| Solar eclipse of March 29, 2006 | |
|---|---|
 Totality from Side, Turkey | |
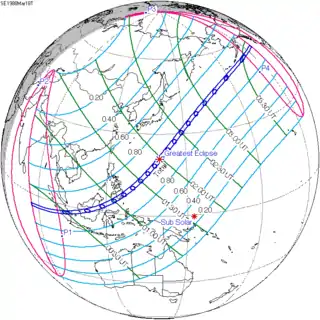
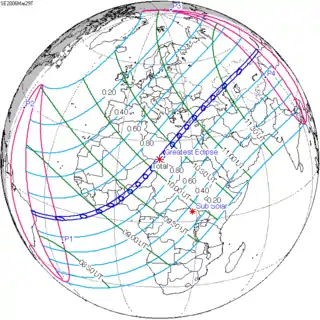 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 0.3843 |
| Magnitude | 1.0515 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 247 sec (4 m 7 s) |
| Coordinates | 23°12′N 16°42′E / 23.2°N 16.7°E |
| Max. width of band | 184 km (114 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| (P1) Partial begin | 7:36:50 |
| (U1) Total begin | 8:34:20 |
| Greatest eclipse | 10:12:23 |
| (U4) Total end | 11:47:55 |
| (P4) Partial end | 12:45:35 |
| References | |
| Saros | 139 (29 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9521 |
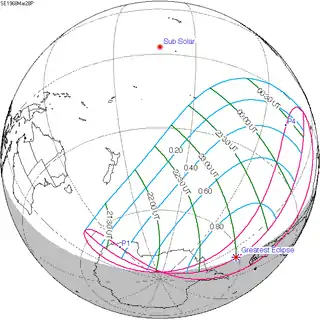
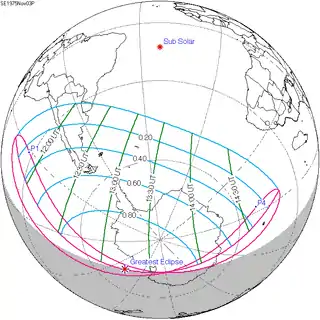
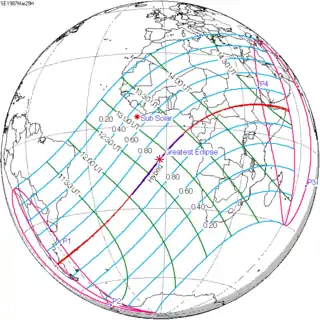
A total solar eclipse occurred on March 29, 2006.[1][2] A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. It was visible from a narrow corridor which traversed half the Earth. The magnitude, that is, the ratio between the apparent sizes of the Moon and that of the Sun, was 1.052, and it was part of Saros 139.
It was the second solar eclipse visible in Africa in just 6 months.
Visibility
.gif)
The path of totality of the Moon's shadow began at sunrise in Brazil and extended across the Atlantic to Africa, traveling across Ghana, the southeastern tip of Ivory Coast, Togo, Benin, Nigeria, Niger, Chad, Libya, and a small corner of northwest Egypt, from there across the Mediterranean Sea to Greece (Kastellórizo) and Turkey, then across the Black Sea via Georgia, Russia, and Kazakhstan to Western Mongolia, where it ended at sunset. A partial eclipse was seen from the much broader path of the Moon's penumbra, including the northern two-thirds of Africa, the whole of Europe, and Central Asia.
Observations
People around the world gathered in areas where the eclipse was visible to view the event. The Manchester Astronomical Society, the Malaysian Space Agency, the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, as well as dozens of tour groups met at the Apollo temple and the theater in Side, Turkey. The San Francisco Exploratorium featured a live webcast from the site, where thousands of observers were seated in the ancient, Roman-style theater.[3]
Almost all actively visited areas in the path of totality had perfect weather. Many observers reported an unusually beautiful eclipse, with many or all effects visible, and a very nice corona, despite the proximity to the solar minimum. The partial phase of the eclipse was also visible from the International Space Station, where the astronauts on board took spectacular pictures of the moon's shadow on Earth's surface. It initially appeared as though an orbit correction set for the middle of March would bring the ISS into the path of totality, but this correction was postponed.
