| Part of a series on the |
| Culture of Indonesia |
|---|
 |
| People |
| Languages |
| Mythology and Folklore |
| Cuisine |
| Literature |
| Music and Performing arts |
| Sport |
There are 1,340[1][2] recognised ethnic groups in Indonesia. The vast majority of those belong to the Austronesian peoples, with a sizeable minority being Melanesians.[3][4][5][6] Indonesia has the world's largest number of Austronesians and Melanesians.
Based on ethnic classification, the largest ethnic group in Indonesia is the Javanese who make up about 40% of the total population. The Javanese are concentrated on the island of Java, particularly in the central and eastern parts. It is also the largest ethnic group in Southeast Asia. The Sundanese are the next largest group; their homeland is located in the western part of the island of Java and the southern edge of Sumatra. The Sunda Strait is named after them.[7] The Malays, Batak, Madurese, Betawi, Minangkabau, and Bugis are the next largest groups in the country.[8]
Many ethnic groups, particularly in Kalimantan and Papua, have only hundreds of members. Most of the local languages belong to the Austronesian language family, although a significant number of people, particularly in eastern Indonesia, speak unrelated Papuan languages. Indonesians of Chinese, Arab and Indian descent each make up less than 3% of the total Indonesian population.[8]
The classification of ethnic groups in Indonesia is not rigid and in some cases unclear due to migrations, cultural and linguistic influences; for example, some may consider the Bantenese to be members of the Sundanese people; however, others argue that they are different ethnic groups altogether since they have their own distinct dialects. This is also the case with the Baduy people, who share many cultural similarities with the Sundanese people. An example of hybrid ethnicity is the Betawi people, descended not only from marriages between different peoples native to Indonesia, but also intermarriages with Arab, Chinese and Indian migrants since the era of colonial Batavia (modern-day Jakarta).
Statistics
2010
Number and percentage of population of ethnic groups with more than a million members according to the 2010 census.[9][lower-alpha 1]
2000
The proportions of Indonesian ethnic groups according to the (2000 census) are as follows.[10] Some ethnic groups which are now recognized as being distinct were subsumed under larger umbrella groups up until 2001. Since the 2010 census, they are counted separately.
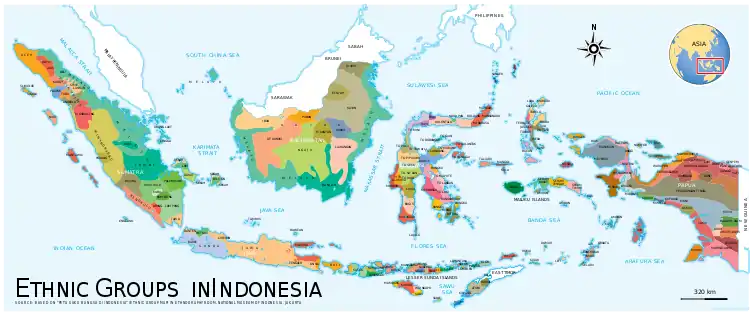
Indigenous ethnic groups


Most ethnic groups are indigenous to certain regions of Indonesia. Due to migration within Indonesia (as part of government transmigration programs or otherwise), significant proportions of those ethnic groups reside outside of their traditional regions.
- Java: Javanese (Tenggerese, Osing, Banyumasan, etc.), Sundanese (Bantenese, Badui, Ciptagelar), Cirebonese, Betawi, Madurese
- Madura: Madurese
- Sumatra: Acehnese, Gayonese, Alas, Batak, Malay, Minangkabau, Rejang, Lampungese, Nias, Mentaweian, Engganese, Kubu, Sekak, and others
- Kalimantan: Dayak, Banjarese, Malays, Kutai, and others
- Sulawesi: Makassarese, Buginese, Mandarese, Minahasan, Torajan, Gorontaloan, Bajau, and others
- Lesser Sunda Islands: Balinese, Sasak, Sumbawan, Bimanese, Manggarai, Lamaholot, Dawan, Tetunian, Helong, Roti, Savu, Sumban, Alorese, and others
- Moluccas: Alfur, Ambonese, Buru, Nuaulu, Manipa, Manusela, Wemale, Tanimbarese, and others
- Papua: Asmat, Amungme, Bauzi, Dani, Sawi, Yaur, and others (see List of ethnic groups of West Papua)
Non-indigenous ethnicities
Throughout Indonesian history, various ethnic groups of foreign origin spread throughout Indonesia in several migration waves, and usually established themselves in urban centres, seldom settling rural parts of the country.
- Arabs: Arabic settled the Indonesian archipelago, Arabs have lived in Indonesia for a very long time and helped spread Islam in Indonesia; They are mostly concentrated around Pasar Kliwon in Surakarta, also at Jakarta, Surabaya, Malang, Probolinggo, and Pekalongan.
- Chinese: The most significant ethnic minority of foreign origin in Indonesia, officially amounting to around 2.8 million, with other sources estimating them at anywhere between 2 and 4 million. Chinese people began migrating to Indonesia in the 16th century, with significant waves in the 19th and 20th centuries. They are mostly concentrated in locations called pecinan (chinatowns) in urban Java with significant numbers in Jakarta, Surabaya, Tangerang, North Sumatra, Riau, Riau Islands, Bangka-Belitung Islands, and West Kalimantan. Currently, they have lived together peacefully with the local ethnicities such as the Betawi, Malay, Javanese, and Sundanese; and also, few cities in Indonesia have significant Chinese populations that preserve their heritage links to China. They are spread throughout Indonesian archipelagoes, and significant numbers can be found in Palembang, Jakarta, Surabaya and other coastal cities.
