| Solar eclipse of August 19, 1887 | |
|---|---|
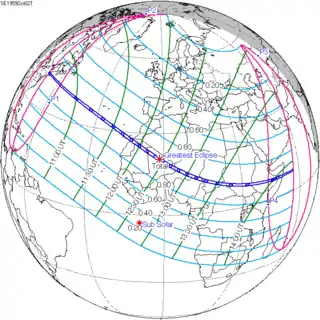
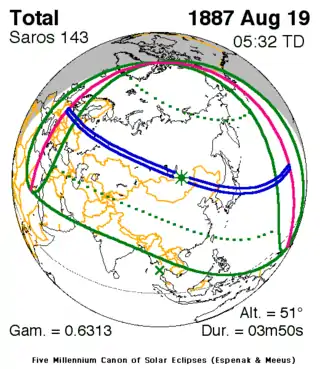 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 0.6312 |
| Magnitude | 1.0518 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 230 sec (3 m 50 s) |
| Coordinates | 50°36′N 111°54′E / 50.6°N 111.9°E |
| Max. width of band | 221 km (137 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 5:32:05 |
| References | |
| Saros | 143 (16 of 72) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9251 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on 19 August 1887. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. It was visible across Europe, Asia, and Japan.
Observations
The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev ascended in a balloon near Moscow to observe this eclipse. The weather in Tver Governorate was cloudy and it was rain at morning, so Mendeleev forced to fly alone. He made some notes at 6:55, 20 minutes after the start, and made some observations of the solar corona. For this flight, the scientist was awarded the medal of the Academy of Aerostatic Meteorology.[1]
 |
_b_509_2.jpg.webp) Partiality at sunrise from Berlin, Germany |
.jpg.webp) Ilya Repin, “The Solar Eclipse of 1887” (“Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev on the aerostat”), 1887. |
Russian writer Anton Chekhov published the short story "From the Diary of a Hot-Tempered Man" six weeks before the eclipse passed through Russia. The story includes a major section about the frustrations of a man who is trying to make a great variety of observations during the short interval of totality. In the story the eclipse date is given as 7 August 1887, as per the Julian Calendar then in use in Russia.
Related eclipses
Solar 143
It is a part of Saros cycle 143, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 72 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on March 7, 1617 and total event from June 24, 1797 through October 24, 1995. It has hybrid eclipses from November 3, 2013 through December 6, 2067, and annular eclipses from December 16, 2085 through September 16, 2536. The series ends at member 72 as a partial eclipse on April 23, 2873. The longest duration of totality was 3 minutes, 50 seconds on August 19, 1887. All eclipses in this series occurs at the Moon’s ascending node.
| Series members 17–28 occur between 1741 and 2100 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 8 | 9 | 10 |
 May 23, 1743 |
 June 3, 1761 |
 June 14, 1779 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 |
 June 24, 1797 |
 July 6, 1815 |
 July 17, 1833 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 |
 July 28, 1851 |
 August 7, 1869 |
 August 19, 1887 |
| 17 | 18 | 19 |
 August 30, 1905 |
 September 10, 1923 |
 September 21, 1941 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 |
 October 2, 1959 |
 October 12, 1977 |
 October 24, 1995 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 |
 November 3, 2013 |
 November 14, 2031 |
 November 25, 2049 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 |
 December 6, 2067 |
 December 16, 2085 | |
Notes
- ↑ Кирилл Яблочкин. (19 October 2014). "Менделеев на воздушном шаре: история рискованного полёта великого химика" [Mendeleev in a balloon: the story of a risky flight of the great chemist] (in Russian). Retrieved 15 February 2022.
References
- NASA graphic
- Googlemap
- NASA Besselian elements
- American Eclipse Expedition to Japan: The Total Solar Eclipse of 1887 "Preliminary Report of Prof. David P. Todd, Astronomer in Charge of the Expedition." Published by the Observatory Amherst, Mass., 1888
- Mabel Loomis Todd (1900). Total Eclipses of the Sun. Little, Brown.
- The total solar eclipse of August 19, 1887 Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 48, p. 202
- Sketchs of Solar Corona August 19, 1887
- Solar eclipse of August 19, 1887 in Russia Archived May 5, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
.jpg.webp)

