Chuvash Republic — Chuvashia | |
|---|---|
| Чувашская Республика — Чувашия | |
| Other transcription(s) | |
| • Chuvash | Чӑваш Республики — Чӑваш Ен |
| • Transliteration | Çăvaš Respubliki — Çăvaš Jen |
 Coat of arms | |
| Anthem: "State Anthem of the Chuvash Republic"[1] | |
.svg.png.webp) | |
| Coordinates: 55°33′N 47°06′E / 55.550°N 47.100°E | |
| Country | Russia |
| Federal district | Volga[2] |
| Economic region | Volga-Vyatka[3] |
| Capital | Cheboksary |
| Government | |
| • Body | State Council[4] |
| • Head[5] | Oleg Nikolayev[6] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 18,343 km2 (7,082 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 74th |
| Population | |
| • Total | 1,186,909 |
| • Estimate (2018)[9] | 1,231,117 |
| • Rank | 39th |
| • Density | 65/km2 (170/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 63.9% |
| • Rural | 36.1% |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (MSK |
| ISO 3166 code | RU-CU |
| License plates | 21, 121 |
| OKTMO ID | 97000000 |
| Official languages | Russian;[11] Chuvash[12] |
| Website | http://www.cap.ru |
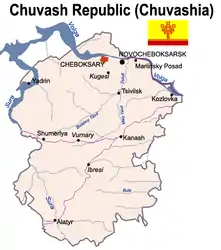
Chuvashia (Russian: Чувашия; Chuvash: Чӑваш Ен, romanized: Çăvaš Jen), officially the Chuvash Republic — Chuvashia,[note 1] is a republic of Russia located in Eastern Europe. It is the homeland of the Chuvash people, a Turkic ethnic group. It borders with the Mari El Republic in the north, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast in the west, the Republic of Mordovia in the southwest, Ulyanovsk Oblast in the south, and the Republic of Tatarstan in the east and southeast. Its capital is the city of Cheboksary. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 1,251,619.[13]
Geography
The Chuvash Republic is located in the center of European Russia, in the heart of the Volga-Vyatka economic region, mostly to the west of the Volga River, in the Volga Upland. It borders with the Mari El Republic in the north, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast in the west, the Republic of Mordovia in the southwest, Ulyanovsk Oblast in the south, and the Republic of Tatarstan in the east and southeast. There are over two thousand rivers in the republic—with the major ones being the Volga, the Sura, and the Tsivil—as well as four hundred lakes. Some of the Volga River valley reservoirs are in the north of the republic, and the Sura River flows towards the Volga along much of the republic's western boundary.
The climate is moderately continental, with the average temperatures ranging from −13 °C (9 °F) in January to +19 °C (66 °F) in July. Annual precipitation varies between 450 and 700 millimeters (18 and 28 in), but is uneven from one year to another. Natural resources include gypsum, sand, clay, sapropel deposits, phosphorite, and peat. There are oil and natural gas deposits, although their extraction has not yet been commercially pursued. Forests, mostly in the south along the Sura River, cover approximately 30% of the land.[14]
History


The ancestors of the Chuvash were Bulgars and Suars, Oghur Turkic tribes residing in the Northern Caucasus in the 5th to 8th centuries. In the 7th and 8th centuries, a part of the Bulgars left for the Balkans, where, together with local South Slavs, they established the state of modern Bulgaria. Another part moved to the Middle Volga Region (see Volga Bulgaria), where the Bulgar population that did not adopt Islam formed the foundation of the Chuvash people.[14]
During the Mongol invasion of Volga Bulgaria, the steppe-dwelling Suar migrated north, where Volga Finnic tribes, such as the Mordvins and Mari lived. The Chuvash claim to be the descendants of these Suars who assimilated with the Mari. In 1242, they became vassals of the Golden Horde. Later Mongol and Tatar rulers did not intervene in local internal affairs as long as tribute was paid annually to Sarai. When the power of the Golden Horde began to diminish, local Mişär Tatar Murzas from Piana and Temnikov tried to govern the Chuvash area.