- Indians: Indians (mostly Tamils) also have settled the Indonesian archipelago; They are mostly concentrated in urban centres, with significant numbers around Pasar Baru in Jakarta, and the most well known at Kampung Madras in Medan. Almost 95% of all Indian Indonesians are living in the province of North Sumatra.
- Indos: Indos or Eurasians are people of mixed native Indonesian and Dutch/European ancestry. They emerged in the Dutch East Indies colonial era. Today, less than one million Indonesians with varying degrees of mixed ancestry can trace their ancestors to Europeans. Nowadays, Indos live mostly in Jakarta, many of them having dual citizenship, Dutch and Indonesian. As of 2011, an estimated 124,000 Indos live outside the Netherlands (including Indonesia).[11]
- Japanese: Japanese people who initially migrated to Indonesia after the defeat of the Japanese empire in World War II. In the years following, the percentage of Japanese people decreased as they had migrated back to Japan, with only small numbers of ex-Japanese soldiers remaining in Indonesia and becoming Indonesian citizens. The recent increase of Japanese residents in Indonesia has been driven by the increase of Japanese business and investment in the country since the 1990s, with majority of those residents being expatriates who retain their Japanese citizenship. They live mostly in Jakarta and Bali.
- Mardijkers: Their name means "freeman" and derives from the Dutch pronunciation of the Malay word "merdeka", which means "free". The ancestors of the Mardijkers were enslaved by the Portuguese in India, Africa and the Malay Peninsula. They were brought to Indonesia by the Dutch East India Company and were freed right after being settled here. Over long periods of time, they have gradually returned to their respective home countries. However, they still exists in small numbers in the capital city today and retains its own distinct culture characteristic of the Mardijker people.
Migrants
According to the United Nations, there were 355,505 international migrants in Indonesia in 2020. Their most common countries of origin were as follows:
| International migrants in Indonesia in 2020 | |
|---|---|
76,028 | |
33,580 | |
32,911 | |
23,681 | |
19,879 | |
12,697 | |
12,590 | |
11,400 | |
8,645 | |
7,306 | |
4,230 | |
| Source: "International Migrant Stock 2020: Destination and origin". United Nations. 2020. Retrieved 6 June 2023. | |
See also
References
Notes
- ↑ Ethnic classification follows the New Classification presented in Ananta et al. 2015, based on raw data from the 2010 census.
Citations
- ↑ Na'im, Akhsan; Syaputra, Hendry (2011). "Nationality, Ethnicity, Religion, and Languages of Indonesians" (PDF) (in Indonesian). Statistics Indonesia. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 23 September 2015.
- ↑ "Mengulik Data Suku di Indonesia" (in Indonesian). Statistics Indonesia. 18 November 2015. Retrieved 1 January 2021.
- ↑ Taylor 2003, pp. 5–7.
- ↑ Witton 2003, pp. 139, 181, 251, 435.
- ↑ Dawson, B.; Gillow, J. (1994). The Traditional Architecture of Indonesia. London: Thames and Hudson Ltd. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-500-34132-2.
- ↑ Truman Simanjuntak; Herawati Sudoyo; Multamia R.M.T. Lauder; Allan Lauder; Ninuk Kleden Probonegoro; Rovicky Dwi Putrohari; Desy Pola Usmany; Yudha P.N. Yapsenang; Edward L. Poelinggomang; Gregorius Neonbasu (2015). Diaspora Melanesia di Nusantara (in Indonesian). Direktorat Sejarah, Direktorat Jenderal Kebudayaan, Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan. ISBN 978-602-1289-19-8. Retrieved 24 August 2022.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ↑ Ananta, Aris (29 April 2016). Demography of Indonesia's Ethnicity. Flipside Digital Content Company Inc. ISBN 978-981-4695-94-7.
- 1 2 Suryadinata, Leo; Arifin, Evi Nurvidya; Ananta, Aris (2003). Indonesia's Population: Ethnicity and Religion in a Changing Political Landscape. Institute of Southeast Asian Studies. ISBN 9789812302120.
- ↑ Ananta et al. 2015, pp. 119–122.
- ↑ Leo Suryadinata, Evi Nurvidya Arifin, Aris Ananta; Indonesia's Population: Ethnicity and Religion in a Changing Political Landscape, 2003
- ↑ Beets, Gijs; van Imhoff, Evert (2004). "A Demographic History of The Indo-Dutch Population, 1930–2001" (PDF). Journal of Population Research. 21 (1): 47–72. doi:10.1007/BF03032210. S2CID 53645470. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 May 2019.
Bibliography
- Ananta, Aris; Arifin, Evi Nurvidya; Hasbullah, M Sairi; Handayani, Nur Budi; Pramono, Agus (2015). Demography of Indonesia's Ethnicity. Institute of Southeast Asian Studies. ISBN 978-981-4519-87-8.
- Taylor, Jean Gelman (2003). Indonesia. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-09709-2.
- Witton, Patrick (2003). Indonesia. Melbourne: Lonely Planet. ISBN 978-1-74059-154-6.