Gallery
.jpg.webp) Cape Coast, Ghana (9:10 UTC)
Cape Coast, Ghana (9:10 UTC) Murzuq District, Libya (10:16 UTC)
Murzuq District, Libya (10:16 UTC) Valencia, Spain (10:16 UTC)
Valencia, Spain (10:16 UTC).jpg.webp) Oria, Italy (10:39 UTC)
Oria, Italy (10:39 UTC) The Moon's shadow as seen from the International Space Station (10:50 UTC)
The Moon's shadow as seen from the International Space Station (10:50 UTC) Berkhamsted, England (11:01 UTC)
Berkhamsted, England (11:01 UTC).jpg.webp) Marousi, Greece (11:01 UTC)
Marousi, Greece (11:01 UTC) Krasnoyarsk, Russia (11:20 UTC)
Krasnoyarsk, Russia (11:20 UTC) Lagan, Russia (11:23 UTC)
Lagan, Russia (11:23 UTC) Novosibirsk, Russia (11:42 UTC)
Novosibirsk, Russia (11:42 UTC).jpg.webp) Kathmandu, Nepal (12:01 UTC)
Kathmandu, Nepal (12:01 UTC) Degania A, Israel: Partial Solar Eclipse
Degania A, Israel: Partial Solar Eclipse Animation from Sallum, Egypt
Animation from Sallum, Egypt
Satellite failure
The satellite responsible for SKY Network Television, a New Zealand pay TV company, failed the day after this eclipse at around 1900 local time. While SKY didn't directly attribute the failure to the eclipse, they said in a media release that it took longer to resolve the issue because of it, but this claim was refuted by astronomers. The main reason for the failure was because of an aging and increasingly faulty satellite.[4]
Related eclipses
Eclipses of 2006
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on March 14.
- A total solar eclipse on March 29.
- A partial lunar eclipse on September 7.
- An annular solar eclipse on September 22.
This solar eclipse was preceded by the penumbral lunar eclipse on March 14, 2006.
Tzolkinex
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of February 16, 1999
- Followed: Solar eclipse of May 10, 2013
Half-Saros
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of March 24, 1997
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of April 4, 2015
Tritos
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of April 29, 1995
- Followed: Solar eclipse of February 26, 2017
Solar Saros 139
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of March 18, 1988
- Followed: Solar eclipse of April 8, 2024
Inex
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of April 18, 1977
- Followed: Solar eclipse of March 9, 2035
Solar eclipses 2004–2007
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[5]
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 119 | 2004 April 19 Partial (south) |
−1.13345 | 124 | 2004 October 14 Partial (north) |
1.03481 | |
129_(cropped).jpg.webp) Partial from Naiguatá |
2005 April 08 Hybrid |
−0.34733 | 134 Annular from Madrid, Spain |
2005 October 03 Annular |
0.33058 | |
139 Total from Side, Turkey |
2006 March 29 Total |
0.38433 | 144.jpg.webp) Partial from São Paulo, Brazil |
2006 September 22 Annular |
−0.40624 | |
149_(cropped).jpg.webp) From Jaipur, India |
2007 March 19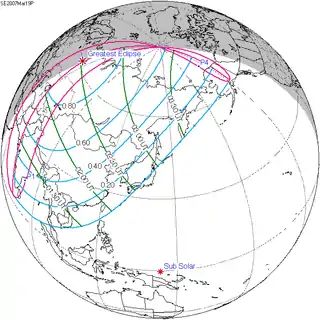 Partial (north) |
1.07277 | 154_(cropped).jpg.webp) From Córdoba, Argentina |
2007 September 11 Partial (south) |
−1.12552 | |
Saros 139
It is a part of saros series 139, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, 8 hours, containing 71 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on May 17, 1501. It contains hybrid eclipses on August 11, 1627 through to December 9, 1825 and total eclipses from December 21, 1843 through to March 26, 2601. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on July 3, 2763. Its eclipses are entabulated in three columns; each one in the same column, every third eclipse, is one exeligmos apart so cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The solar eclipse of June 13, 2132 will be the longest total solar eclipse since July 11, 1991 at 6 minutes, 55.02 seconds.
The longest duration of totality will be produced by member 39 at 7 minutes, 29.22 seconds on July 16, 2186.[6] After that date each duration will decrease, until the series end. This date is the longest solar eclipse computed between 4000 BC and 6000 AD.[7] Saros series eclipses are during the Moon’s ascending node (a term related to our equator and polar-naming conventions).
