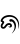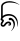| Ja | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Example glyphs | |
| Bengali-Assamese | |
| Tibetan | |
| Tamil | ஜ |
| Thai | ช |
| Malayalam | ജ |
| Sinhala | ජ |
| Ashoka Brahmi | |
| Devanagari | |
| Cognates | |
| Hebrew | ז |
| Greek | Ζ |
| Latin | Z, Ʒ, ẞ |
| Cyrillic | З |
| Properties | |
| Phonemic representation | /d͡ʒ/ /t͜ɕʰ/B /s/C /t͜ɕ/D /t͜s/E /z/F |
| IAST transliteration | ja Ja |
| ISCII code point | BA (186) |
^B in Thai ^C in Lao ^D in Northern Thai, Tai Khün ^E in Tai Lü ^F in Burmese | |
| Indic letters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consonants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vowels | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other marks | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Punctuation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ja is the eighth consonant of Indic abugidas. In modern Indic scripts, ja is derived from the early "Ashoka" Brahmi letter ![]() after having gone through the Gupta letter
after having gone through the Gupta letter ![]() .
.
Āryabhaṭa numeration
Aryabhata used Devanagari letters for numbers, very similar to the Greek numerals, even after the invention of Indian numerals. The values of the different forms of ज are:[1]
- ज [d͡ʒə] = 8 (८)
- जि [d͡ʒɪ] = 800 (८००)
- जु [d͡ʒʊ] = 80,000 (८० ०००)
- जृ [d͡ʒri] = 8,000,000 (८० ०० ०००)
- जॢ [d͡ʒlə] = 8×108 (८०८)
- जे [d͡ʒe] = 8×1010 (८०१०)
- जै [d͡ʒɛː] = 8×1012 (८०१२)
- जो [d͡ʒoː] = 8×1014 (८०१४)
- जौ [d͡ʒɔː] = 8×1016 (८०१६)
Historic Ja
There are three different general early historic scripts - Brahmi and its variants, Kharoṣṭhī, and Tocharian, the so-called slanting Brahmi. Ja as found in standard Brahmi, ![]() was a simple geometric shape, with variations toward more flowing forms by the Gupta
was a simple geometric shape, with variations toward more flowing forms by the Gupta ![]() . The Tocharian Ja
. The Tocharian Ja ![]() did not have an alternate Fremdzeichen form. The third form of ja, in Kharoshthi (
did not have an alternate Fremdzeichen form. The third form of ja, in Kharoshthi (![]() ) was probably derived from Aramaic separately from the Brahmi letter.
) was probably derived from Aramaic separately from the Brahmi letter.
Brahmi Ja
The Brahmi letter ![]() , Ja, is probably derived from the Aramaic Zayin
, Ja, is probably derived from the Aramaic Zayin ![]() , and is thus related to the modern Latin Z and Greek Zeta. Several identifiable styles of writing the Brahmi Ja can be found, most associated with a specific set of inscriptions from an artifact or diverse records from an historic period.[2] As the earliest and most geometric style of Brahmi, the letters found on the Edicts of Ashoka and other records from around that time are normally the reference form for Brahmi letters, with vowel marks not attested until later forms of Brahmi back-formed to match the geometric writing style.
, and is thus related to the modern Latin Z and Greek Zeta. Several identifiable styles of writing the Brahmi Ja can be found, most associated with a specific set of inscriptions from an artifact or diverse records from an historic period.[2] As the earliest and most geometric style of Brahmi, the letters found on the Edicts of Ashoka and other records from around that time are normally the reference form for Brahmi letters, with vowel marks not attested until later forms of Brahmi back-formed to match the geometric writing style.
| Ashoka (3rd-1st c. BCE) | Girnar (~150 BCE) | Kushana (~150-250 CE) | Gujarat (~250 CE) | Gupta (~350 CE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Tocharian Ja
