

The ranchos of Los Angeles County were large-scale land grants made by the governments of Spain and Mexico between 1784 and July 7, 1846, to private individuals within the current boundary lines (last adjusted in 1919) of Los Angeles County in California, United States.
Background
The earliest colonial land grants called ranchos were established by the Commandancy and General Captaincy of the Internal Provinces of the Spanish Empire's Viceroyalty of New Spain. The Spanish colonial authorities of Alta California also established four presidios, three pueblos, and 20 Catholic missions.[lower-alpha 1] Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo first claimed California for Spain in 1542 but until 1784 there were no land grants to Spanish subjects, except for small plots within pueblos, the balance of land in Spain's possession "being held for the benefit of the king."[1] The rancho period of California—land grants specifically to individuals outside of misiones and presidios—began in 1784, in what would become L.A. County, with vast grants to three Spanish military veterans.[2][3] All three were grants of traditional Tongva lands.[4] The greater portion of the rancho grants were created under Mexican dominion, which began with independence from Spain on September 27, 1821, and—according to the U.S. Land Commission—ended amidst the Mexican–American War on July 7, 1846. (Grants made after that date were deemed invalid.)[5]
Mission San Fernando Rey de España, Mission San Gabriel Arcángel, and El Pueblo de Los Ángeles lay within the current boundaries of Los Angeles County. Mission San Gabriel was founded in 1771 under Charles III of Spain; its lands were confiscated in 1833 under the Mexican secularization act, which was passed to protect nascent nation-state of Mexico from the influence of the Roman Catholic Church, which was perceived to be an ally of Spain. A land patent application made by Archbishop of San Francisco Joseph Sadoc Alemany on behalf of the church was confirmed for 191 acres (77 ha; 0.298 sq mi; 0.77 km2) in 1859. Mission San Fernando was established 1797 under Charles IV of Spain and similarly had its lands confiscated in 1833. A land claim of 77 acres (31 ha; 0.120 sq mi; 0.31 km2) for Mission San Fernando was approved and patented in 1865.[5] In 1875, the City of Los Angeles patented a little more than 17,000 acres of land that had been granted to the pobladores. There were a handful of other, smaller land grants[lower-alpha 2] made by Mexican authorities that were patented under the U.S. land law but that are not traditionally identified as ranchos. For example, "tract of land 1000 varas square near Mission San Gabriel" (patented to Mr. Sexton in 1871) was one of 10 such small grants near that mission, ranging in size from 19–180 acres (7.7–72.8 ha).[5]
.jpg.webp)
In the decades following the initial grants, many of the ranches listed were further subdivided. Rancho Los Nietos, for example, was partitioned and re-granted as Rancho Los Alamitos, Rancho Los Cerritos, Rancho Los Coyotes, Rancho Las Bolsas, and Rancho Santa Gertrudes. A couple of the ranches that were patented under the U.S. system were conglomerates of originally smaller ranches—notably, Rancho Guaspita and Rancho Salinas became Sausal Redondo.[6][7] (Additionally, at least two sets of patented rancho land grants in Los Angeles County had overlapping areas; these disputes were eventually resolved in federal court.)[3]
Diseños are hand-drawn maps submitted to the U.S. government indicating the extent of a land grant as understood by the grantees.[8] Diseños and expedientes (written descriptions of the grants) were used during the U.S. land-patent process that began when Mexican Alta California became the U.S. state of California in 1850.[8] Diseños are distinct from later maps produced by U.S. surveyors within the extant American rectangular survey system.[8] Several of the earliest surveys, or plats, of Los Angeles-area ranchos were done by Henry Hancock, who himself owned Rancho La Brea and through his son is a namesake of the Hancock Park neighborhood. As for the cattle brands, many of the large ranchos had multiple brands for various herds or during various eras; the single one included here is the earliest known example.[9] Land patents were ultimately granted to over 60 Mexican, Anglo and indigenous Angelenos; the indigenous contingent was represented by Doña Victoria Reid of Rancho Huerta de Cuati, who was Gabrieleño Tongva, and Odón Chihuya, Urbano Chari, and Manuel (later Espíritu Chijulla) of Rancho El Escorpión, who were from a leading family of Fernandeño Tongva.[3]
The ranchos had three main elements: the rancho buildings, including the residential hacienda; the adjacent market gardens and vineyards; and, above all, a vast pasturage for cattle, which were the major economic products of the ranchos.[10]
List
Following the conventions of the California Land Commission records, the default alphabetization of this list begins after the Spanish-language articles (el, la, las, los) and prepositions (de, del), so Rancho Los Encinos is sorted by the E in Encinos, Rancho de los Palos Verdes is sorted by the P in Palos, etc.
The grants were originally measured in leguas (Spanish leagues) and varas (yards), two Spanish customary units.
