| Solar eclipse of December 27, 2084 | |
|---|---|
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | −0.4094 |
| Magnitude | 1.0396 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 184 sec (3 m 4 s) |
| Coordinates | 47°18′S 47°42′E / 47.3°S 47.7°E |
| Max. width of band | 146 km (91 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 9:13:48 |
| References | |
| Saros | 133 (49 of 72) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9698 |
A total solar eclipse will occur on December 27, 2084. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 2083–2087
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2083–2087 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||
| 118 | July 15, 2083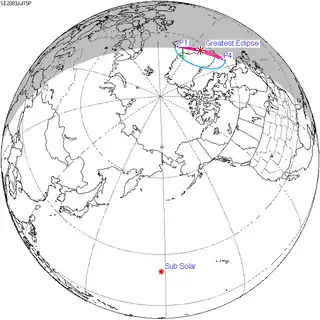 Partial |
123 | January 7, 2084 Partial | |
| 128 | July 3, 2084 Annular |
133 | December 27, 2084 Total | |
| 138 | June 22, 2085 Annular |
143 | December 16, 2085 Annular | |
| 148 | June 11, 2086 Total |
153 | December 6, 2086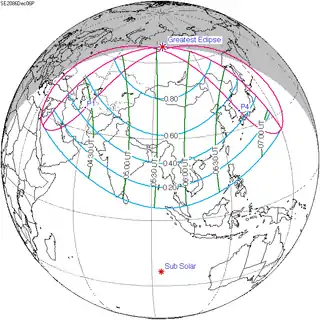 Partial | |
| 158 | June 1, 2087 Partial | |||
Tritos
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of January 27, 2074
- Followed: Solar eclipse of November 27, 2095
Tzolkinex
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of November 15, 2077
- Followed: Solar eclipse of February 7, 2092
Saros 133
Solar Saros 133, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, contains 72 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on July 13, 1219. It contains annular eclipses from November 20, 1435, through January 13, 1526, with a hybrid eclipse on January 24, 1544. It has total eclipses from February 3, 1562, through June 21, 2373. The series ends at member 72 as a partial eclipse on September 5, 2499. The longest duration of totality was 6 minutes, 49.97 seconds on August 7, 1850.[2] The total eclipses of this saros series are getting shorter and farther south with each iteration. All eclipses in this series occurs at the Moon’s ascending node.
| Series members 30–56 occur between 1742 and 2211 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 30 | 31 | 32 |
| June 3, 1742 | June 13, 1760 | 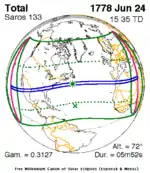 June 24, 1778 |
| 33 | 34 | 35 |
| July 4, 1796 | July 17, 1814 | July 27, 1832 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 |
| August 7, 1850 |  August 18, 1868 |
 August 29, 1886 |
| 39 | 40 | 41 |
 September 9, 1904 |
 September 21, 1922 |
 October 1, 1940 |
| 42 | 43 | 44 |
 October 12, 1958 |
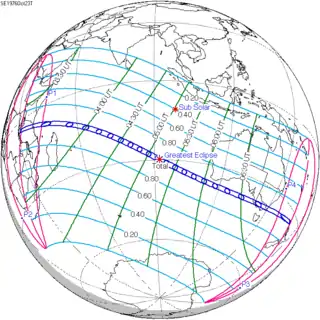 October 23, 1976 |
 November 3, 1994 |
| 45 | 46 | 47 |
 November 13, 2012 |
 November 25, 2030 |
 December 5, 2048 |
| 48 | 49 | 50 |
 December 17, 2066 |
 December 27, 2084 |
 January 8, 2103 |
| 51 | 52 | 53 |
 January 19, 2121 |
 January 30, 2139 |
 February 9, 2157 |
| 54 | 55 | 56 |
 February 21, 2175 |
 March 3, 2193 |
 March 15, 2211 |
Notes
- ↑ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ↑ http://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/SEsaros/SEsaros133.html
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
.jpg.webp)