During Ivan the Terrible's war of conquest against the Khanate of Kazan, in August 1552, the Chuvash Orsai and Mari Akpar Tokari princes swore their loyalty to the Grand Duchy of Muscovy at Alatyr on the Sura River. Between 1650 and 1850, the Russian Orthodox Church sent Chuvash-speaking missionaries to try to convert the Chuvash to the Orthodox faith. A group of these missionaries created a written Chuvash language. Most of the Chuvash who stayed in the area became Orthodox Christians, but some remained pagan.
On May 15, 1917, the Chuvash joined the Idel-Ural Movement and in December 1917 joined the short-lived Idel-Ural State, when an agreement was reached with Tatar representatives to draw the eastern border of Chuvashia at the Sviyaga River. In 1918–1919, the Russian Civil War encompassed the area. This ended with victory for the Bolsheviks. To gain support from the local population, Lenin ordered the creation of a Chuvash state within the Russian SFSR. On June 24, 1920, the Chuvash Autonomous Oblast was formed, which was transformed into the Chuvash ASSR in April 1925.
Administrative divisions
Politics
Until 2012, the Chuvash Republic officially had the status of a state. In the constitution of Chuvashia (version 6 - dated September 13, 2011 No. 46), the following was fixed: "The Chuvash Republic is a republic (state) within the Russian Federation."
During the Soviet period, the high authority in the republic was shared between three persons: The first secretary of the Chuvashia CPSU Committee (who in reality had the biggest authority), the chairman of the oblast Soviet (legislative power), and the Chairman of the Republic Executive Committee (executive power). Since 1991, CPSU lost all the power, and the head of the Republic administration, and eventually the governor was appointed/elected alongside elected regional parliament.
The Charter of Republic of Chuvashia is the fundamental law of the region. The State Council of the Chuvash Republic is the republic's regional standing legislative (representative) body. The highest executive body is the Republic's Government, which includes territorial executive bodies such as district administrations, committees, and commissions that facilitate development and run the day to day matters.
Demographics
Despite not being large, the republic is one of the most densely populated regions in the Russian Federation. Population: 1,251,619 (2010 Census);[13] 1,313,754 (2002 Census);[15] 1,336,066 (1989 Census).[16]
The capital (and largest city) is Cheboksary (population 464,000 in 2010). Cheboksary is situated mostly on the southern bank of the Volga in the northern part of the republic (one northern bank district was added in the second part of the 20th century), approximately 650 kilometers (400 mi) east of Moscow. Nearby to the east is the next largest city, Novocheboksarsk (population 124,000 in 2010).
Settlements
Largest cities or towns in Chuvashia 2010 Russian Census | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Administrative Division | Pop. | |||||||
 Cheboksary .jpg.webp) Novocheboksarsk |
1 | Cheboksary | City of republic significance of Cheboksary | 453,721 |  Kanash  Alatyr | ||||
| 2 | Novocheboksarsk | City of republic significance of Novocheboksarsk | 124,097 | ||||||
| 3 | Kanash | Kanashsky District | 45,607 | ||||||