| Grant patented by U.S. land commission and district courts |
|---|
| Grant either not claimed (due to sale, abandonment, amalgamation, subdivision, et al.) or not recognized during U.S. era |
| Grant[5][6] | Year[6] | Grantees[6] | Country[6] | Grant area[6] | Diseño | Expediente No.[11] | Patentees[6][5] | Patent area[5] | U.S. survey map | Patent date | GLO Plat No. | Brand[9][12] | Etymology[6] | Alt names[6] | Counties[6] | Case file online[lower-alpha 3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rancho Aguaje de la Centinela | 1844 | Ygnacio Machado | Mexico | 382 | Bruno Ávila | 2,219.26 acres (898.10 ha) | .04.jpg.webp) |
August 23, 1872 | 437 | Spanish; el aguaje is watering place or spring, la centinela is guardian | Rancho Centinella,[5] El Centinela[11] | Los Angeles | Case no. 125, Southern District of California. | |||
| Rancho Los Alamitos | 1834 | Juan José Nieto | Mexico | 06 (6 Spanish leagues) |  |
28,027.17 acres (11,342.19 ha) |  |
August 29, 1874 | 468 |  |
Spanish; diminutive form of el álamo, describing Populus fremontii | Orange, Los Angeles | Case no. 290, Southern District of California | |||
| Rancho Azusa | 1837 | Ignacio Palomares, Ricardo Véjar | Mexico | 04 (4 Spanish leagues) | Indigenous, Tongva language; Tongva (Gabrieleño) community Asuksa'nga[13] | Los Angeles | ||||||||||
| Rancho Azusa de Dalton | 1841 | Luis Arenas | Mexico |  |
Henry Dalton | 4,431.47 acres (1,793.35 ha) |  |
May 29, 1876 | 455 | Personal name; "Azusa ranch of Henry Dalton" | Rancho El Susa,[3] Rancho de San José de San Gabriel | Los Angeles | ||||
| Rancho Azusa de Duarte | 1841 | Andrés Duarte | Mexico | 236 | Andrés Duarte | 6,595.62 acres (2,669.15 ha) | 1878-06-06 | 456 |  |
Personal name; "Azusa ranch of Andrés Duarte" | Rancho Susita[3] | Los Angeles | ||||
| Rancho La Ballona | 1839 | Agustín Machado, Ygnacio Machado, Felipe Talamantes, Tomás Talamantes | Mexico | 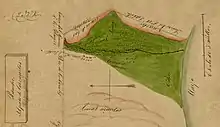 |
184 | Agustín Machado, Ygnacio Machado, Felipe Talamantes, Tomás Talamantes | 13,919.90 acres (5,633.18 ha) | .03_Rancho_La_Ballona_1858.jpg.webp) |
December 8, 1873 | 434 | .jpg.webp) |
Disputed | Rancho Paseo de Las Carretas (wagon pass); Rancho de Los Quintos[14] | Los Angeles | Case no. 123, Southern District of California. | |
| Rancho Boca de Santa Mónica | 1839 | Ysidro Reyes | Mexico | 01.5 (11⁄2 Spanish leagues) |  |
330 | Ysidro Reyes, Francisco Marquez, et al. | 6,656.93 acres (2,693.96 ha) |  |
July 21, 1881 | 539 |  |
Spanish; la boca meaning mouth, entrance, or opening; the flowing waters of the Tongva Sacred Springs were reminiscent of the tears of Monica, a Roman Catholic saint | Los Angeles | Case no. 141, Southern District of California | |
| Rancho La Brea | 1828 | José Antonio Rocha[15] | Mexico | 01 (1 Spanish league) |  |
José Antonio Rocha | 4,439.07 acres (1,796.43 ha) |  |
April 15, 1873 | 429 |  |
Spanish; la brea meaning asphalt or tar | Los Angeles | Case no. 287, Southern District of California. | ||
| Rancho Cahuenga | Twice granted;
(1) 1843 (2) 1846 |
Twice granted;
(1) José Yvez Limantour, José Miguel Triunfo (2) Luis Arenas |
Mexico | Twice granted;
(1) 06 Spanish leagues (2) 04 Spanish leagues |
D. W. Alexander | 388.34 acres (157.16 ha) |  |
August 2, 1872 | 425 | Indigenous, Tongva language; Tongva community Kawee'nga[16] | Cajuenga | Los Angeles | ||||
| Rancho La Cañada | 1843 | Ygnacio Coronel | Mexico | 02 (2 Spanish leagues) |  |
J.R. Scott, et al. | 5,832.10 acres (2,360.17 ha) | August 1, 1866 | 414 | Spanish; la cañada describes a "dale or glen" between mountains | Los Angeles | |||||
| Rancho La Cañada atras de Verdugos | 1846 | Antonio Francisco Coronel (claim rejected by U.S.) | Mexico |  |
Spanish; la cañada meaning dale or glen between mountains; atras "behind or in back of" the Verdugo Mountains of Rancho San Rafael | Rancho Sierra de los Verdugos | Los Angeles | |||||||||
| Rancho La Cañada de Los Nogales | 1844 | José Maria Águilar | Mexico | 0.5 (1⁄2 Spanish league) |  |
380 | José M. Águila | 1,199.56 acres (485.44 ha) | May 4, 1882 | 546 | Spanish; la cañada meaning dale or glen between mountains; el nogal meaning walnut tree, describing Juglans californica | Los Angeles | ||||
| Rancho Castac | 1843 | José M. Covarrubias | Mexico | 05 (5 Spanish leagues) |  |
326 | José M. Covarrubias | 22,178.28 acres (8,975.23 ha) |  |
Indigenous, Chumash language; Chumash community of Kaštɨq | Kern, Los Angeles | |||||
| Rancho Los Cerritos | 1834 | Maria Manuela Nieto | Mexico | 05 (5 Spanish leagues) |  |
John Temple | 27,054.36 acres (10,948.51 ha) |  |
December 7, 1867 | 467 |  |
Spanish; cerrito meaning hillock or little hill | Rancho Los Sierritos | Orange, Los Angeles | ||
| Rancho La Ciénega ó Paso de la Tijera | 1843 | Vicente Sánchez | Mexico | .jpg.webp) |
532 | Tomás Sánchez | 4,481.05 acres (1,813.42 ha) |  |
