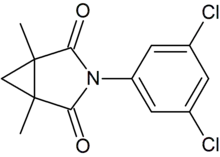 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-1,5-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-2,4-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.046.561 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H11Cl2NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 284.138 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Procymidone is a pesticide. It is often used for killing unwanted ferns and nettles, and as a dicarboximide fungicide for killing fungi, for example as seed dressing, pre-harvest spray or post-harvest dip of lupins, grapes, stone fruit, strawberries.[1] It is a known endocrine disruptor (androgen receptor antagonist) which interferes with the sexual differentiation of male rats.[2] It is considered to be a poison.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicine Authority. "Chemical Review Program/Procymidone". Archived from the original on 26 January 2012. Retrieved 9 February 2012.
- ↑ Ostby J, Kelce WR, Lambright C, Wolf CJ, Mann P, Gray LE (1999). "The fungicide procymidone alters sexual differentiation in the male rat by acting as an androgen-receptor antagonist in vivo and in vitro". Toxicol Ind Health. 15 (1–2): 80–93. doi:10.1191/074823399678846718. PMID 10188193.
- ↑ Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicine Authority, Chemical Review Program. "procymidone_poster.pdf" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 February 2012. Retrieved 9 February 2012.
External links
- Procymidone in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.