 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
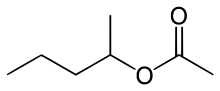
| Preferred IUPAC name
Pentan-2-yl acetate | |
| Other names
1-Methylbutyl acetate 2-Pentanol acetate 2-Pentyl ester of acetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.952 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H14O2 | |
| Molar mass | 130.187 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[1] |
| Odor | Mild,[1] like bananas[2] |
| Density | 0.87 g/mL (20°C)[1] |
| Melting point | −78 °C; −109 °F; 195 K[1] |
| Boiling point | 121 °C; 249 °F; 394 K[1] |
| 0.2g/100g water (20°C)[2] | |
| Vapor pressure | 7 mmHg (20°C)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Warning[2] | |
| H226[2] | |
| Flash point | 32 °C; 89 °F; 305 K[1] |
| 380 °C (716 °F; 653 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 1–7.5% (20°C)[1] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LCLo (lowest published) |
9200 ppm (guinea pig, 7 hr) 10,000 ppm (guinea pig, 5 hr)[3] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 125 ppm (650 mg/m3)[1] |
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 125 ppm (650 mg/m3)[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
1000 ppm[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
sec-Amyl acetate is an organic compound and an ester. It is formed in an esterification reaction of sec-amyl alcohol (2-pentanol) and acetic acid.[2] It is a colorless liquid.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0032". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- 1 2 3 4 5 "2-Pentyl Acetate". PubChem. NCBI.
- ↑ "sec-Amyl acetate". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.