May 22, 1873 | 436 |  |
Spanish; la ciénega meaning wetland, marsh, or muddy place; paso is pass or passage; la tijera apparently has several definitions: scissors, an X-shaped tool, a person who shears animals, and channel or drain | Rancho Cienega y Tijeras[11] | Los Angeles | ||
| Rancho Las Ciénegas | 1823 | Januario Ávila | Mexico | 01 (1 Spanish league) | Januario Ávila | Spanish; la ciénega meaning wetland, marsh, or muddy place | Los Angeles | |||||||||
| Rancho El Conejo | Twice granted;
(1) 1803 (2) 1822 |
Twice granted;
(1) José Polanco, Ygnacio Rodriguez (2) José de la Guerra y Noriega |
Twice granted; (1) Spain
(2) Mexico |
Twice granted;
(1) 11 Spanish leagues (2) 48,672 acres (as claimed 1873) |
 |
José de la Guerra y Noriega | 48,671.56 acres (19,696.68 ha) |  |
January 8, 1873 | 408 | Spanish; el conejo meaning rabbit, describing Sylvilagus audubonii and Sylvilagus bachmani | Rancho Señora de Altagracia | Los Angeles | |||
| Rancho Los Coyotes | 1834 | Juan José Nieto | Mexico | 10 (10 Spanish leagues) |  |
Andrés Pico, et al. | 48,806.17 acres (19,751.16 ha) | March 9, 1875 | 472 | Spanish; borrowing of Nahuatl language coyōtl; coyotes remain common mammals of Southern California[17] | Rancho La Buena Esperanza[18] | Los Angeles | ||||
| Rancho Los Encinos | Twice granted;
(1) 1785–1797 (2) 1845 |
Twice granted;
(2) Ramon, Francisco, Roque (described as "presumably Indians")[lower-alpha 4] |
Twice granted;
(1) Spain (2) Mexico |
01 (1 Spanish league) | 458 | Vicente de la Osa | 4,460.73 acres (1,805.19 ha) | .01_Rancho_Encino_San_Fernando_Valley_1868_survey.jpg.webp) |
January 8, 1873 | 411 |  |
Spanish; el encino is oak; California has 20 native species of oak tree[19] | Rancho El Encino | Los Angeles | Case no. 392, Southern District of California | |
| Rancho El Escorpión | 1845 | Odón Chihuya, Urbano Chari, Manuel[20] | Mexico | 01.5 (11⁄2 Spanish leagues) | 461 | Odón Chihuya, Urbano Chari, Manuel | 1,109.65 acres (449.06 ha) |  |
1876-12-11 | 409 | Spanish; there are 54 known scorpion species in the state, including the California common scorpion | Los Angeles | ||||
| Rancho Ex Mission de San Fernando | 1846 | Eulogio de Célis | Mexico | 13 Spanish leagues | Eulogio de Célis | 116,858.46 acres (47,290.94 ha) |  |
January 8, 1873 | 410 |  |
Descriptive; lands previously held by the Catholic Church were confiscated and redistributed under the Mexican secularization act of 1833 | Los Angeles | ||||
| Rancho Los Féliz | 1802 | José Vicente Féliz | Spain | 01.5 (11⁄2 Spanish leagues) |  |
350 | Juan Diego | 6,647.46 acres (2,690.13 ha) | April 8, 1871 | 426 |  |
Personal name; initial grantee | Los Angeles | |||
| Rancho Guaspita | 1822 | Antonio Ygnacio Ávila | Mexico |  |
Indigenous, Tongva language; Tongva community of Guashna[21] | Los Angeles | ||||||||||
| Rancho La Habra | 1839 | Mariano Reyes Roldan | Mexico | 01.5 (11⁄2 Spanish leagues) |  |
131 | Andrés Pico | 6,698.57 acres (2,710.82 ha) | April 18, 1872 | 462 | Spanish; la abra is an opening | Rancho Cañada de La Habra | Orange, Los Angeles | |||
| Rancho Huerta de Cuati | Uncertain; 1820 or 1828 | Victoria Reid | Uncertain | Victoria Reid | 128.26 acres (51.90 ha) |  |
June 30, 1858 | 421 | Uncertain; huerta is orchard or kitchen garden in Spanish but the meaning of cuati in this context is unknown, although it is a word in Nahuatl, which is in the same language family as Tongva | Los Angeles | ||||||
| Rancho Isla de Santa Catalina | 1846 | Thomas M. Robbins | Mexico | José María Covarrubias | 6,698.57 acres (2,710.82 ha) | April 10, 1867 | 470 | Named for figure of religious significance; Sebastián Vizcaíno named the island for Catherine of Alexandria, a Roman Catholic saint | Los Angeles | |||||||
| Rancho La Liebre | 1846 | José M. Flores | Mexico | 11 Spanish leagues | 547 | José M. Flores | 48,799.59 acres (19,748.49 ha) | June 21, 1875 | 347 | Spanish; la liebre is hare, describing Lepus californicus | Los Angeles | |||||
| Rancho Matzultaquea | 1845 | Ramon Carrillo (J. B. Frisbie claim rejected by U.S.) | Mexico | 04 (4 Spanish leagues) | Unknown | Los Angeles | ||||||||||
| Rancho La Merced | 1844 | Casilda Soto | Mexico | 01 (1 Spanish league) |  |
Francis Pliny F. Temple, et al. | 2,363.75 acres (956.58 ha) | February 13, 1872 | 443 | Spanish; la merced is literally a mercy but is also used to describe income earned by labor | Los Angeles | |||||
| Rancho Los Nietos | 1784 | Manuel Nieto | Spain | 33 (33 Spanish leagues) | Personal name; initial grantee | Orange, Los Angeles | ||||||||||
| Rancho Los Nogales | 1840 | José de la Luz Linares | Mexico | 01 (1 Spanish league) |  |
195 | M. de Jesus García | 1,003.67 acres (406.17 ha) |  |
June 29, 1882 | 459 | Spanish; el nogal meaning walnut tree, describing Juglans californica | Los Angeles | |||
