 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H15NO |
| Molar mass | 177.247 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 193.2 °C (379.8 °F) ± 0.2°C (hydrochloride salt) |
| Boiling point | 280.5 °C (536.9 °F) ± 23.0°C at 760 mm Hg |
| Solubility in water | 3-MMC is sparingly soluble in PBS; slightly soluble in ethanol, dimethyl sulfoxide, and dimethyl formamide.[1] mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
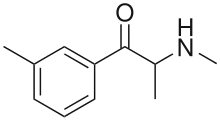
3-Methylmethcathinone, also known as 3-MMC and metaphedrone,[2] is a designer drug from the substituted cathinone family. 3-MMC is closely related in structure to the more commonly known illicit drug mephedrone (4-MMC), and is also illegal in most countries that have banned mephedrone due to 3-MMC being a structural isomer of 4-MMC. However, 3-MMC has still appeared on the recreational drug market as an alternative to mephedrone, and was first identified being sold in Sweden in 2012.[3] Unlike some synthetic cathinones, 3-MMC has been evaluated in at least one large mammal study.[4] 3-MMC is a monoamine transporter substrate that potently inhibits norepinephrine uptake and displays more pronounced dopaminergic vs. serotonergic activity.[5]
History
3-MMC was first encountered in Sweden in 2012,[6] it was created as a designer drug following the control in many countries of the related compound mephedrone. It was sold as a research chemical, usually in powder form. There is no known or reported medical use of 3-MMC and it is being used for recreation. Some fatal intoxications have been reported, most involving multiple drugs of abuse.[1]
Structure
3-Methylmethcathinone (3-MMC) chemical name is 2-(methylamino)-1-(3-methylphenyl)propan-1-one) and is a cathinone derivative, which is a synthetic form of phenylethylamines. 3-MMC has a cathinone which is substituted with a methyl group at the 3 position which makes it a structural isomer of Mephedrone.
3-MMC contains a chiral center at the C-2 carbon. Therefore two enantiomers exist, the R and S enantiomer. It is assumed that the S form is more potent due to its similarity to cathinone. But further research has to be done to confirm this.[7]
Synthesis
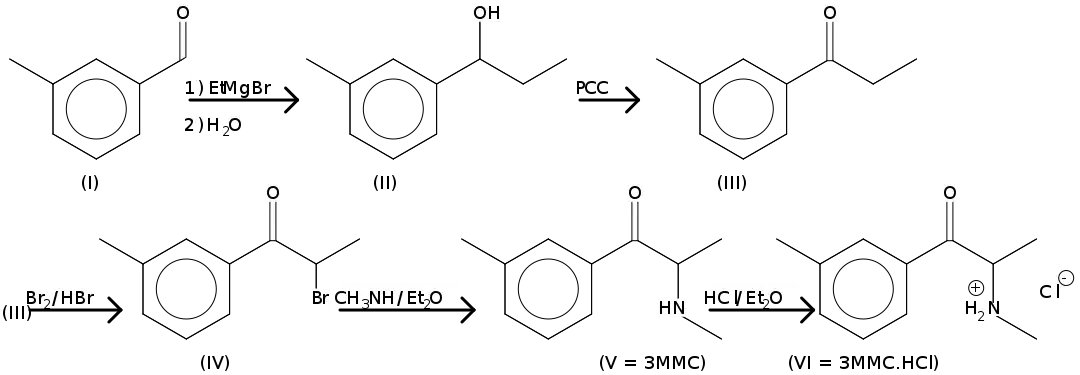
There are several ways to synthesize 3-MMC. One of ways to synthesize 3-MMC, which is adapted from Power et al, is to add ethylmagnesium bromide to 3-methylbenzaldehyde (I). The product (II) is then oxidized by pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) on silica gel to the ketone (III) and brominated with hydrobromic acid to yield the bromo ketone (IV). This bromo ketone is reacted with ethanolic methylamine to produce the 3-MMC free base (V), which can be converted to the hydrochloride salt (VI) by addition of ethereal hydrogen chloride (VI).[8]
Available forms
The most common form of 3-MMC is as a white crystalline powder or as white solid crystals. Sometimes however it is also sold as capsules filled with 3-MMC. There is no information available whether it is a racemate or enantiomerically pure.