| 4 | Alatyr | Alatyrsky District | 38,203 | ||||||
| 5 | Shumerlya | Shumerlinsky District | 31,722 | ||||||
| 6 | Tsivilsk | Tsivilsky District | 13,479 | ||||||
| 7 | Kugesi | Cheboksarsky District | 11,917 | ||||||
| 8 | Kozlovka | Kozlovsky District | 10,359 | ||||||
| 9 | Vurnary | Vurnarsky District | 10,086 | ||||||
| 10 | Yadrin | Yadrinsky District | 9,614 | ||||||
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1926 | 888,960 | — |
| 1959 | 1,097,859 | +23.5% |
| 1970 | 1,223,675 | +11.5% |
| 1979 | 1,292,486 | +5.6% |
| 1989 | 1,336,066 | +3.4% |
| 2002 | 1,313,754 | −1.7% |
| 2010 | 1,251,619 | −4.7% |
| 2021 | 1,186,909 | −5.2% |
| Source: Census data | ||
Vital statistics


- Source: Russian Federal State Statistics Service Archived April 12, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
| Average population (× 1,000) | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1,000) | Crude death rate (per 1,000) | Natural change (per 1,000) | Fertility rates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970 | 1,227 | 22,465 | 10,993 | 11,472 | 18.3 | 9.0 | 9.3 | |
| 1975 | 1,266 | 22,956 | 12,450 | 10,506 | 18.1 | 9.8 | 8.3 | |
| 1980 | 1,302 | 22,612 | 13,908 | 8,704 | 17.4 | 10.7 | 6.7 | |
| 1985 | 1,311 | 24,385 | 13,913 | 10,472 | 18.6 | 10.6 | 8.0 | |
| 1990 | 1,339 | 21,116 | 13,545 | 7,571 | 15.8 | 10.1 | 5.7 | 2.12 |
| 1991 | 1,342 | 19,113 | 13,459 | 5,654 | 14.2 | 10.0 | 4.2 | 1.96 |
| 1992 | 1,346 | 16,673 | 14,141 | 2,532 | 12.4 | 10.5 | 1.9 | 1.72 |
| 1993 | 1,347 | 14,410 | 16,876 | −2,466 | 10.7 | 12.5 | −1.8 | 1.48 |
| 1994 | 1,345 | 14,498 | 18,003 | −3,505 | 10.8 | 13.4 | −2.6 | 1.48 |
| 1995 | 1,345 | 13,842 | 17,727 | −3,885 | 10.3 | 13.2 | −2.9 | 1.41 |
| 1996 | 1,343 | 13,542 | 16,880 | −3,338 | 10.1 | 12.6 | −2.5 | 1.37 |
| 1997 | 1,341 | 12,822 | 16,762 | −3,940 | 9.6 | 12.5 | −2.9 | 1.30 |
| 1998 | 1,339 | 13,300 | 15,957 | −2,657 | 9.9 | 11.9 | −2.0 | 1.34 |
| 1999 | 1,337 | 12,129 | 17,997 | −5,868 | 9.1 | 13.5 | −4.4 | 1.22 |
| 2000 | 1,331 | 12,363 | 18,640 | −6,277 | 9.3 | 14.0 | −4.7 | 1.25 |
| 2001 | 1,324 | 11,986 | 18,980 | −6,994 | 9.1 | 14.3 | −5.3 | 1.20 |
| 2002 | 1,314 | 12,956 | 19,808 | −6,852 | 9.9 | 15.1 | −5.2 | 1.30 |
| 2003 | 1,304 | 13,171 | 19,978 | −6,807 | 10.1 | 15.3 | −5.2 | 1.32 |
| 2004 | 1,295 | 13,734 | 19,371 | −5,637 | 10.6 | 15.0 | −4.4 | 1.38 |
| 2005 | 1,286 | 13,133 | 19,682 | −6,549 | 10.2 | 15.3 | −5.1 | 1.32 |
| 2006 | 1,277 | 13,291 | 18,900 | −5,609 | 10.4 | 14.8 | −4.4 | 1.34 |
| 2007 | 1,269 | 14,835 | 18,642 | −3,807 | 11.7 | 14.7 | −3.0 | 1.50 |
| 2008 | 1,262 | 14,967 | 18,436 | −3,469 | 11.9 | 14.6 | −2.7 | 1.51 |
| 2009 | 1,257 | 16,103 | 17,492 | −1,389 | 12.8 | 13.9 | −1.1 | 1.63 |
| 2010 | 1,252 | 16,174 | 18,186 | −2,012 | 12.9 | 14.5 | −1.6 | 1.65 |
| 2011 | 1,249 | 16,165 | 16,923 | −758 | 12.9 | 13.6 | −0.7 | 1.67 |
| 2012 | 1,245 | 17,472 | 16,607 | 865 | 14.0 | 13.3 | 0.7 | 1.83 |
| 2013 | 1,242 | 17,351 | 16,324 | 1,027 | 14.0 | 13.1 | 0.9 | 1.85 |
| 2014 | 1,240 | 17,224 | 16,535 | 689 | 13.9 | 13.3 | 0.6 | 1.88 |
| 2015 | 1,237 | 17,138 | 16,266 | 872 | 13.8 | 13.1 | 0.7 | 1.91 |
| 2016 | 1,236 | 16,403 | 16,258 | 145 | 13.3 | 13.1 | 0.2 | 1.87 |
| 2017 | 1,233 | 13,947 | 15,571 | −1,624 | 11.3 | 12.6 | -1.3 | 1.65 |
| 2019 | 11,624 | 15,196 | −3,572 | 9.5 | 12.4 | -2.9 | ||
