 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H21NO2 |
| Molar mass | 247.338 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Ciclafrine (INN) is a sympathomimetic phenethylamine and antihypotensive that was never marketed.[1][2] The compound belongs to the class of hemiaminal ethers.
Synthesis
Ciclafrine can be prepared by the reaction of norfenefrine with cycloheptanone.[3]
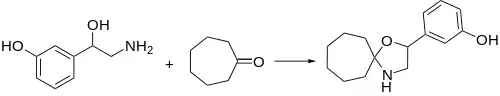 Ciclafrine synthesis
Ciclafrine synthesis
References
- ↑ Ganellin CR, Triggle DJ (21 November 1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. pp. 586–. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4.
- ↑ Korolkovas A (1988). Essentials of medicinal chemistry. John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated. p. 405. ISBN 978-0-471-88356-2.
- ↑ DE 2336746, Satzinger, Gerhard & Herrmann, Manfred, "2-Hydroxyphenyl-1-oxa-4-azaspiro-alkan-Derivate [2-Hydroxyphenyl-1-oxa-4-azaspiro-alkane derivatives]", published 1975-02-13, assigned to Gödecke AG
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.