuspids have a pointed edge to tear food.
- (3) Premolars (or bicuspids), the four pairs of molars are located next to the cuspids. They crush and tear food.
- (4) Molars, there are twelve molars, in sets of three, at the back of the mouth. They have wide surfaces that help to grind food.
The white visible part of a tooth is called the crown. The rounded upper projections of the back teeth are cusps. The hard white exterior covering of the tooth is the enamel. As the tooth tapers below the gumline, the neck is formed. Below the neck, holding the tooth into the bone, is the root of the tooth. The inner portions of the tooth consist of the dentin, a bonelike tissue, and the pulp. The pulp is a soft tissue area containing the nerve and blood vessels to nourish and protect the tooth, located within the pulp cavity.
A tooth sits in a specialized socket called the alveolus. The tooth is held in location by a periodontal ligament, with the assistance of cementum. Teeth are surrounded by gingiva, or gums, part of the periodontium, support tissue of oral cavity protection. The periodontium includes all of the support membranes of the dental structures surround and support the teeth such as the gums and the attachment surfaces and membranes. These include epithelial tissues (epithelium), connective tissues, (ligaments and bone), muscle tissue and nervous tissue.
Salivary glands
There are three sets of salivary glands: the parotid, the submandibular and the sublingual glands. The (exocrine) glands secrete saliva for proper mixing of food and provides enzymes to start chemical digestion. Saliva helps to hold together the formed bolus which is swallowed after chewing. Saliva is composed primarily of water, ions, salivary amylase, lysozymes, and trace amounts of urea.
Tongue
The tongue is a specialized skeletal muscle that is specially adapted for the activities of speech, chewing, developing gustatory sense (taste) and swallowing. The tongue contains two sets of muscles, the intrinsic- involved with shape of tongue, and the extrinsic- involved with tongue movement. It is attached to the hyoid bone. Terms meaning tongue include "glosso" (from Greek) and "lingual" ((from Latin).
Nose
Microanatomy
The outer surfaces of the head and neck are lined by epithelium. The protective tissues of the oral cavity are continuous with the digestive tract are called mucosa or mucous membranes. The cells of the inner oral cavity are called the buccal mucosa.
The oral cavity is lined by a stratified squamous epithelium containing about three layers of cells. They line the oral, nasal, and external auditory meatus, (ear), providing lubrication and protection against pathogens.
The lips are also protected by specialized sensory cells called Meissner's corpuscles.
Blood, lymph and nerve supply
Blood supply
Blood circulates from the upper systemic loop originating at the aortic arch, and includes: the brachiocephalic artery, left common carotid artery and left subclavian artery. The head and neck are emptied of blood by the subclavian vein and jugular vein.
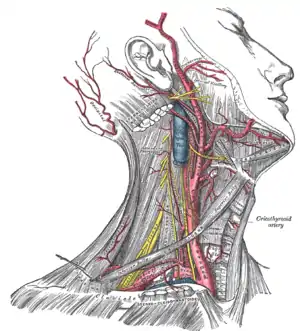
The brachiocephalic artery or trunk is the first and largest artery that branches to form the right common carotid artery and the right subclavian artery. This artery provides blood to the right upper chest, right arm, neck, and head, through a branch called right vertebral artery. The right and left vertebral artery feed into the basilar artery and upward to the posterior cerebral artery, which provides most of the brain with oxygenated blood. The posterior cerebral artery and the posterior communicating artery are within the circle of Willis.
The left common carotid artery divides to form the: internal carotid artery (ICA) and an external carotid artery (ECA). The ICA supplies the brain. The ECA supplies the neck and face.
The left subclavian artery and the right subclavian artery, one on each side of the body form the internal thoracic artery, the vertebral artery, the thyrocervical trunk, and the costocervical trunk. The subclavian becomes the axillary artery at the lateral border of the first rib. The left subclavian artery also provides blood to the left upper chest and left arm.
Blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is semi-permeable membrane that controls the capillary leak potential of the circulatory system. In most parts of the body, the smallest blood vessels, called capillaries, are lined with endothelial cells, which have small spaces between each individual cell so substances can move readily between the inside and the outside of the capillary. The endothelial cells of capillaries in the brain lack these spaces. Instead, the endothelial cells fit tightly together to create a tight junction which prevents substances from passing out of the bloodstream.
Specialized glial cells called astrocytes form a tight junction or protective barrier around brain blood vessels and may be important in the development of the BBB. Astrocytes may also be responsible for transporting ions (electrolytes) from the brain to the blood.
Venous drainage
Blood from the brain and neck flows from: (1) within the cranium via the internal jugular veins, a continuation of the sigmoid sinuses. The right and left external jugular veins drain from the parotid glands, facial muscles, scalp into the subclavian veins. The right and left vertebral veins drain the vertebrae and muscles into the right subclavian vein and into the superior vena cava, into the right atrium of the heart.
Lymphatic system
The lymphatic system drains the head and neck of excess interstitial fluid via lymph vessels or capillaries, equally into the right lymphatic duct and the thoracic duct.
