| This article is written in American English, which has its own spelling conventions (color, defense, traveled) and some terms that are used in it may be different or absent from other varieties of English. According to the relevant style guide, this should not be changed without broad consensus. |
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Brevital Sodium |
| Other names | Methohexitone |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous, rectal |
| Drug class | Barbiturate |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | I.V. ~100% Rectal ~17% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 5.6 ± 2.7 minutes |
| Excretion | excreted in feces |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.272 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H18N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 262.309 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Methohexital or methohexitone (marketed under the brand names Brevital and Brietal) is a drug which is a barbiturate derivative. It is classified as short-acting, and has a rapid onset of action.[2] It is similar in its effects to sodium thiopental, a drug with which it competed in the market for anesthetics.
Pharmacology
Methohexital binds to a distinct site which is associated with Cl− ionophores at GABAA receptors.[3] This increases the length of time which the Cl− ionopores are open, thus causing an inhibitory effect.
Metabolism of methohexital is primarily hepatic via demethylation and oxidation.[1] Side-chain oxidation is the primary means of metabolism involved in the termination of the drug's biological activity.
Indications
Methohexital is primarily used to induce anesthesia, and is generally provided as a sodium salt (i.e. methohexital sodium). It is only used in hospital or similar settings, under strict supervision.[1] It has been commonly used to induce deep sedation or general anesthesia for surgery and dental procedures. Unlike many other barbiturates, methohexital actually lowers the seizure threshold, a property that makes it particularly useful when anesthesia is provided for an electroconvulsive therapy (ECT).[4] Its rapid recovery rate with consciousness being gained within three to seven minutes after induction and full recovery within 30 minutes is a major advantage over other ECT barbiturates.[4]
Synthesis
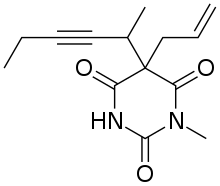
Methohexital can be synthesized in the classic manner of making barbituric acid derivatives, in particular by the reaction of malonic ester derivatives with derivatives of urea.[5] The resulting allyl-(1-methyl-2-pentynyl) malonic ester is synthesized by subsequent alkylation of the malonic ester itself, beginning with 2-bromo-3-hexyne, which gives (1-methyl-2-pentynyl)malonic ester, and then by allylbromide. In the final step, reaction of the disubstituted malonic ester with N-methylurea gives methohexital.
 Methohexital synthesis
Methohexital synthesis
References
- 1 2 3 "Brevital Sodium". DailyMed. July 24, 2019. Retrieved November 20, 2019.
- ↑ "Methohexital". MeSH.
- ↑ Katzung BG. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (10th ed.). pp. 406–407.
- 1 2 Schulgasser H, Borowitz AH (August 1963). "Methohexital anaesthesia in electroconvulsive therapy". South African Medical Journal. 37: 870–1. PMID 14045806.
- ↑ US 2872448, Doran WJ, "1,5,5-Trisubstituted barbituric acids", issued February 3, 1959, assigned to Eli Lily and Company (U.S. Patent 2,872,448)
External links
- "Methohexital". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Methohexital sodium". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.