| 2020 | 11,305 | 18,845 | −7,540 | 9.3 | 15.5 | -6.2 |
Note: TFR[17]
Ethnic groups
According to the 2021 Census, ethnic Chuvash make up 63.7% of the republic's population. Other groups include Russians (30.7%), Tatars (2.7%), Mordvins (0.7%), and a host of smaller groups, each accounting for less than 0.5% of the total population.[18]
| Ethnic group |
1926 Census | 1939 Census | 1959 Census | 1970 Census | 1979 Census | 1989 Census | 2002 Census | 2010 Census[13] | 2021 census[18] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| Chuvash | 667,695 | 74.6% | 777,202 | 72.2% | 770,351 | 70.2% | 856,246 | 70.0% | 887,738 | 68.4% | 906,922 | 67.8% | 889,268 | 67.7% | 814,750 | 67.7% | 684,930 | 63.7% |
| Russians | 178,890 | 20.0% | 241,386 | 22.4% | 263,692 | 24.0% | 299,241 | 24.5% | 338,150 | 26.0% | 357,120 | 26.7% | 348,515 | 26.5% | 323,274 | 26.9% | 329,991 | 30.7% |
| Tatars | 22,635 | 2.5% | 29,007 | 2.7% | 31,357 | 2.9% | 36,217 | 3.0% | 37,573 | 2.9% | 35,689 | 2.7% | 36,379 | 2.8% | 34,214 | 2.8% | 29,092 | 2.7% |
| Mordvins | 23,958 | 2.7% | 22,512 | 2.1% | 23,863 | 2.2% | 21,041 | 1.7% | 20,276 | 1.6% | 18,686 | 1.4% | 15,993 | 1.2% | 13,014 | 1.1% | 7,707 | 0.7% |
| Others | 1,301 | 0.1% | 6,703 | 0.6% | 8,596 | 0.7% | 10,930 | 0.9% | 14,874 | 1.3% | 19,606 | 1.4% | 23,599 | 1.8% | 18,298 | 1.6% | 23,085 | 2.2% |
| 1 112,104 people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.[19] | ||||||||||||||||||
Genetics
Osteopetrosis affects 1 newborn out of every 20,000 to 250,000[20] worldwide, but the odds are much higher in the Russian region of Chuvashia (1 of every 3,500–4,000 newborns) due to genetic traits of the Chuvash people.[21][22]
HLA genes in the Chuvashian Population from European Russia was studied by Antonio Arnaiz-Villena in this article[23]
Religion
According to a 2012 survey,[24] 64.7% of the population of Chuvashia adheres to the Russian Orthodox Church, 4% are Orthodox Christian believers without belonging to any church or members of non-Russian Orthodox churches, 3% of the population (mostly Tatars) follow Islam, 3% are unaffiliated Christians, 1% follow indigenous faiths (Vattisen Yaly, Chuvash folk religion). In addition, 24% of the population declares to be "spiritual but not religious", 1% is atheist and 2.3% follows other religions or did not answer to the question.[24] There is a growing population of Jehovah's Witnesses among the people despite the official ban by the Russian Government.
Study of religion is compulsory for schoolchildren in Chuvashia. Of the students, approximately 76.9% are enrolled for Orthodox Studies, 16.0% for Secular Studies, 15.7% for World Religions Studies and 1.4% for Islamic Studies.[26]
Education
There are five higher educational institutions, including the Chuvash State University, the Chuvash State Pedagogical University, and the Chuvash State Agrarian University located in Cheboksary. These, together with 28 colleges and technical schools, are currently attended by approximately 45,000 students.
Economy

The Chuvash Republic is the most populous and fertile area in the middle Volga region. There are deciduous woodlands on fertile black earth. In agriculture, wheat and sugar-beet, pigs and beef cattle have become more important than the rye, oats, barley and dairy cattle which are typical for the whole area.