The Tocharian letter ![]() is derived from the Brahmi
is derived from the Brahmi ![]() , but does not have an alternate Fremdzeichen form.
, but does not have an alternate Fremdzeichen form.
| Ja | Jā | Ji | Jī | Ju | Jū | Jr | Jr̄ | Je | Jai | Jo | Jau | Jä |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Kharoṣṭhī Ja
The Kharoṣṭhī letter ![]() is generally accepted as being derived from the Aramaic Zayin
is generally accepted as being derived from the Aramaic Zayin ![]() , and is thus related to Z and Zeta, in addition to the Brahmi Ja.
, and is thus related to Z and Zeta, in addition to the Brahmi Ja.
Devanagari script
| Devanāgarī |
|---|
 |
Ja (ज) is the eighth consonant of the Devanagari abugida. It ultimately arose from the Brahmi letter ![]() , after having gone through the Gupta letter
, after having gone through the Gupta letter ![]() . Letters that derive from it are the Gujarati letter જ and Modi letter 𑘕.
. Letters that derive from it are the Gujarati letter જ and Modi letter 𑘕.
Devanagari Jja
Jja (ॼ) is the character ज with an underbar to represent the voiced palatal implosive [ʄ] that occurs in Sindhi. This underbar is distinct from the Devanagari stress sign anudātta. The underbar is fused to the stem of the letter while the anudātta is a stress accent applied to the entire syllable. This underbar used for Sindhi implosives does not exist as a separate character in Unicode. When the ु or ू vowel sign is applied to jja (ॼ), the ु and ू vowel signs are drawn beneath jja. When the उ ( ु) vowel sign or ऊ ( ू) vowel sign is applied to ja with an anudātta (ज॒), the उ ( ु) vowel sign or ऊ ( ू) vowel sign is first placed under ja (ज) and then the anudātta is placed underneath the उ ( ु) vowel sign or ऊ ( ू) vowel sign.[3]
| Character Name | उ ( ु) vowel sign | ऊ ( ू) vowel sign |
|---|---|---|
| ॼ (Implosive ja) | ॼु | ॼू |
| ज॒ (Ja with anudātta) | जु॒ | जू॒ |
An example of a Sindhi word that uses jja (ॼ) is ॼाण (ڄاڻَ), which is of the feminine grammatical gender and means information or knowledge.[4]
Devanagari Za
Za (ज़) is the character ज with a single dot underneath. It is used in Devanagari transcriptions of Urdu, English, and other languages to denote the voiced alveolar sibilant [z]. Za (ज़) should not be confused with ža (झ़), which is the character jha (झ) combined with a nuqta, and is used to transcribe the voiced post-alveolar fricative [ʒ] from Urdu (ژ) and English. Za (ज़) should also not be confused zha (ॹ), which is used in Devanagari transcriptions of the Avestan letter zhe (𐬲) to denote the voiced post-alveolar fricative [ʒ].
Devanagari Zha
Zha (ॹ) is the character ज with three dots underneath. It is used in Devanagari transcriptions of the Avestan letter zhe (𐬲) to denote the voiced palatal fricative [ʝ]. An example of its usage is in Kavasji Edulji Kanga's Avesta, yazna 41.3 to write ईॹीम्.[5] Zha (ॹ) should not be confused with za (ज़), which is used to denote the voiced alveolar sibilant [z] from Urdu, English, and other languages. Zha (ॹ) should also not be confused with ža (झ़), which is the character jha (झ) combined with a nuqta, and is used to transcribe the voiced post-alveolar fricative [ʒ] from Urdu (ژ) and English.
Devanagari-using Languages
In many languages, ज is pronounced as [d͡ʒə] or [d͡ʒ] when appropriate. In Marathi, ज is sometimes pronounced as [d͡zə] or [d͡z] in addition to [d͡ʒə] or [d͡ʒ]. Like all Indic scripts, Devanagari uses vowel marks attached to the base consonant to override the inherent /ə/ vowel:
| Ja | Jā | Ji | Jī | Ju | Jū | Jr | Jr̄ | Jl | Jl̄ | Je | Jai | Jo | Jau | J |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ज | जा | जि | जी | जु | जू | जृ | जॄ | जॢ | जॣ | जे | जै | जो | जौ | ज् |
Conjuncts with ज