| Series members 24–45 occur between 1901 and 2300 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 24 | 25 | 26 |
 February 3, 1916 |
 February 14, 1934 |
 February 25, 1952 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 |
 March 7, 1970 |
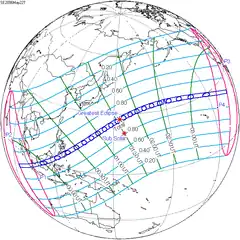
 March 18, 1988 |
 March 29, 2006 |
| 30 | 31 | 32 |
 April 8, 2024 |
 April 20, 2042 |
 April 30, 2060 |
| 33 | 34 | 35 |
 May 11, 2078 |
 May 22, 2096 |
 June 3, 2114 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 |
 June 13, 2132 |
 June 25, 2150 |
 July 5, 2168 |
| 39 | 40 | 41 |
 July 16, 2186 |
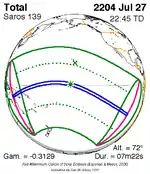 July 27, 2204 |
 August 8, 2222 |
| 42 | 43 | 44 |
 August 18, 2240 |
 August 29, 2258 |
 September 9, 2276 |
| 45 | ||
 September 20, 2294 | ||
Inex series
This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Inex series members between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
 May 29, 1919 (Saros 136) |
 May 9, 1948 (Saros 137) |
 April 18, 1977 (Saros 138) |
 March 29, 2006 (Saros 139) |
 March 9, 2035 (Saros 140) |
 February 17, 2064 (Saros 141) |
 January 27, 2093 (Saros 142) |
||
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| 21 eclipse events, progressing from south to north between June 10, 1964, and August 21, 2036 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| June 10–11 | March 27–29 | January 15–16 | November 3 | August 21–22 |
| 117 | 119 | 121 | 123 | 125 |
 June 10, 1964 |
 March 28, 1968 |
 January 16, 1972 |
 November 3, 1975 |
 August 22, 1979 |
| 127 | 129 | 131 | 133 | 135 |
 June 11, 1983 |
 March 29, 1987 |
 January 15, 1991 |
 November 3, 1994 |
 August 22, 1998 |
| 137 | 139 | 141 | 143 | 145 |
 June 10, 2002 |
 March 29, 2006 |
 January 15, 2010 |
 November 3, 2013 |
 August 21, 2017 |
| 147 | 149 | 151 | 153 | 155 |
 June 10, 2021 |
 March 29, 2025 |
 January 14, 2029 |
 November 3, 2032 |
 August 21, 2036 |
Notes
- ↑ "Total solar eclipse: World witnesses rare event". Bristol Herald Courier. 2006-03-30. p. 4. Retrieved 2023-10-25 – via Newspapers.com.
- ↑ "There goes the sun". The Toronto Star. 2006-03-30. p. 3. Retrieved 2023-10-25 – via Newspapers.com.
- ↑ Total Solar Eclipse: Live from Turkey in 2006
- ↑ Press release by Sky TV. Solar eclipse interferes with satellite restoration Archived 2005-02-10 at the Wayback Machine Friday, 31 March 2006.
- ↑ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ↑ Saros Series Catalog of Solar Eclipses NASA Eclipse Web Site.
- ↑ Ten Millennium Catalog of Long Solar Eclipses, −3999 to +6000 (4000 BCE to 6000 CE) Fred Espenak.
References
- Fred Espenak and Jay Anderson. "Total Solar Eclipse of 2006 March 29". NASA Technical publication (NASA/TP-2004-212762), November 2004.
- NASA – Total Solar Eclipse of 2006 March 29
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- solar-eclipse-2006.info Information about the March 29th Solar Eclipse.
- Interactive 2006 March 29 Total Solar Eclipse map with local circumstances
- Eclipse.za.net, Umbral Paths of March 29 Eclipse in Africa
Photos:
- Prof. Druckmüller's eclipse photography site. Turkey, Cappadocia
- Prof. Druckmüller's eclipse photography site. Egypt
- Prof. Druckmüller's eclipse photography site. Libya
- Total eclipse photographs from Turkey
- Another set of total eclipse photographs from Turkey
- Photo gallery from Turkey
- Phases of solar eclipse view from Antalya
- NASA videos and photos from Libya and Turkey
- Pictures taken from Smolyan, Bulgaria
- NASA video of eclipse Archived 2007-03-10 at the Wayback Machine
- Solar eclipse images and videos from Libya by traveling NASA employees and scientists
- Images by Crayford Manor House Astronomical Society from Libya and Turkey Archived 2013-02-09 at archive.today
- Spaceweather.com Eclipse gallery
- Antwrp.gsfc.nasa.gov APOD, March 30, 2006, When Diamonds Aren't Forever, totality from Greek island of Kastelorizo in the eastern Aegean
- Antwrp.gsfc.nasa.gov APOD, April 4, 2006, A Total Solar Eclipse over Turkey, totality from Adrasan, Kumluca, Antalya Province, Turkey
- Antwrp.gsfc.nasa.gov APOD, April 7, 2006, totality from Side, Turkey, a larger version of the same picture chosen as APOD again on July 26, 2009, The Big Corona, Koenvangorp.be
- Antwrp.gsfc.nasa.gov APOD, April 8, 2006, Vanishing Umbra, from Mount Hasan southeast of İncesu, Aksaray, Turkey
- The 2006 Eclipse in Turkey
- Russian scientist observed eclipse
- University of Athens – Solar Eclipse 29/3/2006, Solar Party
- Solar Total Eclipse of 2006 March 29
- Tubitak.gov.tr, 29 March 2006 Total Solar Eclipse, Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TÜBİTAK)
- Solar Eclipse over Kemer, Turkey 060329
External links
![]() Media related to Solar eclipse of 2006 March 29 at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Solar eclipse of 2006 March 29 at Wikimedia Commons
.jpg.webp)

