 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Buphedrone |
| Routes of administration | Vaporization, insufflation, Intravenous injection, intramuscular injection, orally, rectal, buccal |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H15NO |
| Molar mass | 177.247 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
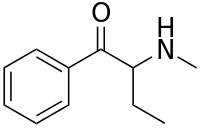
Buphedrone, also known as α-methylamino-butyrophenone (MABP), is a stimulant of the phenethylamine and cathinone chemical classes that was first synthesized in 1928.[1] It is legal in most countries as a research chemical, as long as it is not intended for human consumption.
Chemistry
Buphedrone is a beta-ketone and is related to the naturally occurring compounds, cathinone and cathine. It is also related to methamphetamine, differing by the β-ketone substituent (at the beta carbon) and an ethyl group replacing the methyl group at the carbon alpha to the amine. One other name for buphedrone is phenylacetoethyl-methylamine.
Buphedrone as free base is very unstable; it is prone to dimerization like other α-amino ketones. Because of this, it is sold as various salts, with a hydrochloride being most common.
Effects
Buphedrone increases spontaneous rodent locomotor activity, potentiates the release of dopamine from dopaminergic nerve terminals in the brain, and causes appetite suppression. It also causes a possibly dangerous effect of decreasing subjective feeling of thirst. The effects of buphedrone have also been compared to methamphetamine, with more euphoria and less physical stimulation. Most commonly reported effects include:
- Elevated mood, euphoria
- Increased alertness
- Dilated pupils (rare)
- Slurred speech (rare)
- Increased heart rate
- Talkativeness
- Increased empathy and sense of communication
- Increased sex drive
- Temporary erectile dysfunction in men
- Restlessness
- Insomnia
- Increased motivation
Depending on the route of administration, the duration varies from approximately 2.5 (IV) to 6 hours (orally) and may be followed by unpleasant symptoms associated with withdrawal, which may include:
- Dysphoria
- Tiredness
- Sweating
- Loss of concentration
Legal status
As of October 2015 buphedrone was a controlled substance in China.[2]
Buphedrone is an Anlage II controlled drug in Germany.
In the United States Buphedrone is considered a schedule 1 controlled substance as a positional isomer of Mephedrone.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Hyde JF, Browning E, Adams R (August 1928). "Synthetic Homologs of d,l-Ephedrine". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 50 (8): 2287–2292. doi:10.1021/ja01395a032.
- ↑ "关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知" (in Chinese). China Food and Drug Administration. 27 September 2015. Archived from the original on 1 October 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2015.
- ↑ "Lists of: Scheduling Actions Controlled Substances Regulated Chemicals" (PDF). U.S. Department of Justice. February 2023. Retrieved 7 March 2023.