| Rancho Ojo de Agua | 1840 | Encarnacio Sepúlveda (no U.S. claim presented) | Mexico | 02 (2 Spanish leagues) | Spanish; el ojo is eye, la agua is water | Los Angeles | ||||||||||
| Rancho de los Palos Verdes | 1827 | José L. Sepúlveda | Mexico |  |
565 | José L. Sepúlveda, et al. | 31,629.43 acres (12,799.98 ha) |  |
June 22, 1880 | 439 |  |
Spanish; el palo is a wooden stick; verde is green en Español | Rancho de Los Palos Colorados | Los Angeles | ||
| Rancho Paso de Bartolo Viejo | 1835 | Juan Crispin Perez | Mexico | 02 (2 Spanish leagues) |  |
061 | Patented in 3 parts;
(1) Joaquin Sepúlveda (208 acres) 2) Pico & Perez (8991 acres) (3) Rafael Guirado (876 acres) |
10,075 acres (4,077 ha) |  |
1867-09-27, 1881-03-17, 1881-08-05 | 465, 458, 464 |  |
Mixed; an old (viejo in Spanish) San Gabriel River crossing was named for a person called Bartolo[22] | Rancho San Rafael | Los Angeles | |
| Rancho Portezuela | 1795 | Mariano de la Luz Verdugo (grant abandoned c. 1810) | Spain | Spanish; el portezuelo is a pass | Los Angeles | |||||||||||
| Rancho Potrero Chico | 1843 | Antonio Valenzuela | Mexico | Ramon Valenzuela, et al. | 83.46 acres (33.78 ha) |  |
April 4, 1923 | 444 | Spanish; el potrero is a paddock, or pasturage for horses; chico as an adjective means little | Rancho Potrero de la Misíon Vieja de San Gabriel | Los Angeles | |||||
| Rancho Potrero de Felipe Lugo | 1845 | Teodoro Romero, Jorge Morillo | Mexico |  |
Jorge Morillo | 2,042.81 acres (826.70 ha) |  |
June 15, 1871 | 446 |  |
Spanish; el potrero is a paddock, or pasturage for horses; Felipe Lugo was a member of the prominent Californio Lugo family | Rancho Dolores | Los Angeles | |||
| Rancho Potrero Grande | 1845 | Manuel Antonio | Mexico | 01 (1 Spanish league) |  |
439 | J. Matías Sanchez | 4,431.95 acres (1,793.55 ha) |  |
1859-07-19 | 445 | Spanish; el potrero is a paddock, or pasturage for horses; grande is big | Los Angeles | |||
| Rancho La Providencia | 1843 | Vicente de la Osa | Mexico | 01 (1 Spanish league) |  |
D. W. Alexander | 4,064.33 acres (1,644.78 ha) |  |
August 6, 1872 | 424 | Spanish; providence, foresight, divine superintendence | Possibly Rancho Osa after Vicente de la Osa[6] | Los Angeles | |||
| Rancho La Puente | 1845 | John A. Rowland, William H. Workman | Mexico |  |
270 | John Rowland, William Workman | 48,790.55 acres (19,744.84 ha) | 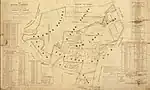 |
April 19, 1867 | 460 |  |
Spanish; la puente is a bridge over water | Los Angeles | |||
| Rancho Rincón de la Brea | 1841 | Gil Ibarra | Mexico | 01 (1 Spanish league ) |  |
222 | Gil Ibarra | 4,452.59 acres (1,801.90 ha) |  |
1864-11-14 | 461 | Spanish; el rincón meaning corner or angle, la brea meaning asphalt or tar | Rancho Cañada de la Brea | Los Angeles | ||
| Rancho Rincón de los Bueyes | 1821 | Bernardo Higuera | Spain | 0.6 (3⁄5 Spanish league) |  |
Francisco Higuera, et al. | 3,127.89 acres (1,265.81 ha) |  |
August 27, 1872 | 435 | Spanish; el rincón meaning corner or angle, los bueyes are oxen | Los Angeles | Case no. 131, Southern District of California | |||
| Rancho Río de Las Ánimas | 1846 | Leonardo Cota, Julián A. Chávez (claim rejected by U.S.) | Mexico | 06 (6 Spanish leagues) | Spanish; "river of souls" | Los Angeles | ||||||||||
| Rancho Rodeo de las Aguas | Uncertain; c. 1820 | Vicente Ferrer Villa | Spain | 4000 varas | María Rita Valdés | 4,449.31 acres (1,800.57 ha) | June 27, 1871 | 430 |  |
Spanish; "gathering of the waters";[23] literally, rodeo is a cattle herd round-up, agua is water describing pre-settlement watershed features | Rancho San Antonio | Los Angeles | ||||
| Rancho Rosa Castilla | 1831 | Juan Ballesteros (Claim of A. Lestrada was rejected.) | Mexico | 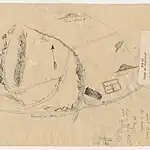 |
Spanish; wild roses grew here;[24] the ranch is named for Castile roses, the plants were likely one of the nine recognized species of roses native to California,[25] such as Rosa californica | Los Angeles | ||||||||||
| Rancho Salinas | 1822 | Antonio Ygnacio Ávila | Mexico |  |
Spanish; salinas are salt flats; given the location,[7] the name of the rancho likely referred to the Old Salt Lake | Los Angeles | ||||||||||
| Rancho San Antonio | 1810 | Antonio María Lugo | Spain |  |
Antonio María Lugo | 29,513.35 acres (11,943.63 ha) |  |
1866-07-20 | 442 |  |
Named for figure of religious significance; Anthony of Padua, a Roman Catholic saint | Los Angeles | ||||
| Rancho San Francisco | 1839 | Antonio del Valle | Mexico | 08 (8 Spanish leagues) |  |
Jacoba Féliz | 48,611.88 acres (19,672.53 ha) |  |
1875-02-12 | 399 |  |
Named for figure of religious significance; Francis of Assisi, a Roman Catholic saint | Kern, Los Angeles | |||
| Rancho San Francisquito | 1845 | Henry Dalton | Mexico |  |
Henry Dalton | 8,893.62 acres (3,599.12 ha) |  |