The republic is Russia's center for growing hops and is famous throughout the country for its long history of beer brewing. It is also a major center for electrical engineering, especially in the area of power transmission and control systems.[14] Other leading industries are metalworking, electricity generation, and chemical manufacturing. There are also large timber-working mills at Shumerlin.
The largest companies in the region include Khimprom Novocheboksarsk (revenues of $164.54 million in 2017), Accond (confectionery maker$, 152.55 million), Cheboksary Instrument-Making Plant ($142.26 million), NPP EKRA (power engineering$, 101.13 million).[27]
Transportation
The transport network in the republic is one of the most developed in Russia. The republic's system of roads, railroads, waterways, and airports closely ties the region with others in and outside of Russia.[14]
Roads
Only four roads in the Chuvash Republic are classified as important federal highways. The most important is Highway M-7, which runs from Nizhny Novgorod through the northern parts of the republic from Yadrinsky Nikolskoye via Malye Tyumerli, Kalmykovo, Khyrkasy, Novye Lapsary, Kugesi, Shivlinsk, Staraya Tyurlema, to Kazan in the Republic of Tatarstan. It also forms a connection via Chuvashia through the southern suburbs of Cheboksary and Novocheboksary to the Mari El Republic and the Vyatka Highway. Part of this road is classified as a motorway, the only one in the republic. From Yadrinsky Nikolskoye, the federal road P-178 runs through Yadrin, Shumerlya, Alatyr, to Surskoye in Ulyanovsk Oblast and further to Ulyanovsk. In the eastern part of Chuvashia, the federal road A-151 runs from Tsivilsk through Kanash, Komsomolskoye, Chkalovskoye, Karabay-Shemursha, Shemursha to Ulyanovsk and Saratov. All other roads in Chuvashia are classified as local area roads.
Automobiles, trucks, and buses are the major forms of transportation, with the republic ranking fourth in highway density in all of Russia.[14] Cheboksary is situated on one of the main highways of the Russian Federation leading from Moscow to the industrial areas of Tatarstan, the southern Urals, and Siberia. A recently completed bridge across the Volga River in the north connects the republic to the developed Ural and Volga Federal Districts. To the south, highways connect Chuvashia with Saratov and Volgograd. Extensive public and private bus systems connect all towns within the republic with each other and with the surrounding regions.[14]
The standard speed of transportation of containers by road is 400 kilometers (250 mi) per day. The average time of delivery from Cheboksary to Moscow is 1.5 days; to Saint Petersburg, 2.5 days; and to Western Europe, 10 to 15 days.[14]
Railways
The railway network is highly developed, convenient, and accessible year-round. One of the largest railway junctions of Russia – Kanash—is in the center of the republic. Via Kanash, the rail system connects the major towns in Chuvashia with the big industrial centers of eastern Siberia, the Urals, and Moscow. Express trains are reliable and provide a low-cost, comfortable way to travel. Express trains to and from Moscow are available every day, with the overnight journey taking approximately fourteen hours each way.
The following lines serve railway traffic in the Chuvash Republic:
- Arzamas-Kanash line
- Krasny Usel – Kanash -Sviyazhsk line
- Kanash – Cheboksary II – Cheboksary I – Cheboksary II – Novocheboksarsk line
In addition to these lines, there are 26 kilometers (16 mi) of 1,520 mm (4 ft 11+27⁄32 in) gauge industrial lines running from Altyshevo station, on Alatyr-Kanash section, to Pervomaysky, located just west of Starye Aybesi in Alatyrsky District.
All railway lines in Chuvashia are operated by the MPS Gorky Railway Division. Steam locomotives were mostly replaced in 1970 by diesel locomotives and when the main Arzamas-Kanash-Sviyazhsk line was electrified, the diesel locomotives were replaced by electric ones.
The Arzamas-Kanash-Sviyazhsk line is a double track main line, while the others are single track lines. The 84 km (52 mi) Sviyazhsk-Kanash section was electrified in 1986, the 142 km (88 mi) Kanash-Sergach section in 1987.