Lymph nodes line the cervical spine and neck regions as well as along the face and jaw.
The tonsils also are lymphatic tissue and help mediate the ingestion of pathogens.
Tonsils in humans include, from superior to inferior: nasopharyngeal tonsils (also known as adenoids), palatine tonsils, and lingual tonsils.
Together this set of lymphatic tissue is called the tonsillar ring or Waldeyer's ring.
Nerve supply
The spinal nerves arise from the spinal column. The top section of the spine is the cervical section, which contains nerves that innervate muscles of the head, neck and thoracic cavity, as well as transmit sensory information to the CNS.
The cervical spine section contains seven vertebrae, C-1 through C-7, and eight nerve pairs, C-1 through C-8.
There is the formation of an extensive network of nerve groups or tracts attaching to the spinal cord in arrangements called rami or plexus.
The sensory branches of spinal nerves include: lesser occipital, C-2, great auricular, (C-2 and C-3); transverse cervical, C-2 and C-3; and supraclavicular, C-3 and C-4. These nerve groups transmit afferent (sensory) information from the scalp, neck, and shoulders to the brain.
The motor branches of spinal nerves include: ansa cervicalis, dividing into a superior root, C-1, and an inferior root, C-2 and C-3, and the phrenic nerve, C-3 to C-5, the segmental nerve branches, C-1 to C-5. These nerve groups transmit efferent nerve (motor) information from the brain to muscle groups of the scalp, neck, diaphragm (anatomy), and shoulders.
Additionally there are: (C5-C8, and T1) Brachial plexus, providing the entire nerve supply of the shoulder and upper limb; and includes supraclavicular branches (dorsal scapular, suprascapular, long thoracic) lateral cord (musculocutaneous, lateral antibrachial cutaneous, lateral head of median nerve), medial cord (ulnar, medial head of median nerve, medial antibrachial cutaneous, medial brachial cutaneous), posterior cord (axillary, radial), controlling the arm.
Damage to a person's spinal cord above C-5 may result in respiratory arrest and death if medicinal aid does not intervene.
Cranial nerves
Twelve pairs of cranial nerves emerge from the brain; these affect movements and sensation, and some special organs such as hearing of parts of the head and neck.
Function
Movements of the neck includes: flexion, extension, (nodding yes), and rotation (shaking head no).
The mouth has evolved to support chewing, (mastication) and swallowing (deglutition), and speech (phonation).
In addition to the teeth, other structures that aid chewing are the lips, cheeks, tongue, hard palate, soft palate, and floor of the mouth.
Endocrine glands
Several glands of the endocrine system are found within the head and neck. Endocrine means that the secretion is used within the body. Endocrine glands are termed as ductless and release their secretions directly into the blood. The endocrine system is under the direct supervision of the nervous system, using the negative feedback principal of homeostasis, to create hormones which act as chemical instant messengers.
The hypothalamus connects directly to the pituitary gland, both through the circulatory system and by direct connection of neurons. Also, within the cranium, the pineal gland, which attaches to the thalamus, controls the body's 24-hour rhythms circadian rhythm through the release of melatonin.
The pituitary gland secretes hormones that directly impact the body as well as hormones that indirectly control body functions because they activate other endocrine glands, such as the adrenal cortex (ACTH) and the thyroid gland (TSH). These two glands when stimulated by pituitary hormones then release their own hormones. The pituitary gland has two lobes, the anterior lobe and the posterior lobe. The anterior lobe secretes: growth hormone (GH), Luteinizing hormone (LH), Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), Prolactin (PRL), and the posterior lobe secretes: Antidieuretic hormone (ADH), and Oxytocin. There is an intermediate lobe, in adult humans it is just a thin layer of cells between the anterior and posterior pituitary, nearly indistinguishable from the anterior lobe. The intermediate lobe produces melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH).
In the neck are the thyroid and parathyroid glands, that secrete hormones that control metabolism and blood calcium levels. The four parathyroid glands are situated upon the back surface of the thyroid gland.
Respiratory system
The respiratory system begins in the head and neck, with air entering and leaving the body through the mouth and nose. The respiratory system involving the head and neck includes:
- the nasal cavity for filtering, moistening, and warming the air
- the pharynx or throat which is the combining point for respiratory and digestive system
- the larynx or voice box containing the epiglottis
- the trachea, or windpipe
These lead down into the lower respiratory tract. A critical junction between the respiratory and digestive systems is the epiglottis, a cartilage flap which shuts during swallowing to prevent aspiration. The epiglottis is normally open to support respiration and shuts during swallowing to prevent food and fluids from entering the trachea, activating the gag reflex or initiates the choking mechanism.
Central nervous system
The nervous system is composed of a central nervous system (CNS), brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), cranial nerves and spinal nerves. The CNS is located within the dorsal cavity, and the PNS extends through the ventral cavity. The central nervous system provides control and coordination of all eleven body systems and utilizes the endocrine system to form hormone chemical messengers that transport through the blood to influence the activity of individual cells of the body and their associated tissues, organs and systems.
