| Subdivisions of England | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
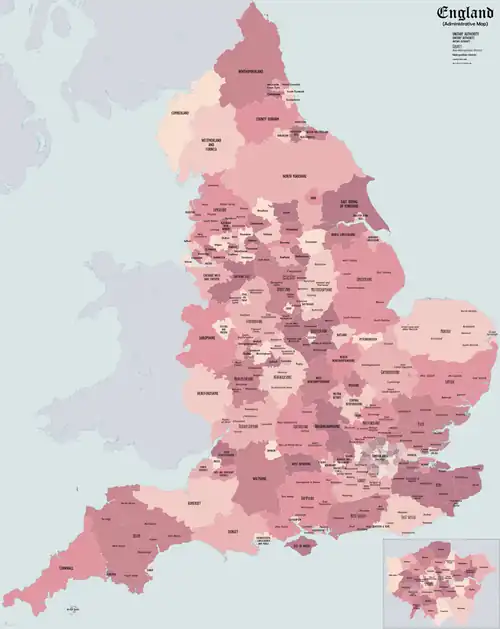 Subdivisions of England (as of 1 April 2023) that have a principal local authority: two-tier non-metropolitan counties and their non-metropolitan districts; metropolitan boroughs; unitary authorities; London boroughs; and the sui generis City of London and Isles of Scilly. | |||||||||||||||
| Location | England | ||||||||||||||
| Subdivisions |
| ||||||||||||||
| This article is part of a series within the Politics of the United Kingdom on the |
 |
|---|
|
The subdivisions of England constitute a hierarchy of administrative divisions and non-administrative ceremonial areas.
Overall, England is divided into nine regions and 48 ceremonial counties, although these have only a limited role in public policy. For the purposes of local government, the country is divided into counties, districts and parishes. In some areas, counties and districts form a two-tier administrative structure, while in others they are combined under a unitary authority. Parishes cover only part of England.
The current system is the result of incremental reform which has its origins in legislation enacted in 1965 and 1972.[1]

ceremonial county boundary
non-metropolitan county boundary
Administrative
England has a non-universal structure of local government subdivisions. There are two tiers of local government subdivision - (administrative) counties and districts (known as boroughs in London).[2]
Different local divisions exist across England:[2]
- Tier structure:
- County tier
- District tier
- Authority structure:
The authority structure is slowly replacing the tier structure and metropolitan boroughs with all the metropolitan boroughs in combined authorities and periodic abolitions of the tier structure councils into unitary authority councils.
Tiers
The 1974 reform of local government established the tier structure throughout England with county authorities in metropolitan and Greater London also existing, 1986 reform abolished these. From the 1996 reform the structure's use has been declining, 21 tiered areas remain out of the original 48. The county tier provides the majority of services, including education and social services while the 164 district-tier councils have a more limited role.[1]
Authorities
As of April 2023, there are 62 unitary authorities.[2] Unitary authorities have control of their areas functioning.[3] There is a general push towards the reorganisation of English local government to the authority structure, often reorganisation is a condition of new devolution powers.[4] 46 unitary authorities were created from the 1996 reform, nine more were created in 2009, followed by further changes in 2019, 2020, 2021 and 2023. The Greater London administrative area was created in 1965 with 32 boroughs, excluding the City of London.[5] Six Metropolitan two-tiered areas were created in 1974, similar to the Greater London model. These county-tier councils had extra devolved powers to others. In 1986, the county-tier was abolished with the London boroughs, Metropolitan boroughs and combined boards remaining. Apart from status these boroughs have the same powers to unitary authorities.
Combined authorities operate the opposite way round to the county in a tier structure, the combined authority acts on what the unitary authorities have agreed upon to focus on and what powers have been given by central government. In 2000, the Greater London Authority was created with an elected Mayor of London and the London Assembly.[5] In 2010, the Greater Manchester Comined Authority was created with a similar modal to the GLA a with further combined authorities based on the GMCA created. As of June 2023, 10 combined authorities and the Greater London Authority currently exist.
Other
Sui generis
The Isles of Scilly are governed by a sui generis local authority called the Council of the Isles of Scilly. The authority was established in 1890 as the Isles of Scilly Rural District Council. It was renamed but otherwise unreformed by the changes in local government that occurred in 1974 in the rest of England outside Greater London.[6] Although effectively a unitary authority, for example it is an education authority,[7] the Isles of Scilly are part of the Cornwall ceremonial county and combine with Cornwall Council for services such as health[8] and economic development.[9]
The ancient City of London forms a 33rd division and is governed by the City of London Corporation, a sui generis authority unlike any other in England[5] that has largely avoided any of the reforms of local government in the 19th and 20th centuries.[10]
Civil parishes
The civil parish is the most local unit of government in England.[1] A parish is governed by a parish council or parish meeting, which exercises a limited number of functions that would otherwise be delivered by the local authority. There is one civil parish in Greater London (Queen's Park, in the City of Westminster),[11] and not all of the rest of England is parished. The number of parishes and total area parished is growing.
Non-administrative
Regions
At the highest level, all of England is divided into nine regions that are each made up of a number of counties and districts. These 'government office regions' were created in 1994,[12] and from the 1999 Euro-elections up until the UK's exit from the EU, they were used as the European Parliament constituencies in the United Kingdom and in England's European Parliament constituencies.