1867-05-30 | 447 | Named for figure of religious significance; Francis of Assisi, a Roman Catholic saint, diminutive form | Azuchzana | Los Angeles | Case no. 22, Southern District of California | |||
| Rancho San José | 1837 | Ignacio Palomares, Ricardo Véjar | Mexico | 141 | Ignacio Palomares, Ricardo Véjar, Henry Dalton | 26,771.05 acres (10,833.86 ha)[lower-alpha 5] |  |
January 20, 1875 | 458 |  |
Named for figure of religious significance; Joseph, a Roman Catholic saint | Los Angeles | Case no. 122, Southern District of California, Case no. 128, Southern District of California. | |||
| Rancho San José de Buenos Ayres | 1819 | Máximo Alanis, José Polanco | Spain | 01 (1 Spanish league) |  |
Benjamin D. Wilson | 4,438.69 acres (1,796.27 ha) |  |
July 5, 1866 | 431 |  |
Named for figure of religious significance; Joseph, a Roman Catholic saint, modifier buenos ayres translates roughly to fair winds or fresh air | Los Angeles | Case no. 305, Southern District of California | ||
| Rancho San Pascual | 1835 | Juan Maríne | Mexico | 03.5 (31⁄2 Spanish leagues) |  |
Patented in 2 parts;
(1) Manuel Garfias |
Patented in 2 parts;
(1) 13,693.93 acres (5,541.74 ha) (2) 709 acres (287 ha) |
 |
422, 415 |  |
Named for figure of religious significance; Paschal Baylón, a Roman Catholic saint | Rancho El Rincón de San Pasqual | Los Angeles | Case no. 173, Southern District of California | ||
| Rancho San Pedro | 1784[lower-alpha 6] | Juan José Dominguez | Spain |  |
Manuel Dominguez | 43,119.13 acres (17,449.69 ha) |  |
December 18, 1858 | 440 |  |
Named for figure of religious significance; Peter, a Roman Catholic saint | Dominguez Rancho, Suanga, Rancho de los Gutierrez | Los Angeles | Case no. 273, Southern District of California | ||
| Rancho San Rafael | 1784 | José María Verdugo | Spain | Julio Verdugo, et al. | 36,403.32 acres (14,731.90 ha) | January 28, 1882 | 423 |  |
Named for figure of religious significance; Raphael, an archangel | Rancho La Zanja (la zanja was a local form of irrigation canal), Hahaonuput, Arroyo Hondo | Los Angeles | Case no. 381, Southern District of California | ||||
| Rancho San Vicente y Santa Mónica | 1828 | Francisco Sepúlveda | Mexico | .png.webp) |
357 | Sepúlveda | 30,259.65 acres (12,245.65 ha) |  |
July 23, 1881 | 432 | Named for figures of religious significance; Vincent of Saragossa and Saint Monica, both Roman Catholic saints | Los Angeles | Case no. 143, Southern District of California | |||
| Rancho Santa Anita | 1841 | Hugo Reid | Mexico | 03 (3 Spanish leagues) | _CHS_USC_digital_collection.jpg.webp) |
Henry Dalton | 13,319.06 acres (5,390.03 ha) |  |
August 9, 1866 | 454 |  |
Named for figure of religious significance; Ann, a Roman Catholic saint, diminutive form[23] | Los Angeles | Case no. 86, Southern District of California | ||
| Rancho Santa Gertrudes | 1833 | Josefa Cota de Nieto | Mexico | 05 (5 Spanish leagues) | _1846%252C_Dise%C3%B1o_475%252C_GLO_No._463%252C_Los_Angeles_County.jpg.webp) |
103 | Patented in 2 parts;
(1) Tomás Sanchez Colima (2) Jas. P. McFarland, John G. Downey |
38,900.25 acres (15,742.37 ha)[lower-alpha 7] |  |
463, 466 |  |
Named for figure of religious significance; Gertrude the Great, a Roman Catholic saint | Los Angeles | Case no. 193, Southern District of California, Case no. 194, Southern District of California | ||
| Rancho Sausal Redondo | 1822 | Antonio Ygnacio Ávila | Mexico | 05 (5 Spanish leagues) | 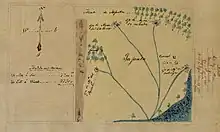 |
337 | Antonio Ygnacio Ávila | 22,458.94 acres (9,088.81 ha) |  |
1875-03-22 | 438 | Spanish; el sauzal is willow grove, describing Baccharis salicifolia, California seep willow; redondo is literally round, but here refers to a pasturage | Rancho Santa Elena, see also Rancho Gauspita and Rancho Salinas | Los Angeles | Case no. 354, Southern District of California. | |
| Rancho Simi | 1795 | Santiago Pico | Spain | 14 (14 Spanish leagues) |  |
271 | José de la Guerra y Noriega | 113,009.21 acres (45,733.20 ha) |  |
1865-06-29 | 400 | Indigenous, Chumash language; Chumash community of Šimiyi | Rancho San José de Gracia de Simí | Ventura, Los Angeles | Case no. 103, Southern District of California | |
| Rancho La Tajauta | 1843 | Anastasio Ávila | Mexico | 01 (1 Spanish league) |  |
Enrique Ávila | 3,559.86 acres (1,440.62 ha) | January 8, 1873 | 441 | 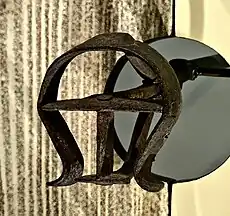 |
Indigenous, Tongva language; Tongva community of Tajáuta | Tajanta, Tajuanta, Cuerbas, Rancho Los Cuerbos (or Cuervos)[6][26] | Los Angeles | Case no. 167, Southern District of California | ||
| Rancho Temescal | 1843 | Francisco Lopez | Mexico | 03 (3 Spanish leagues) |  |
R. de la Cuesta | 13,339.07 acres (5,398.13 ha) | September 13, 1871 | 398 | Spanish; borrowing of the Nahuatl word temāzcalli, meaning sweat house, steam bath, sauna[27][28] | Ventura, Los Angeles | |||||
