 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
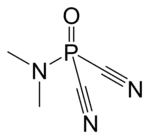
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N-Dimethylphosphoramidic dicyanide | |
| Other names
(Dimethylamido)phosphoryl dicyanide N,N-Dimethylphosphoramidodicyanidate N-Dicyanophosphoryl-N-methylmethanamine | |
| Identifiers | |
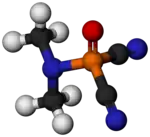
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6N3OP | |
| Molar mass | 143.086 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
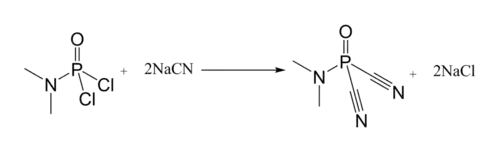
Dimethylamidophosphoric dicyanide is an important chemical for the final process of synthesizing Tabun, a nerve agent used as a chemical weapon.[1]
Preparation
Dimethylamidophosphoric dicyanide could be prepared by reacting Dimethylamidophosphoric dichloride with sodium cyanide.
Safety
This chemical is very flammable, highly toxic, and reactive. If ingested or absorbed through skin, it will cause mild nerve agent symptoms directly as well as blood agent symptoms due to release of HCN. If mixed with water, it gives off poisonous hydrogen cyanide fumes and dimethylamidophosphoric acid.
See also
References
- ↑ PubChem. "Dimethylamidophosphoric dicyanide". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2022-11-24.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.