| Little Goose Dam | |
|---|---|
 From the north side of the Snake River | |
 Location in the United States  Location in Washington | |
| Country | United States |
| Location | Columbia / Whitman counties, Washington |
| Coordinates | 46°35′13″N 118°01′41″W / 46.587°N 118.028°W |
| Construction began | June 1963 |
| Opening date | 1970 |
| Operator(s) | U.S. Army Corps of Engineers |
| Dam and spillways | |
| Type of dam | Concrete-gravity, run-of-the-river |
| Height | 98 ft (30 m) |
| Length | 2,655 ft (809 m) |
| Elevation at crest | 643 ft (196 m) AMSL |
| Spillway type | Service, gate-controlled |
| Reservoir | |
| Creates | Lake Bryan |
| Total capacity | 516,300 acre⋅ft (0.637 km3)[1] |
| Surface area | 10,025 acres (40.57 km2) |
| Power Station | |
| Turbines | 6 units x 135–153 MW (181,000–205,000 hp) |
| Installed capacity | 932 MW (1,250,000 hp) |
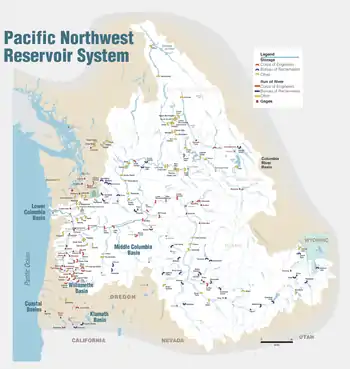 Columbia River Basin | |
Little Goose Lock and Dam is a hydroelectric, concrete, run-of-the-river dam in the northwest United States, on the lower Snake River in southeast Washington. At the dam, the river is the border between Columbia and Whitman counties;[2] it is nine miles (14 km) northeast of Starbuck and 25 miles (40 km) north of Dayton.

Construction began in June 1963 on what was Little Goose Island.[3][4] The main structure and three generators were completed 54 years ago in 1970, with an additional three generators finished in 1978.
Generating capacity is 810 megawatts (1,090,000 hp), with an overload capacity of 932 megawatts (1,250,000 hp); the spillway has eight gates and is 512 feet (156 m) in length.
Little Goose Dam is part of the Columbia River Basin system of dams.
Lake Bryan, named for Doctor Enoch Albert Bryan, is formed behind the dam. The lake stretches to the base of Lower Granite Dam, 37 miles (60 km) upstream. Lake Herbert G. West, formed from Lower Monumental Dam runs 28 miles (45 km) downstream from the base of the dam.
- Navigation lock
- Single-lift
- 86 feet (26 m) wide
- 668 feet (204 m) long
See also
References
- ↑ "The Four Lower Snake River Dams". Bluefish.org. Retrieved July 17, 2010.
- ↑ "The Columbia River System Inside Story" (PDF). BPA.gov. pp. 14–15. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 27, 2010. Retrieved July 17, 2010.
- ↑ "Little Goose's handy site will speed dam building". Spokesman-Review. Spokane, Washington. March 2, 1963. p. 6.
- ↑ "Little Goose Dam moving ahead". Spokesman-Review. Spokane, Washington. (photo). September 3, 1963. p. 6.