| Rancho Topanga Malibu Sequit | 1804 | José Bartolomé Tapia | Spain | Matthew Keller | 13,315.70 acres (5,388.67 ha) |  |
August 29, 1872 | 433 | Indigenous, mixed; Tongva community of Topaa'nga, Chumash community of Humaliwo, Chumash community of Lisiksi or Lisiqsihi[29][30] | Topanza Malibu, Sequit, Simo | Los Angeles | Case no. 147, Southern District of California. | ||||
| Rancho Tujunga | 1840 | Pedro Lopez, Francisco Lopez | Mexico | 01.5 (11⁄2 Spanish leagues) |  |
215 | D.W. Alexander | 6,660.71 acres (2,695.49 ha) |  |
October 19, 1874 | 413 | Indigenous, Tongva language; Tongva community of Tuhuu'nga[16] | Los Angeles | Case no. 52, Southern District of California | ||
| Rancho Las Vírgenes | Uncertain; c. 1810 | Miguel Ortega | Spain | 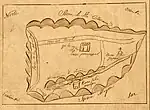 |
054 | Maria Antonia Machado de Reyes | 8,878.76 acres (3,593.11 ha) | September 5, 1883 | 545 | Named for figure of religious significance; originally Nuestra Señora la Reina de las Vírgenes, a Spanish-language honorific for Mary, mother of Jesus, meaning Our Lady, the Queen of the Virgins | Los Angeles | Case no. 256, Southern District of California |
Influence
Many place names in Los Angeles County draw their names from the ranchos and the rancheros.[31] Examples of rancho-derived toponyms include: Ballona (Creek, Wetlands), Brea, Centinela Ave., Cerritos (Auto Square, College), Conejo Valley, Dominguez (Hills, Channel, Rancho, CSUDH), Duarte, Encino, La Brea Ave., La Cañada Flintridge, La Cienega Blvd., La Puente, La Tijera Blvd., Las Virgenes USD, Los Feliz, Mount Baldy, Palos Verdes (Peninsula, Estates, blue butterfly), Park La Brea, Pico Blvd., Pico-Union, Pico Rivera, Rancho Park, Redondo Beach, Rose Hills, Rodeo Dr., San Jose Hills, San Pedro (Bay, neighborhood), San Vicente Blvd., other San Vicente Blvd., Santa Anita Race Track, Santa Monica (Bay, City, Blvd., Mountains), Sepulveda (Blvd., Pass, Transit Corridor, Dam), Verdugo (Mountains, Wash), Walnut, West Whittier-Los Nietos, et al. Rancho boundaries define a portion of the county boundary line; approximately 173 mi (278 km) of roads in the county follow rancho borders; and several major arterial thoroughfares run along former rancho property lines, including Pico, Redondo Beach, Sepulveda, Washington, Whittier, and Wilshire boulevards.[32]

By the 20th century, the popular culture of California often depicted romantic rancheros and idealized missions, but erased the negative consequences for indigenous people of the California mission clash of cultures.[33] Mission Revival (1890–1915), Spanish Colonial Revival (1915–1935), Monterey Colonial Revival and California Churrigueresque were all popular architectural styles in Los Angeles,[34][35] and not coincidentally: "Thanks to architects, writers, and city boosters, Southern California's identity became firmly grounded in an obsession with geography."[36] The appropriation of Spanish colonization by bourgeois whites[36] is typified by projects like Christine Sterling's preservation of Ávila Adobe and establishment of Olvera Street as a tourist attraction.[37] The eventual design shift from adobe-style buildings to the "Mediterranean" style was an intentional separation from the rustic and Mexican roots of the place to what was perceived as a more sophisticated cultural iconography,[36] although "California stucco" was a method for attaching the "Mexican–Indian mode of domestic architecture" to mass production of small family homes.[38] The "romance of the ranchos" was also used as a pretext for discouraging urban density of Los Angeles and promoting a vast decentralized "rural urban" development style that combines vast tracts of single family homes and practices like faux-rural horse-keeping with dense nodes of finance, law and film production.[39]
See also
- History of Los Angeles County, California
- History of the San Fernando Valley to 1915 – Aspect of history
- Ranchos of Orange County
- Zanja – Historical irrigation system used in the American Southwest
- For more on la brea, see bitumen, history of oil in California through 1930, and La Brea Tar Pits
- Ranchería and List of California Rancherías
- Hacienda – Spanish word used to refer to estates with large business enterprises
- Estancia – Large, private plot of land used for farming or cattle-raising
- Spanish colonization of the Americas
Notes
- ↑ One additional pueblo and one additional mission were established in Mexican California, bringing the totals to four and 21.
- ↑ For a complete accounting of the patented small land grants within Los Angeles County, see the California Land Commission report of 1982.
- ↑ Southern District of California refers to the United States District Court for the Southern District of California, a federal-level court.
- ↑ "Ramon Tiburcio" and "Roque" are the listed claimants of Encino on the index of expedientes held by the National Archives.
