 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | IV |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
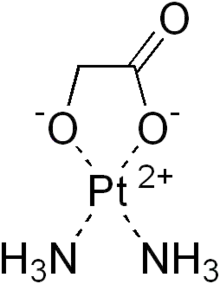
| Formula | C2H8N2O3Pt |
| Molar mass | 303.181 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Nedaplatin (INN, marketed under the tradename Aqupla) is a platinum-based antineoplastic drug which is used for cancer chemotherapy.[1] The complex consists of two ammine ligands and the dianion derived from glycolic acid.
Platinum-based drugs are widely employed as antineoplastic agents, especially cisplatin and carboplatin. Due to issues of their toxicity and number of cisplatin-resistant cancer cells, other platinum derivatives have been developed. Nedaplatin is one example of such new drugs.[2]
References
- ↑ Apps MG, Choi EH, Wheate NJ (August 2015). "The state-of-play and future of platinum drugs". Endocrine-Related Cancer. 22 (4): R219-33. doi:10.1530/ERC-15-0237. hdl:2123/24426. PMID 26113607.
- ↑ Johnstone TC, Park GY, Lippard SJ (January 2014). "Understanding and improving platinum anticancer drugs--phenanthriplatin". Anticancer Research. 34 (1): 471–6. PMC 3937549. PMID 24403503.
External links
- "Aqupla アクプラ" (PDF). Shionogi & Co. March 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2004-08-05.
- "Official Shionogi & Co. Website" (in Japanese).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.