In 1967, there were four daily passenger trains in both directions on the Alatyr-Kanash line. One of them was the semifast Sochi-Sverdlovsk-Sochi long-distance transit train, halting only at Alatyr, Buinsk, and Kanash. Cheboksary was connected by daily semifast passenger train to Moscow. The travel time was 17.30 hours for the 758 km (471 mi) journey. 21 express and passenger trains used the Arzamas-Kanash-Sviyazhsk main line in the summer high season in both directions. Of these, four did not halt in Chuvashia. Most of the remaining semifast trains stopped at Shumerlya, Piner, Burnary, and Kanash. Four pairs of semifast trains also stopped at Tyurmari. In the 1999–2000 timetable, 11 pairs of Moscow-Kanash-Kazan express trains stopped at Kanash. The Chuvashia 53/54 express trains between Moscow and Kanash took 11.23 hours, back 10.57 hours.
In addition to Russian 1,524 mm (5 ft) gauge railways, there were six 750 mm (2 ft 5+1⁄2 in) narrow gauge railway lines: two short peat briquette industry lines at Severny and Sosnovka on the north side of the Volga, and four forest railways at Shumerlya, Atrat and Kirya. All opened in the 1930s. In 1965, their total length was 145 kilometers (90 mi):
- Shumerlya-Kabanovo-Rechnoy-Burak-Krasnobar forest railway – total length 72 kilometers (45 mi)
- Shumerlya-Kumashka-Salantshik-Yakhaykino forest railway – 46 kilometers (29 mi)
- Kirya-Lesopunkt Lyulya forest railway – 13 kilometers (8.1 mi)
- Atrat-Dolnaya Polyana-Lesozavod Gart forest railway – 14 kilometers (8.7 mi)
All lines were closed in the economic uncertainty after the breakup of the Soviet Union.
Rivers

The Volga and Sura Rivers connect Chuvashia to a national and international water network. To the south, Volgograd, Rostov-on-Don, Astrakhan, the Caspian Sea, and Black Sea are directly reachable. To the west, the Volga River connects Cheboksary with Nizhny Novgorod, Yaroslavl, Moscow and the northern regions of Russia. By using river-sea vessels, cargo transportation is possible from Chuvash river ports all the way to Saint Petersburg, Novorossiysk (on the Black Sea), Astrakhan, and ports situated on the Danube River. However, the river is frozen from December through April.[14] Cheboksary is a frequent stop on the many boat tours of the Volga.[14]
Air
The international Cheboksary Airport receives both cargo and passenger aircraft of practically all types and sizes. There are regularly scheduled flights to Moscow and other destinations. Additionally, Cheboksary is about a four-hour drive from Strigino International Airport, the airport primarily serving Nizhny Novgorod, which offers a greater number of flights, including connections through Aeroflot and Belavia.
Culture
While Russian is the predominant business language, the Chuvash language is still spoken by many, especially in the country. The Chuvash language belongs to the Oghur subgroup of the Turkic language group. In ancient times a runic system of writing was used. Chuvashi now uses a modified Cyrillic script that was adopted in 1871.
There has been a resurgence of native Chuvash pride, with many people looking back to their Chuvash roots and exploring the culture and heritage and relearning the language. Most building signs, road signs, and announcements are in both Russian and Chuvash.
At present Chuvash Republic has six professional theaters:
- Chuvash State Opera and Ballet Theater
- Chuvash State Academic Drama Theater
- Chuvash State Academic Song and Dance Ensemble
- Chuvash Children's Theater
- Chuvash State Puppet Theater
- Chuvash State Philharmonic Society
- Russian State Drama Theater
- Chuvash State Youth Theater
- Chuvash State Experimental Drama Theater
and over 30 amateur theaters, a Philharmonic Society, an Academic Folk Song and Dance Group, an Academic Choir, a Chamber Orchestra, and some professional concert groups.
There are also more than 20 museums, exhibition halls and modern art galleries.
- Chuvash National Museum.
- Art Museum
- Museum of Vasily Chapayev
- Literature Museum named after K.Ivanov
- Museum and Exhibition Center
- Culture and Exhibition Center «Raduga»
- Chuvash Beer Museum
- Chuvash State Geological Museum
- Museum of Cheboksary
- Space Museum
- Art Gallery
- Contemporary Art Center
- Art Gallery «6Х7»
Chuvash Republic has more than 565 public libraries, the book collection being over 10 million units.
