Instructions
- Add a new Selected article to the next available subpage. Use {{Selected article}}
- Update
|max=to new total for its {{Random portal component}} on the main page.
Selected article 1
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/1

Selected article 2
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/2

Selected article 3
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/3

Selected article 4
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/4

Selected article 5
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/5

Selected article 6
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/6

Selected article 7
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/7

Selected article 8
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/8

Selected article 9
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/9
.jpg.webp)
Selected article 10
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/10

The airport's location and lack of transport links, as well as Montreal's economic decline relative to Toronto, made it unpopular with airlines. Eventually relegated to the simple role of a cargo airport, Mirabel became an embarrassment widely regarded in Canada as being a boondoggle, or a "white elephant," and one of the best examples of a failed megaproject. (Full article...)
Selected article 11
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/11
.jpg.webp)
Selected article 12
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/12 Gliding is a recreational activity and competitive sport where pilots fly un-powered aircraft known as gliders or sailplanes. Properly, the term gliding refers to descending flight of a heavier-than-air craft, whereas soaring is the correct term to use when the craft gains altitude or speed from rising air. After launching glider pilots search for rising air to gain height. If conditions are good enough, experienced pilots can fly many hundreds, or even thousands, of kilometers before returning to their home airfields. However if the weather deteriorates, they must often land elsewhere, but some can avoid this by using engines. While many glider pilots merely enjoy the sense of achievement, some competitive pilots fly in races round pre-defined courses. These competitions test the pilots' abilities to make best use of local weather conditions as well as their flying skills. Local and national competitions are organized in many countries and there are also biennial World Gliding Championships. Powered aircraft or winches are the most common methods of launching gliders. These and other methods (apart from self-launching motor-gliders) require assistance from other participants. Gliding clubs have thus been established to share airfields and equipment, train new pilots and maintain high safety standards. (Full article...)
Selected article 13
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/13

Had it been successful, the planned amphibious and airborne landings in Britain of Operation Sea Lion would have followed. The Battle of Britain was the first major campaign to be fought entirely by air forces. It was the largest and most sustained bombing campaign attempted up until that date. The failure of Nazi Germany to destroy Britain's air defence or to break British morale is considered its first major defeat.
British historians date the battle from 10 July to 31 October 1940, which represented the most intense period of daylight bombing. German historians usually place the beginning of the battle in mid-August 1940 and end it in May 1941, on the withdrawal of the bomber units in preparation for the attack on the USSR. (Full article...)
Selected article 14
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/14

External aerodynamics is the study of flow around solid objects of various shapes. Evaluating the lift and drag on an airplane, the shock waves that form in front of the nose of a rocket is an example of external aerodynamics. Internal aerodynamics is the study of flow through passages in solid objects. For instance, internal aerodynamics encompasses the study of the airflow through a jet engine.
The ratio of the problem's characteristic flow speed to the speed of sound comprises a second classification of aerodynamic problems. A problem is called subsonic if all the speeds in the problem are less than the speed of sound, transonic if speeds both below and above the speed of sound are present (normally when the characteristic speed is approximately the speed of sound), supersonic when the characteristic flow speed is greater than the speed of sound, and hypersonic when the flow speed is much greater than the speed of sound. Aerodynamicists disagree over the precise definition of hypersonic flow; minimum Mach numbers for hypersonic flow range from 3 to 12. Most aerodynamicists use numbers between 5 and 8. (Full article...)
Selected article 15
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/15

With numerous skyscrapers and mountains located to the north and its only runway jutting out into Victoria Harbour, landings at the airport were dramatic to experience and technically demanding for pilots. The History Channel program Most Extreme Airports ranked it as the 6th most dangerous airport in the world.
The airport was home to Hong Kong's international carrier Cathay Pacific, as well as regional carrier Dragonair, freight airline Air Hong Kong and Hong Kong Airways. The airport was also home to the former RAF Kai Tak. (Full article...)
Selected article 16
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/16