- ↑ Rancho San José was patented in two sections, one titled to Dalton-Palomares & Véjar, and a smaller one labeled "Addition" just to Dalton-Palomares.[5]
- ↑ The Rancho San Pedro grant was made sometime before October 20, 1784 and regranted in 1820, less Palos Verdes.
- ↑ Rancho Santa Gertrudes was patented in two parts, the smaller to Colima and the larger to McFarland & Downey.[5]
References
- ↑ Melvill, J.H. (July 21, 1890). "Early Land Grants: A short history of them in this county". Los Angeles Herald. Vol. 34, no. 98. p. 2. ISSN 2166-5494. Archived from the original on March 31, 2023. Retrieved March 31, 2023 – via California Digital Newspaper Collection.
- ↑ Robinson, W. W. (1948). Land in California, the story of mission lands, ranchos, squatters, mining claims, railroad grants, land scrip and homesteads. Chronicles of California. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 46–47 (1784 in Los Angeles). LCCN 48010331. OCLC 504383948. Archived from the original on April 2, 2023. Retrieved April 2, 2023 – via HathiTrust.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Baker, Charles C. (January 1, 1914). "Mexican Land Grants in California". Annual Publication of the Historical Society of Southern California. 9 (3): 236–243. doi:10.2307/41168710. ISSN 2162-9145. JSTOR 41168710. Archived from the original on April 2, 2023. Retrieved April 2, 2023.
- ↑ Phillips, George Harwood (August 1, 1980). "Indians in Los Angeles, 1781-1875: Economic Integration, Social Disintegration". Pacific Historical Review. 49 (3): 427–451. doi:10.2307/3638564. ISSN 0030-8684. JSTOR 3638564. Archived from the original on April 2, 2023. Retrieved April 2, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Minnick, Roy; Perez, Cris, eds. (1982). "Grants of Land in California made by Spanish or Mexican Authorities" (PDF). California State Lands Commission (slc.ca.gov). Prepared by the Staff of the State Lands Commission. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 26, 2023. Retrieved March 28, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Cowan, Robert G. (1956). Ranchos of California; a list of Spanish concessions, 1775-1822, and Mexican grants, 1822-1846. Fresno, Calif.: Academy Library Guild. Archived from the original on March 25, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023 – via HathiTrust.
- 1 2 "Titles Will Be Clouded: Many Acres of Land Affected by Ancient Claims". Los Angeles Herald. Vol. 43, no. 126. February 14, 1895. p. 5. ISSN 2166-5494. Archived from the original on March 31, 2023. Retrieved March 31, 2023 – via California Digital Newspaper Collection.
- 1 2 3 "Diseños Collection". California State Archives Exhibits. Archived from the original on March 28, 2023. Retrieved March 28, 2023.
- 1 2 de Packman, Ana Begue (December 1, 1945). "California's Cattle Brands and Earmarks". The Quarterly: Historical Society of Southern California. 27 (4): 127–149. doi:10.2307/41168069. ISSN 2162-9358. JSTOR 41168069. Archived from the original on March 27, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- ↑ Fogelson, Robert Michael (1993) [1967]. The fragmented metropolis: Los Angeles, 1850-1930. Classics in urban history. Berkeley: University of California press. location 358 of 4935. ISBN 978-0-520-08230-4.
- 1 2 3 "Alphabetical List of the 580 Complete Expedientes, Undated", National Archives Documents, California State University, Monterey Bay (CSUMB) Digital Commons, 2016
- ↑ Title Insurance and Trust and C.C. Pierce Photography Collection 1860-1960; California Historical Society (CHS); University of Southern California (USC) Libraries. "Brands of the California ranches, ca.1840-1900". USC Digital Libraries. Archived from the original on September 24, 2022. Retrieved April 2, 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ "Azusa History". City of Azusa, CA - Official Website. Archived from the original on March 30, 2023. Retrieved March 30, 2023.
- ↑ Bancroft, Hubert Howe (1886). "Chapter XVI: Local Annals of the South (1801–1820)". History of California, Vol. II, 1801–1824. The Works of Hubert Howe Bancroft (Vol. XIX). San Francisco: History Company Publishers. p. 354. Archived from the original on April 1, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023 – via Google Books.
- ↑ SEAMAN, FLORENCE JOSEPHINE (1914). "A Brief History of Rancho la Brea". Annual Publication of the Historical Society of Southern California. 9 (3): 253–256. doi:10.2307/41168712. ISSN 2162-9145. JSTOR 41168712. Archived from the original on March 31, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- 1 2 Munro, Pamela (October 28, 2014). Cook, Jia-Rui; Maclaren, Becca (eds.). "Topanga, Cahuenga and Tujunga — sounds from a rediscovered local language: The words of L.A.'s Tongva Indians live on". Zócalo Public Square. Archived from the original on April 2, 2023. Retrieved March 31, 2023.
- ↑ Larson, Rachel N.; Brown, Justin L.; Karels, Tim; Riley, Seth P. D. (February 5, 2020). Apollonio, Marco (ed.). "Effects of urbanization on resource use and individual specialization in coyotes (Canis latrans) in southern California". PLOS ONE. 15 (2): e0228881. Bibcode:2020PLoSO..1528881L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0228881. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 7001990. PMID 32023321.
- ↑ "The Story of Cerritos Chapter 3". cerritos.ca.us. Archived from the original on July 6, 2022. Retrieved March 30, 2023.
- ↑ Nixon, Kevin C. (2002). The Oak (Quercus) Biodiversity of California and Adjacent Regions (Report). USDA Forest Service Gen. Tech. Rep. PSW-GTR-184. Archived from the original on March 30, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- ↑ Johnson, John R. (October 1, 1997). "The Indians of Mission San Fernando". Southern California Quarterly. 79 (3): 249–290. doi:10.2307/41172612. ISSN 0038-3929. JSTOR 41172612. Archived from the original on December 24, 2022. Retrieved April 2, 2023.