- The Chuvash National Library
Monuments of Architecture
There are about 627 monuments of architecture in Chuvashia, including 54 of national importance: the Vvedensky Cathedral (1657), the Holy Trinity Monastery (1566), the Salt House, the houses of Chuvash famous merchants (Zeleischikov, Solovtsov, the Efremov family) (18th-19th century) in Cheboksary, the Tolmachev family house and Trinity Cathedral (18th century) in the town of Tsivilsk, the Burashnikov house in the town of Yadrin.
Sport
Chuvashia, along with Mordovia, has given some of the best modern race walkers, as Vera Sokolova, Olimpiada Ivanova, Yelena Nikolayeva and Vladimir Andreyev. Additionally, the 2008 IAAF World Race Walking Cup was held in Cheboksary. Also Chuvashia is represented with Baketball team named as Cheboksary Hawks which performs in Russia Superleague 2
Creative unions
Radio
See also
Notes
References
- ↑ Law #12
- ↑ Президент Российской Федерации. Указ №849 от 13 мая 2000 г. «О полномочном представителе Президента Российской Федерации в федеральном округе». Вступил в силу 13 мая 2000 г. Опубликован: "Собрание законодательства РФ", No. 20, ст. 2112, 15 мая 2000 г. (President of the Russian Federation. Decree #849 of May 13, 2000 On the Plenipotentiary Representative of the President of the Russian Federation in a Federal District. Effective as of May 13, 2000.).
- ↑ Госстандарт Российской Федерации. №ОК 024-95 27 декабря 1995 г. «Общероссийский классификатор экономических регионов. 2. Экономические районы», в ред. Изменения №5/2001 ОКЭР. (Gosstandart of the Russian Federation. #OK 024-95 December 27, 1995 Russian Classification of Economic Regions. 2. Economic Regions, as amended by the Amendment #5/2001 OKER. ).
- ↑ Constitution of the Chuvash Republic, Article 77
- ↑ Constitution of the Chuvash Republic, Article 68
- ↑ "Putin dismissed the head of Chuvashia, Mikhail Ignatiev, in connection with a loss of confidence". NewsRU (in Russian). January 29, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ↑ "Сведения о наличии и распределении земель в Российской Федерации на 01.01.2019 (в разрезе субъектов Российской Федерации)". Federal Service for State Registration, Cadastre and Cartography. Archived from the original on February 9, 2022. Retrieved August 29, 2023.
- ↑ "Оценка численности постоянного населения по субъектам Российской Федерации". Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved September 1, 2022.
- ↑ "26. Численность постоянного населения Российской Федерации по муниципальным образованиям на 1 января 2018 года". Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved January 23, 2019.
- ↑ "Об исчислении времени". Официальный интернет-портал правовой информации (in Russian). June 3, 2011. Retrieved January 19, 2019.
- ↑ Official throughout the Russian Federation according to Article 68.1 of the Constitution of Russia.
- ↑ Constitution of the Chuvash Republic, Article 8
- 1 2 3 Russian Federal State Statistics Service (2011). Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года. Том 1 [2010 All-Russian Population Census, vol. 1]. Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года [2010 All-Russia Population Census] (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Steven Brown and Olin Lagon (June 2001). "Economic Overview of the Republic of Chuvashia". United States Peace Corps Business Development Volunteers in Chuvashia. Archived from the original on July 4, 2005. Retrieved August 9, 2008.
- ↑ Russian Federal State Statistics Service (May 21, 2004). Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек [Population of Russia, Its Federal Districts, Federal Subjects, Districts, Urban Localities, Rural Localities—Administrative Centers, and Rural Localities with Population of Over 3,000] (XLS). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года [All-Russia Population Census of 2002] (in Russian).