Selected article 17
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/17

The airport is located near the city of Lod, 15 km (9 mi) southeast of Tel Aviv. It is operated by the Israel Airports Authority, a government-owned corporation that manages all public airports and border crossings in Israel. Ben Gurion Airport is on Highway 1, the main Jerusalem-Tel Aviv Highway, accessible by car or public bus.
Ben Gurion Airport is the hub of El Al, Israir Airlines, Arkia Israel Airlines, and Sun d'Or International Airlines. During the 1980s and 1990s, it was a focus city of the now-defunct Tower Air. Today, Terminal 3 is used for international flights, and Terminal 1 is used for domestic flights. The airport has three runways and is used by commercial, private, and military aircraft.
Ben Gurion Airport is considered to be among the five best airports in the Middle East due to its passenger experience and its high level of security. Security forces such as Israel Police officers, IDF and Israel Border Police soldiers are complemented by airport security guards who operate both in uniform and undercover. The airport has been the target of several terrorist attacks, but no attempt to hijack a plane departing from Ben Gurion airport has succeeded. (Full article...)
Selected article 18
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/18

Selected article 19
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/19

Wind shear itself is a microscale meteorological phenomenon occurring over a very small distance, but it can be associated with mesoscale or synoptic scale weather features such as squall lines and cold fronts. It is commonly observed near microbursts and downbursts caused by thunderstorms, weather fronts, areas of locally higher low level winds referred to as low level jets, near mountains, radiation inversions that occur due to clear skies and calm winds, buildings, wind turbines, and sailboats. Wind shear has a significant effect during take-off and landing of aircraft due to their effects on steering of the aircraft, and was a significant cause of aircraft accidents involving large loss of life within the United States.
Sound movement through the atmosphere is affected by wind shear, which can bend the wave front, causing sounds to be heard where they normally would not, or vice versa. Strong vertical wind shear within the troposphere also inhibits tropical cyclone development, but helps to organize individual thunderstorms into living longer life cycles which can then produce severe weather. The thermal wind concept explains with how differences in wind speed with height are dependent on horizontal temperature differences, and explains the existence of the jet stream. (Full article...)
Selected article 20
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/20
The Luftwaffe became an essential component in the "Blitzkrieg" battle plan. Operating as a tactical close support air force, it helped the German armies to conquer the bulk of the European continent in a series of short and decisive campaigns in the first nine months of the war, experiencing its first defeat during the Battle of Britain in 1940 as it could not adapt into a strategic role, lacking heavy bombers with which to conduct a strategic bombing campaign against the British Isles.
Despite this setback the Luftwaffe remained formidable and in June 1941 embarked on Adolf Hitler's quest for an empire in eastern Europe by invading the USSR, with much initial success. However, the Luftwaffe's striking victories in the Soviet Union were brought to a halt in the Russian winter of 1942-1943. From then on, it was forced onto the strategic defensive contesting the ever increasing numbers of Soviet aircraft, whilst defending the German homeland and German occupied Europe from the growing Allied air forces pounding all aspects of German industry.
Having failed to achieve victory in the Soviet Union in 1941 or 1942, the Luftwaffe was drawn into a war of attrition which extended to North Africa and the Channel Front. The entry of the United States into the war and the resurgence of the Royal Air Force's (RAF) offensive power created the Home Front, known as Defense of the Reich operations. The Luftwaffe's strength was slowly eroded and by mid 1944 had virtually disappeared from the skies of Western Europe leaving the German Army to fight without air support. It continued to fight into the last days of the war with revolutionary new aircraft, such as the Messerschmitt Me 262, Messerschmitt Me 163 and the Heinkel He 162, even though the war was already hopelessly lost. (Full article...)
Selected article 21
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/21
.jpg.webp)
Selected article 22
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/22
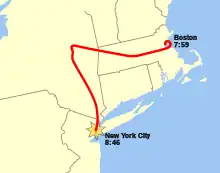
The aircraft crashed into the North Tower of the World Trade Center at 08:46 local time; the impact killed all 92 people aboard, including the hijackers. Many people in the streets witnessed the collision, and Jules Naudet captured the impact on video. News agencies began to report on the incident soon after and speculated that the crash had been an accident. The impact and subsequent fire caused the North Tower to collapse, which resulted in thousands of additional casualties. During the recovery effort at the World Trade Center site, workers recovered and identified dozens of remains from Flight 11 victims, but many other body fragments could not be identified. (Full article...)
Selected article 23
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/23

A hot air balloon consists of a bag called the envelope that is capable of containing heated air. Suspended beneath is the gondola or wicker basket (in some long-distance or high-altitude balloons, a capsule) which carries the passengers and a source of heat. The heated air inside the envelope makes it buoyant since it has a lower density than the relatively cold air outside the envelope. Unlike gas balloons, the envelope does not have to be sealed at the bottom since the air near the bottom of the envelope is at the same pressure as the surrounding air. In today's sport balloons the envelope is generally made from nylon fabric and the mouth of the balloon (closest to the burner flame) is made from fire resistant material such as Nomex.
Recently, balloon envelopes have been made in all kinds of shapes, such as hot dogs, rocket ships, and the shapes of commercial products. Hot air balloons that can be propelled through the air rather than just being pushed along by the wind are known as airships or, more specifically, thermal airships. (Full article...)
Selected article 24
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/24