Mechanism of action
3-MMC (like 4-MMC) inhibits norepinephrine (NET), serotonin (SERT) and dopamine (DAT) transport. 3-MMC inhibits NET and DAT more potently than SERT which suggests that 3-MMC has stronger amphetamine-like stimulant properties compared to mephedrone.[5]
3-MMC strongly binds to serotonin 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors. In addition, 3-MMC binds weakly to the α1A and α2A adrenergic receptors.[9]
Non-human studies
Metaphadrone oral bioavailability was 7% in rodent studies, with peak blood concentrations (Tmax) attained within 5 to 10 minutes, and a plasma half-life of 0.8 hours. 3-MMC levels dropped below detectable levels after 24 hours of oral ingestion. Decreased feeding behaviour resulted in weight loss in some.
Metabolism
The metabolic pathway of 3-MMC is not well described. Known metabolites include 3-methylephedrine and 3-methylnorephedrine. A possible metabolic pathway is β-keto-reduction followed by N-demethylation.[10]
Toxicity
Metaphedrone dose-response in humans is not well described in the literature, likely due to limited academic interest to date. Fatalities have been reported over a wide range of blood concentrations, from 249 and 1600 ng/mL.[11] Toxicokinetics are thought to be similar to those for mephedrone, however.
Effects
The desired effects of 3-MMC are stimulation, spontaneous bodily sensations, euphoria, enhancement of empathy, affection and sociability, happiness, awareness which are similar effects of other stimulants.[12] Adverse effects can range from stuttering, fatigue, verbosity, reduced level of consciousness, depression, aggression, delirium and confusion, double vision, difficulty in concentration, headaches, dehydration, hallucinations, fear to more serious effects such as hyponatremia, diaphoresis, seizures, hyperthermia and rhabdomyolysis.[12][6]
Abuse
3-MMC is taken via inhalation, injection, insufflation or oral administration. Single session repeat dosing is typical, sometimes via different routes. Common self-reported doses range from 50 to 150 mg, up to single 500 mg doses.
Users may dose repeatedly in order to extend effect duration, leading to 0.5 g to 2 g "sessions." Single-dose effects last from 4–6 hours, typically peaking around 2-hours post-dose. In a questionnaire-based study of self-reported 3-MMC users in Slovenia, it was found that 88.8% of users insufflated the drug while 42.6% took it orally. The study did not find any instances of users injecting 3-MMC. Moreover, 26% of the users reported taking more than 1.5 g of 3-MMC in a single sitting and over 50% reported having consuming more than 0.5 g in a single sitting.[13]
Legal status
In the United States, 3-MMC is illegal as a positional isomer of the schedule 1 controlled substance Mephedrone (4-MMC).[14] It was explicitly designated as a controlled substance itself on 13 December 2023.[15]
3-MMC is currently being developed as a medicine by a publicly traded company MindMed Inc NASDAQ:MNMD based on a patent titled "Use of 3-methylmethcathinone"[16]
Since October 2015, 3-MMC is a controlled substance in China.[17]
3-MMC is banned in the Czech Republic.[18]
3-MMC was not banned by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) after a critical review.[19]
Effective 28 October 2021, 3-MMC has been scheduled under the Dutch Opium Law and is therefore illegal in the Netherlands.[20]
References
- 1 2 "3-Methylmethcathinone (3-MMC) Critical Review Report" (PDF). World Health Organization. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 November 2021.
- ↑ Preedy V (26 April 2016). Neuropathology of Drug Addictions and Substance Misuse Volume 2: Stimulants, Club and Dissociative Drugs, Hallucinogens, Steroids, Inhalants and International Aspects (2 ed.). London: King's College. ISBN 978-0-12-800212-4.
- ↑ "EMCDDA 2012 Annual report on the state of the drugs problem in Europe" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 April 2014. Retrieved 17 April 2014.
