 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Dizinc diphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.367 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Zn2P2O7 | |
| Molar mass | 304.72 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Density | 3.75 g/cm3 |
| Insoluble | |
| Solubility | Soluble in dilute acids |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
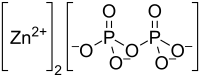
Zinc pyrophosphate (Zn2P2O7) is an ionic inorganic chemical compound composed of Zn2+ cations and pyrophosphate anions.
Preparation
Zinc pyrophosphate can be obtained from the thermal decomposition of zinc ammonium phosphate.[2]
- 2 ZnNH4PO4 → Zn2P2O7 + 2 NH3 + H2O
It can also be obtained from the reaction between sodium carbonate, zinc oxide, and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate.[3]
- Na2CO3 + 2 ZnO + 2 (NH4)H2PO4 → Zn2P2O7 + 2 NaOH + 2 NH3 + 2 H2O + CO2
It is also produced when a strongly acidic solution of zinc sulfate is heated with sodium pyrophosphate.[4]
- 2 ZnSO4 + Na4P2O7 → Zn2P2O7 + 2 Na2SO4
Another method is precipitating zinc as a phosphate, then heating over 1123 K.
Properties
Zinc pyrophosphate is a white crystalline solid that is insoluble in water.[5] On heating in water, it decomposes to form Zn3(PO4)2 and ZnHPO4. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system. The α-form crystallizes at low temperatures and the β-form crystallizes at high temperatures.[2][3]
Uses
Zinc pyrophosphate is used as a pigment.[5] It is useful in gravimetric analysis of zinc.[6]
References
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 4–96, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- 1 2 Calvo, Crispin (1965-05-01). "THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE AND PHASE TRANSITIONS OF β-Zn 2 P 2 O 7". Canadian Journal of Chemistry. 43 (5): 1147–1153. doi:10.1139/v65-152. ISSN 0008-4042.
- 1 2 Jarboui, A.; Ben Rhaeim, A.; Hlel, F.; Guidara, K; Gargouri, M. (2010). "NMR study and electrical properties investigation of Zn2P2O7". Ionics. 16 (1): 67–73. doi:10.1007/s11581-009-0333-5. ISSN 0947-7047. S2CID 94790682.
- ↑ Ochs, Rudolf (2013). Praktikum der Qualitativen Analyse Für Chemiker · Pharmazeuten und Mediziner. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag. p. 117. ISBN 978-3-662-28315-8. OCLC 860357745.
- 1 2 Perry, Dale L. (2016). Handbook of Inorganic Compounds (2nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. 469. ISBN 978-1-4398-1462-8. OCLC 759865801.
- ↑ Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (1995). Lehrbuch der anorganischen Chemie (102nd ed.). Berlin: de Gruyter. p. 1493. ISBN 978-3-11-012641-9. OCLC 237142268.