Arkia was founded in 1949 as Israel Inland Airlines when it became clear that there was demand for a local airline to connect the north of Israel (especially Tel Aviv) with the southern region of the Negev, as a subsidiary of El Al, Israel's national airline. Flights starting the following year with the airline unsing De Havilland DH.89 aircraft, followed by Douglas DC-3s, to connect Rosh Pina in the north to the port of Eilat in the south. El Al held a 50% stake in the airline at this time with Histadrut, Israel's labour federation, being the other shareholder. The airline later evolved to become Eilata Airlines, Aviron, and then to Arkia Israel Airlines. In its first year of service, Israel Inland carried 13,485 passengers on their twice weekly flight, operated by a Curtis Commando. (Full article...)
Selected article 25
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/25
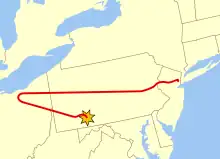
The plane crashed in a field just outside Shanksville, Pennsylvania, about 150 miles (240 km) northwest of Washington, D.C., killing all 44 people aboard, including the hijackers. Many witnessed the impact from the ground and news agencies began reporting on the event within an hour. The plane fragmented upon impact, leaving a crater, and some debris was blown miles from the crash site. The remains of everyone on board the aircraft were later identified. Subsequent analysis of the flight recorders revealed how the actions taken by the passengers prevented the aircraft from reaching either the White House or United States Capitol. A permanent memorial is planned for construction on the crash site. The chosen design has been the source of criticism and is scheduled to be dedicated in 2011. (Full article...)
Selected article 26
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/26

Selected article 27
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/27

Selected article 28
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/28

Selected article 29
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/29
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by one or more engine driven rotors. In contrast with fixed-wing aircraft, this allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forwards, backwards and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft would not be able to take off or land. The capability to efficiently hover for extended periods of time allows a helicopter to accomplish tasks that fixed-wing aircraft and other forms of vertical takeoff and landing aircraft cannot perform.The word 'helicopter' is adapted from the French hélicoptère, coined by Gustave de Ponton d'Amecourt in 1861, which originates from the Greek helix/helik- (ἕλικ-) = 'spiral' or 'turning' and pteron (πτερόν) = 'wing'.
Helicopters were developed and built during the first half-century of flight, with some reaching limited production, but it was not until 1942 that a helicopter designed by Igor Sikorsky reached full-scale production, with 131 aircraft built. Though most earlier designs used more than one main rotor, it was the single main rotor with antitorque tail rotor configuration of this design that would come to be recognized worldwide as the helicopter. (Full article...)
Selected article 30
Portal:Aviation/Selected article/30 The Airbus A300 is a wide-body airliner developed and manufactured by Airbus. In September 1967, aircraft manufacturers in the United Kingdom, France, and West Germany signed a memorandum of understanding to develop a large airliner. Germany and France reached an agreement on 29 May 1969 after the British withdrew from the project on 10 April 1969. European collaborative aerospace manufacturer Airbus Industrie was formally created on 18 December 1970 to develop and produce it. The prototype first flew on 28 October 1972.
The first twin-engine widebody airliner, the A300 typically seats 247 passengers in two classes over a range of 5,375 to 7,500 km (2,900 to 4,050 nmi). Initial variants are powered by CF6-50 or JT9D turbofans and have a three-crew flight deck. The improved A300-600 has a two-crew cockpit and updated GE CF6-80 or PW4000 engines; it made its first flight on 8 July 1983 and entered service later that year. The A300 is the basis of the smaller A310 (first flown in 1982) and was adapted in a freighter version. Its cross section was retained for the larger A340 (1991) and A330 (1992). It is also the basis for the oversize Beluga transport (1994).
Launch customer Air France introduced the type on 23 May 1974. After limited demand initially, sales took off as the type was proven in early service, beginning three decades of steady orders. It has a similar capacity to the Boeing 767-300, introduced in 1986, but lacked the 767-300ER range. During the 1990s, the A300 became popular with cargo aircraft operators, as passenger airliner conversions or as original builds. Production ceased in July 2007 after 561 deliveries (Full article...)