- ↑ Shimshoni JA, Britzi M, Sobol E, Willenz U, Nutt D, Edery N (June 2015). "3-Methyl-methcathinone: Pharmacokinetic profile evaluation in pigs in relation to pharmacodynamics". Journal of Psychopharmacology. 29 (6): 734–43. doi:10.1177/0269881115576687. PMID 25804420. S2CID 26012927.
- 1 2 Luethi D, Kolaczynska KE, Docci L, Krähenbühl S, Hoener MC, Liechti ME (May 2018). "Pharmacological profile of mephedrone analogs and related new psychoactive substances" (PDF). Neuropharmacology. 134 (Pt A): 4–12. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.07.026. PMID 28755886. S2CID 28786127.
- 1 2 European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA), Lisbon, Portugal (European Database on New Drugs)
- ↑ Ferreira B, Dias da Silva D, Carvalho F, de Lourdes Bastos M, Carmo H (February 2019). "The novel psychoactive substance 3-methylmethcathinone (3-MMC or metaphedrone): A review". Forensic Science International. 295: 54–63. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2018.11.024. PMID 30572220. S2CID 58638238.
- ↑ Power JD, McGlynn P, Clarke K, McDermott SD, Kavanagh P, O'Brien J (October 2011). "The analysis of substituted cathinones. Part 1: chemical analysis of 2-, 3- and 4-methylmethcathinone". Forensic Science International. 212 (1–3): 6–12. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2011.04.020. PMID 21601387.
- ↑ Schmidt KT, Weinshenker D (April 2014). "Adrenaline rush: the role of adrenergic receptors in stimulant-induced behaviors". Molecular Pharmacology. 85 (4): 640–50. doi:10.1124/mol.113.090118. PMC 3965894. PMID 24499709.
- ↑ Frison G, Frasson S, Zancanaro F, Tedeschi G, Zamengo L (August 2016). "Detection of 3-methylmethcathinone and its metabolites 3-methylephedrine and 3-methylnorephedrine in pubic hair samples by liquid chromatography-high resolution/high accuracy Orbitrap mass spectrometry". Forensic Science International. 265: 131–7. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2016.01.039. PMID 26901638.
- ↑ Ameline A, Dumestre-Toulet V, Raul JS, Kintz P (March 2019). "Determination of a threshold fatal 3-MMC concentration in human: mission impossible". Psychopharmacology. 236 (3): 865–867. doi:10.1007/s00213-018-4941-5. PMID 29876621. S2CID 46978121.
- 1 2 "Experiences". Erowid. Retrieved 1 March 2021.
- ↑ Sande M (January 2016). "Characteristics of the use of 3-MMC and other new psychoactive drugs in Slovenia, and the perceived problems experienced by users". The International Journal on Drug Policy. 27: 65–73. doi:10.1016/j.drugpo.2015.03.005. PMID 25908121.
- ↑ "Lists of: Scheduling Actions Controlled Substances Regulated Chemicals" (PDF). U.S. Department of Justice. February 2023. Retrieved 5 March 2023.
- ↑ "eCFR :: 21 CFD 1308.11 (Dec 12, 2023) -- Schedule I." Electronic Code of Federal Regulations. Retrieved 21 December 2023.
- ↑ WO 2019026019, Golan E, Haden M, Van Wettum R, "Use of 3-methylmethcathinone", published 7 February 2019, assigned to Therapeutic Adjuncts Inc. and Recraceutical Corp. B.V.
- ↑ "关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知" (in Chinese). China Food and Drug Administration. 27 September 2015. Archived from the original on 1 October 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2015.
- ↑ "Látky, o které byl doplněn seznam č. 4 psychotropních látek (příloha č. 4 k nařízení vlády č. 463/2013 Sb.)" (PDF) (in Czech). Ministerstvo zdravotnictví. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 March 2016. Retrieved 6 February 2016.
- ↑ "Extract from the Report of the 38 th Expert Committee on Drug Dependence, convened from 14 to 18 November 2016, at WHO headquarters in Geneva" (PDF). Commission on Narcotic Drugs. Retrieved 7 December 2016.
- ↑ "Designerdrug 3-MMC vanaf vandaag verboden" (in Dutch). Dutch government. 28 October 2021.