 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
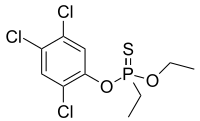
| Preferred IUPAC name
O-Ethyl O-(2,4,5-trichlorophenyl) ethylphosphonothioate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.752 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H12Cl3O2PS | |
| Molar mass | 333.59 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Amber colored odorless liquid[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Trichloronate is a highly toxic organophosphate insecticide.[2] It is used against vegetable fly larvae and soil pests.[1]
Case reports indicate exposure to the chemical can cause fatal encephalopathy.[3] Its aquatic toxicity has been measured at significantly higher against Ceriodaphnia dubia and Daphnia magna.[4]
References
- 1 2 "Hazardous Substance Fact Sheet: Trichloronate" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services. June 1999.
- ↑ Trichloronate at cameochemicals.noaa.gov.
- ↑ de Reuck J, Colardyn F, Willems J (1979). "Fatal encephalopathy in acute poisoning with organophosphorus insecticides. A clinico-pathologic study of two cases". Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 81 (4): 247–54. doi:10.1016/0303-8467(79)90029-5. PMID 233207. S2CID 27093634.
- ↑ Liu W, Lin K, Gan J (2006). "Separation and aquatic toxicity of enantiomers of the organophosphorus insecticide trichloronate". Chirality. 18 (9): 713–6. doi:10.1002/chir.20323. PMID 16845672.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.