- ↑ Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 г. Численность наличного населения союзных и автономных республик, автономных областей и округов, краёв, областей, районов, городских поселений и сёл-райцентров [All Union Population Census of 1989: Present Population of Union and Autonomous Republics, Autonomous Oblasts and Okrugs, Krais, Oblasts, Districts, Urban Settlements, and Villages Serving as District Administrative Centers]. Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года [All-Union Population Census of 1989] (in Russian). Институт демографии Национального исследовательского университета: Высшая школа экономики [Institute of Demography at the National Research University: Higher School of Economics]. 1989 – via Demoscope Weekly.
- ↑ "БГД".
- 1 2 "Национальный состав населения". Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved December 30, 2022.
- ↑ "Впн-2010". Archived from the original on December 25, 2018. Retrieved December 22, 2011.
- ↑ "Osteopetrosis: MedlinePlus Genetics". medlineplus.gov.
- ↑ "Остеопетроз рецессивный (мраморная болезнь костей) - ДНК-диагностика - Центр Молекулярной Генетики". www.dnalab.ru.
- ↑ "Медицинская генетика Чувашии". Archived from the original on February 1, 2016.
- ↑ Arnaiz-Villena, Antonio (January 1, 2003). "HLA Genes in the Chuvashian Population from European Russia: Admixture of Central European and Mediterranean Populations". Human Biology.
- 1 2 3 "Arena: Atlas of Religions and Nationalities in Russia". Sreda, 2012.
- ↑ 2012 Arena Atlas Religion Maps. "Ogonek", № 34 (5243), 27/08/2012. Retrieved 21/04/2017. Archived.
- ↑ "Всё больше чувашских школьников предпочитают изучать светскую этику".
- ↑ Выписки ЕГРЮЛ и ЕГРИП, проверка контрагентов, ИНН и КПП организаций, реквизиты ИП и ООО. СБИС (in Russian). Retrieved October 20, 2018.
Sources
- Нестеров, В. А. (1981) [1981]. Населённые пункты Чувашской АССР. 1917–1981 годы: Справочник об административно-территориальном делении (in Russian). Чувашское книжное издательство.
- Государственный Совет Чувашской Республики. 30 ноября 2000 г. «Конституция Чувашской Республики», в ред. Закона №34 от 26 июня 2014 г. «О внесении изменений в главу 7 Конституции Чувашской Республики». Вступил в силу 10 декабря 2000 г. Опубликован: "Республика", №52, 9 декабря 2000 г. (State Council of the Chuvash Republic. November 30, 2000 Constitution of the Chuvash Republic, as amended by the Law #34 of June 26, 2014 On Amending Chapter 7 of the Constitution of the Chuvash Republic. Effective as of December 10, 2000.).
- Государственный Совет Чувашской Республики. Закон №12 от 14 июля 1997 г. «О государственных символах Чувашской Республики», в ред. Закона №59 от 30 июля 2013 г. «О внесении изменений в Закон Чувашской Республики "О государственных символах Чувашской Республики"». Вступил в силу со дня официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Чаваш ен", No.30, 26 июля – 2 августа 1997 г. (State Council of the Chuvash Republic. Law #12 of July 14, 1997 On the State Symbols of the Chuvash Republic, as amended by the Law #59 of July 30, 2013 On Amending the Law of the Chuvash Republic "On the State Symbols of the Chuvash Republic". Effective as of the day of the official publication.).
- Salmin, Anton K. (2020). "The History of the Chuvash People in Ethnographic Facts" (PDF). Journal Tourism Studies & Practices (RTEP) (2: Geplat: Caderno Suplementar): 1–2. ISSN 2316-1493.
Further reading
- Vovina, Olessia P. (December 2000). "Building the road to the temple: Religion and national revival in the Chuvash Republic". Nationalities Papers. 28 (4): 695–706. doi:10.1080/00905990020009683. S2CID 153834810.
- Культурное наследие Чувашии (in Russian). Национальная библиотека Чувашской Республики. Retrieved February 6, 2012.
External links
 Media related to Chuvashia at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Chuvashia at Wikimedia Commons Chuvashia travel guide from Wikivoyage
Chuvashia travel guide from Wikivoyage- Official website of the Chuvash Republic
- About flag and coat of arms of the Chuvash Republic
- Chuvashia news
- Why do Chuvash people not speak in Chuvash? (article in Russian)
- "As it is in the Chuvash Republic the Chuvash are not needed?!"