The CNS receives sensory (afferent) input from the PNS and directs the flow of information to association neurons (interneurons) to create chemical synapse responses which in turn cause the formation of motor (efferent nerve) responses to stimulus. Association neurons are located in the grey matter of the spinal cord and the brain.
The CNS is protected by the cranium, vertebral column, meninges, cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is an extension of the brain. The spinal cord and the brain stem are joined at the base of the cranium at the foramen magnum. Most of the functions of the head and neck are directly influenced by the brain and transmitted to the PNS via the cranial nerves and spinal nerves of the cervical portion of the spine.
The PNS has two subdivisions
- somatic nervous system (SNS). The SNS is associated with the voluntary control of body movements through the action of skeletal muscles, and also the reception of external stimuli.
- the autonomic nervous system (ANS). The ANS is divided into subsystems: the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic (PNS) nervous systems. The SNS and PNS often have opposing effects in the same organs or physiological systems, and the ANS is a major factor in maintaining homeostasis.
Development
Bones
The facial bones usually form into pairs and then fuse together. As the cranium fuses, sutures are formed that resemble stitching between bone plates. In a newborn, the junction of the parietal bones with the frontal and occipital bones, form the anterior (front) and posterior (back) fontanelle, or soft spots. The separation of the cranial bone plates at time of birth facilitate passage of the head of the fetus through the mother's birth canal, or pelvic girdle. The parietal bones, and occipital bone can overlap each other in the birth canal, and form the unusual looking "cone head" appearance in a newborn when delivered in a natural, or vaginal, delivery.
Teeth
Humans normally will produce two sets of teeth called primary dentition, or deciduous teeth, and secondary dentition, or permanent teeth.
A tooth is the toughest known substance in the body exceeding bones in density and strength. Tooth enamel lends great strength to the tooth structure. The formation of a developing tooth includes the process of dentin formation, (see: dentinogenesis) and enamel formation, (see: amelogenesis). The tooth breaks through the gum into the mouth in a process called eruption. The formation of teeth begins in early fetal development and goes through six stages:
- (1) initiation stage, 6th - 7th week
- (2) bud stage, 8th wk
- (3) cap stage, 9th-10 wk
- (4) bell stage, 11th-12th wk
- (5) apposition
- (6) maturation stage
Clinical significance
Infection
Severe viral infections that affect the mouth, lips, or the oral cavity include: Oral cancer may have a viral link.
- Minor viral infections include: Mumps is a viral infection of the parotid salivary glands. Chicken pox is a viral infection that can spread to the mouth.
- Thrush (candidiasis) fungal infection. Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils and may cause a sore throat and fever. In chronic cases tonsillectomy may be required.
Infected teeth can on rare occasions cause infection to spread leading to cavernous sinus thrombosis, mediastinitis, or Ludwig's angina causing airway blockage.
Diseases may be transmitted by contact of the head, mouth, or body fluids, such as Herpes Simplex Virus Type I (HSV-1), Herpes Simplex Virus Type II (HSV-2) genital herpes, which may present as a lesion on the lips, and contactable via skin to skin contact
Other
- Other diseases include: Gingivitis gum disease, periodontal disease, oral forms of syphilis and gonorrhea. Dental caries or dental cavities.
- Temporomandibular joint diseases and disorders, commonly called TMJ.
- Autoimmune diseases such as: Crohn's disease of the oral cavity, see reference below.
Careful observation of the oral cavity, teeth and gums may reveal indicators of other medical conditions. For example, a person suffering from the eating disorder, bulimia nervosa may show signs of excessive tooth and gum erosion.
Airway obstruction
The airway in the head and neck may be obstructed with swelling associated with an enlarged tongue (macroglossia), tonsils, with swelling associated with anaphylactic shock, angiooedema, or a foreign body.
Anaphylactic shock requires advanced medical care immediately; but other first aid measures include rescue breathing (part of CPR) and administration of epinephrine using an EpiPen for immediate administration of epinephrine (adrenaline) to reverse swelling and to keep the respiratory airway (trachea) open.
References
- http://www.med-ed.virginia.edu/courses/rad/cspine/anatomy1.html
- http://www.pediatric-orthopedics.com/Topics/Bones/Skull/Skullduggery/Foramen_Magnum/foramen_magnum.html
- ADHA Dental Hygiene Archived 2012-12-28 at the Wayback Machine
- Medline, Crohn disease
- Brain-blood barrier, University of Washington
- Skin nerve receptors
- Cells Alive, Anatomy of a splinter
External links
- Core Curriculum Syllabus: Review of Anatomy at Baylor College of Medicine
- Core Curriculum Syllabus: Review of Anatomy - Temporal Bone and Ear at Baylor College of Medicine
- Dental anatomy at Colorado State University
- Neuroscience for Kids at University of Washington
- Histology of peridontium at University of Pittsburgh School of Dental Medicine