The regions vary greatly in their areas covered, populations and contributions to the national economy.[12] All have the same status, except London which has substantive devolved powers.[13]
There was a failed attempt to create elected regional assemblies outside London in 2004 and since then the structures of regional governance (regional assemblies, regional development agencies and local authority leaders' boards) have been subject to review. Following the change of government in 2010, these were scheduled for abolition by 2012.
Ceremonial and historic counties
For non-administrative purposes, England is wholly divided into 48 ceremonial counties.[14] These are used for the purposes of appointing Lords Lieutenant[14] who are the Crown's representatives in those areas as well as a way of grouping non-metropolitan counties. They are taken into consideration when drawing up Parliamentary constituency boundaries. Ceremonial counties are commonly named after historic counties, the ceremonial county acts as an in between for the administrative boundaries and long established areas used in fields such as sport.
Titles, non-metropolitan and metropolitan counties
County-tier councils and each unitary authority are separate non-metropolitan counties, each non-metropolitan county can be known as a district, city or borough. Berkshire is an anomaly in this arrangement whereby its districts became unitary authorities, the non-metropolitan county remain to keep the title of Royal county, in the same way the metropolitan county remained when the county-tier councils were abolished.[15] Each correspond to an administrative body.
Non-metropolitan districts can also be a borough, city or district. Unitary authority areas are joint non-metropolitan counties and non-metropolitan districts.
Lists
Regions
| Type | Created | Number | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Region | 1994 | 9 |
Two-tier non-metropolitan counties
| Type | Created | Number | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-metropolitan county | 1974 | 21 | |
| Non-metropolitan district | 1974 | 164 | List of districts |
Metropolitan counties
| Type | Created | Number | Units | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metropolitan county | 1974 | 6 | Greater Manchester | Merseyside | South Yorkshire | Tyne and Wear | West Midlands | West Yorkshire |
| Metropolitan district | 1974 | 36 | ||||||
London
| Type | Created | Number | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| London borough | 1965 | 32 |
|
| Sui generis | in antiquity | 1 | |
| Total | 33 | ||
Unitary authorities
| Type | Created | Number | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| County gained district functions | 2023 | 2 | |
| District(s) gained county functions | 2023 | 2 | |
| District(s) gained county functions | 2021 | 2 | |
| District(s) gained county functions | 2020 | 1 | |
| District(s) gained county functions | 2019 | 2 | |
| County gained district functions | 2009 | 5 | |
| District(s) gained county functions | 2009 | 4 | |
| District(s) gained county functions | 1998 | 21 | |
| District(s) gained county functions | 1997 | 9 | |
| District gained county functions | 1996 | 13 |
|
| County gained district functions | 1995 | 1 | |
| Sui generis | 1890 | 1 | |
| Total | 63 | ||
Civil parishes
Hierarchical list of regions, strategic authorities, counties and districts
See also
Notes
- ^C1 Also a ceremonial county of identical area.
- ^C2 Also a ceremonial county covering a larger area.
- ^C3 Hertfordshire, Norfolk, Northamptonshire, Oxfordshire, Suffolk, Surrey, Warwickshire, West Sussex and Worcestershire occupy the same area as the ceremonial county; Buckinghamshire, Cambridgeshire, Derbyshire, Devon, Dorset, East Sussex, Essex, Gloucestershire, Hampshire, Kent, Lancashire, Leicestershire, Lincolnshire, Nottinghamshire and Staffordshire are larger for ceremonial purposes, being combined with one or more unitary authorities.
- ^D1 Metropolitan (36); non-metropolitan two-tier (164); unitary authority (62); London borough (32); sui generis (2).
- ^NC Berkshire has no county council and the districts function as unitary authorities.
References
- 1 2 3 Jones, B., Kavanagh, D., Moran, M. & Norton, P., Politics UK, (2004), Pearson Longman.
- 1 2 3 "Local government structure and elections". GOV.UK. Retrieved 27 February 2022.
- ↑ "Local Government Act 1992". Office of Public Sector Information. 1992. Retrieved 8 August 2010.
- ↑ "The political and governance implications of unitary reorganisation | Local Government Association". www.local.gov.uk. Retrieved 27 February 2022.
- 1 2 3 Travers, T., The Politics of London, (2004), Palgrave
- ↑ "Local Government Act 1972". Office of Public Sector Information. 1972. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- ↑ "Education and Learning". Council of the Isles of Scilly. Archived from the original on 4 June 2009. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- ↑ "About Us". Cornwall and Isles of Scilly Primary Care Trust. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- ↑ "The Cornwall and Isles of Scilly Enterprise Partnership". Cornwall Council. 30 July 2010. Retrieved 9 August 2010.
- ↑ Hebbert, Michael (1998). London: More by fortune than design. John Wiley & Sons.
- ↑ "Queen's Park parish council gets go-ahead". BBC News London. 29 May 2012. Retrieved 2 August 2014.
- 1 2 Atkinson, H. & Wilks-Heeg, S. (2000). Local Government from Thatcher to Blair. Polity.
- ↑ Collins, S., Colville, I & Pengelly, S., A Guide to the Greater London Authority, (2000), Sweet and Maxwell
- 1 2 "Lieutenancies Act 1997". Office of Public Sector Information. 1997. Retrieved 8 August 2010.
- ↑ "The Berkshire (Structural Change) Order 1996". National Archives(legislation.gov.uk). 1996. Retrieved 13 September 2012.