- ↑ Stoll, Anne Q.; Douglass, John S.; Ciolek-Torrello, Richard (2009). "SEARCHING FOR GUASPET: A MISSION PERIOD RANCHERÍA IN WEST LOS ANGELES" (PDF). Proceedings of the Society for California Archaeology. Society for California Archaeology. 22. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 5, 2023. Retrieved March 29, 2023.
- ↑ Bowman, Lynn (1974). Los Angeles: Epic of a City. Howell-North Books. p. 126. ISBN 978-0-8310-7109-7. Archived from the original on April 6, 2023. Retrieved May 6, 2023 – via Google Books.
- 1 2 Lovejoy, Ora A. (January 1, 1918). "A Study of Southern California Place Names". Annual Publication of the Historical Society of Southern California. 11 (1): 44–50. doi:10.2307/41168758. ISSN 2162-9145. JSTOR 41168758. Archived from the original on March 31, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- ↑ Lerner, Robert J. (March 8, 1992). "Letter: History of El Sereno". Real Estate. Los Angeles Times. ISSN 0458-3035. Archived from the original on April 2, 2023. Retrieved March 31, 2023 – via Newspapers.com.
- ↑ Ertter, Barbara (2001). "Native California Roses". The Jepson Manual: Higher Plants of California. Berkeley, Calif.: Jepson Arboretum. Archived from the original on March 30, 2023. Retrieved March 30, 2023.
- ↑ Beherec, Marc A. (2020). "Ethnohistoric South Gate?" (PDF). Proceedings of the Society for California Archaeology. Society for California Archaeology. 34: 81–98. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 2, 2023. Retrieved April 2, 2023.
- ↑ Mott, Gertrude (1926). A handbook for Californiacs; a key to meaning and pronunciation of Spanish and Indian place names. San Francisco: Harr Wagner Pub. Co. Archived from the original on March 31, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- ↑ "temazcalli". Nahuatl Dictionary (wired-humanities.org). Archived from the original on December 17, 2022. Retrieved March 31, 2023.
- ↑ Guldimann, Suzanne. "By Any Other Name". Malibu Post. Archived from the original on March 31, 2023. Retrieved March 31, 2023.
- ↑ Applegate, Richard B. (December 1, 1974). "Chumash Placenames". The Journal of California Anthropology. 1 (2). Archived from the original on March 31, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- ↑ "Spanish Colonization, Mexican California, and California Statehood (1850) – LA River Master Plan". Archived from the original on April 1, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- ↑ Nelson, Howard; Loesser, Cornelius; McMillian, Eugene; Reeves, Richard; Scott, Frank; Zierer, Paul (1964). "REMNANTS OF THE RANCHOS IN THE URBAN PATTERN OF THE LOS ANGELES AREA". The California Geographer: Journal of California Geographical Society. V: 1–11. Archived from the original on March 25, 2023. Retrieved March 29, 2023 – via CSUN ScholarWorks.
- ↑ Severn, Carly (July 7, 2020). "'How Do We Heal?' Toppling the Myth of Junípero Serra". KQED. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- ↑ "Architecture of the Pacific Northwest - Popular Styles". content.lib.washington.edu. Archived from the original on December 4, 2022. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- ↑ O'Connor, Pauline (June 21, 2018). "An illustrated guide to Los Angeles architecture". Curbed LA. Archived from the original on April 1, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- 1 2 3 Fu, Albert S. (July 2012). "Materializing Spanish-Colonial Revival Architecture: History and Cultural Production in Southern California". Home Cultures. 9 (2): 149–171. doi:10.2752/175174212X13325123562223. ISSN 1740-6315. S2CID 142555495.
- ↑ Meares, Hadley (July 11, 2017). "Looking Back at Christine Sterling, the Maternalistic, Problematic "Mother of Olvera Street"". LA Weekly. Archived from the original on April 1, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- ↑ Rubin, Barbara (1977). "A Chronology of Architecture in Los Angeles". Annals of the Association of American Geographers. 67 (4): 521–537. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8306.1977.tb01159.x. ISSN 0004-5608. JSTOR 2562480. Archived from the original on April 1, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- ↑ Barraclough, Laura R. (2008). "Rural Urbanism: Producing Western Heritage and the Racial Geography of Postwar Los Angeles". Western Historical Quarterly. 39 (2): 177–202. doi:10.1093/whq/39.2.177. ISSN 0043-3810. JSTOR 25443689. Archived from the original on April 1, 2023. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
Further reading
- Guinn, J. M. (January 1915). "The Passing of the Rancho". Annual Publication of the Historical Society of Southern California. 10 (1/2): 46–53. doi:10.2307/41168911. JSTOR 41168911.
- Livingston, M. M. (January 1, 1914). "The Earliest Spanish Land Grants in California". Annual Publication of the Historical Society of Southern California. 9 (3): 195–199. doi:10.2307/41168705. ISSN 2162-9145. JSTOR 41168705.</ref>
- Sanchez, Nellie Van de Grift (1914). Spanish and Indian place names of California: their meaning and their romance (PDF). San Francisco: A.M. Robertson. LCCN 14018059. OCLC 4268886. OL 6570335M.
External links
- CSUMB Digital Commons: Hornbeck Collection > American Period > California Land Patents > Private Land Claims by County > Los Angeles County
- UCLA Digital Collections: 170/508 Diseños, maps and plans of ranchos of Southern California
 Media related to Ranchos of Los Angeles County, California at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ranchos of Los Angeles County, California at Wikimedia Commons