Devanagari exhibits conjunct ligatures, as is common in Indic scripts. In modern Devanagari texts, most conjuncts are formed by reducing the letter shape to fit tightly to the following letter, usually by dropping a character's vertical stem, sometimes referred to as a "half form". Some conjunct clusters are always represented by a true ligature, instead of a shape that can be broken into constituent independent letters. Vertically stacked conjuncts are ubiquitous in older texts, while only a few are still used routinely in modern Devanagari texts. The use of ligatures and vertical conjuncts may vary across languages using the Devanagari script, with Marathi in particular preferring the use of half forms where texts in other languages would show ligatures and vertical stacks.[6]
Ligature conjuncts of ज

True ligatures are quite rare in Indic scripts. The most common ligated conjuncts in Devanagari are in the form of a slight mutation to fit in context or as a consistent variant form appended to the adjacent characters. Those variants include Na and the Repha and Rakar forms of Ra. Nepali and Marathi texts use the "eyelash" Ra half form ![]() for an initial "R" instead of repha. The conjunct jja also has a unique half form that differs from the regular conjunct.
for an initial "R" instead of repha. The conjunct jja also has a unique half form that differs from the regular conjunct.
- Repha र् (r) + ज (ja) gives the ligature र्ज (rja): note

- Eyelash र् (r) + ज (ja) gives the ligature rja:

- ज् (j) + rakar र (ra) gives the ligature ज्र (jra):

- ज् (j) + न (na) gives the ligature ज्न (jna):

- ज् (j) + ज (ja) gives the ligature ज्ज (jja):

- ज् (j) + ज् (j) + व (va) gives the ligature ज्ज्व (jjva):

- ज् (j) + ज् (j) + य (ya) gives the ligature ज्ज्य (jjya):

Devanagari Jña

One of the most common true ligatures in Devanagari is the conjunct jña ज्ञ. This ligature is a required form for most Devanagari languages, and the conjunct even has its own half form that freely joins other letters in horizontal conjuncts.
- ज् (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature ज्ञ (jña):

- Repha र् (r) + ज् (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature र्ज्ञ (rjña):

- Eyelash र् (r) + ज् (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature rjña:

- भ् (bh) + ज् (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature भ्ज्ञ (bhjña):

- ब् (b) + ज् (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature ब्ज्ञ (bjña):

- छ् (ch) + ज् (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature छ्ज्ञ (chjña):

- च্ (c) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature cjña:

- ढ্ (ḍʱ) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature ḍʱjña:

- ड্ (ḍ) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature ḍjña:

- द্ (d) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature djña:

- घ্ (ɡʱ) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature ɡʱjña:

- ग্ (g) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature gjña:

- ह্ (h) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature hjña:

- ज্ (j) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature jjña:

- झ্ (jh) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature jhjña:

- ख্ (kh) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature khjña:

- क্ (k) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature kjña:

- ल্ (l) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature ljña:

- म্ (m) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature mjña:

- न্ (n) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature njña:

- ञ্ (ñ) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature ñjña:

- ङ্ (ŋ) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature ŋjña:

- फ্ (ph) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature phjña:

- प্ (p) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature pjña:

- श্ (ʃ) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature ʃjña:

- स্ (s) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature sjña:

- ष্ (ṣ) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature ṣjña:

- थ্ (th) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature thjña:

- त্ (t) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature tjña:

- ठ্ (ṭh) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature ṭhjña:

- ट্ (ṭ) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature ṭjña:

- व্ (v) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature vjña:

- य্ (y) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature yjña:

Stacked conjuncts of ज
Vertically stacked ligatures are the most common conjunct forms found in Devanagari text. Although the constituent characters may need to be stretched and moved slightly in order to stack neatly, stacked conjuncts can be broken down into recognizable base letters, or a letter and an otherwise standard ligature.
- भ্ (bh) + ज (ja) gives the ligature bhja:

- ब্ (b) + ज (ja) gives the ligature bja:

- छ্ (ch) + ज (ja) gives the ligature chja:

- च্ (c) + ज (ja) gives the ligature cja:

- ढ্ (ḍʱ) + ज (ja) gives the ligature ḍʱja:

- ड্ (ḍ) + ज (ja) gives the ligature ḍja:

- ध্ (dʱ) + ज (ja) gives the ligature dʱja:

- द্ (d) + ज (ja) gives the ligature dja:

- घ্ (ɡʱ) + ज (ja) gives the ligature ɡʱja:

- ग্ (g) + ज (ja) gives the ligature gja:

- ह্ (h) + ज (ja) gives the ligature hja:

- ज্ (j) + च (ca) gives the ligature jca:

- ज্ (j) + ड (ḍa) gives the ligature jḍa:

- झ্ (jh) + ज (ja) gives the ligature jhja:

- ज্ (j) + ल (la) gives the ligature jla:

- ज্ (j) + ङ (ŋa) gives the ligature jŋa:

- ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature jña:

- ज্ (j) + श (ʃa) gives the ligature jʃa:

- ख্ (kh) + ज (ja) gives the ligature khja:

- क্ (k) + ज (ja) gives the ligature kja:

- ल্ (l) + ज (ja) gives the ligature lja:

- ळ্ (ḷ) + ज (ja) gives the ligature ḷja:

- म্ (m) + ज (ja) gives the ligature mja:

- ङ্ (ŋ) + ज (ja) gives the ligature ŋja:

- न্ (n) + ज (ja) gives the ligature nja:

- ञ্ (ñ) + ज (ja) gives the ligature ñja:

- फ্ (ph) + ज (ja) gives the ligature phja:

- प্ (p) + ज (ja) gives the ligature pja:

- श্ (ʃ) + ज (ja) gives the ligature ʃja:

- स্ (s) + ज (ja) gives the ligature sja:

- ष্ (ṣ) + ज (ja) gives the ligature ṣja:

- त্ (t) + ज (ja) gives the ligature tja:

- ठ্ (ṭh) + ज (ja) gives the ligature ṭhja:

- ट্ (ṭ) + ज (ja) gives the ligature ṭja:

- व্ (v) + ज (ja) gives the ligature vja:

- य্ (y) + ज (ja) gives the ligature yja:

Bengali script
The Bengali script জ is derived from the Siddhaṃ ![]() , and is marked by a similar horizontal head line, but less geometric shape, than its Devanagari counterpart, ज. The inherent vowel of Bengali consonant letters is /ɔ/, so the bare letter জ will sometimes be transliterated as "jo" instead of "ja". Adding okar, the "o" vowel mark, gives a reading of /d͡ʒo/.
Like all Indic consonants, জ can be modified by marks to indicate another (or no) vowel than its inherent "a".
, and is marked by a similar horizontal head line, but less geometric shape, than its Devanagari counterpart, ज. The inherent vowel of Bengali consonant letters is /ɔ/, so the bare letter জ will sometimes be transliterated as "jo" instead of "ja". Adding okar, the "o" vowel mark, gives a reading of /d͡ʒo/.
Like all Indic consonants, জ can be modified by marks to indicate another (or no) vowel than its inherent "a".
| ja | jā | ji | jī | ju | jū | jr | jr̄ | je | jai | jo | jau | j |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| জ | জা | জি | জী | জু | জূ | জৃ | জৄ | জে | জৈ | জো | জৌ | জ্ |
জ in Bengali-using languages
জ is used as a basic consonant character in all of the major Bengali script orthographies, including Bengali and Assamese.
Conjuncts with জ
Bengali জ exhibits conjunct ligatures, as is common in Indic scripts, with a tendency towards stacked ligatures.[7]
- ব্ (b) + জ (ja) gives the ligature bja:

- জ্ (j) + জ (ja) gives the ligature jja:

- জ্ (j) + ঝ (jha) gives the ligature jjha:

- জ্ (j) + জ্ (j) + ব (va) gives the ligature jjva, with the va phala suffix:

- জ্ (j) + ঞ (ña) gives the ligature jña:

- জ্ (j) + র (ra) gives the ligature jra, with the ra phala suffix:

- জ্ (j) + ব (va) gives the ligature jva, with the va phala suffix:

- জ্ (j) + য (ya) gives the ligature jya, with the ya phala suffix:

- ঞ (ñ) + জ (ja) gives the ligature ñja:

- র্ (r) + জ (ja) gives the ligature rja, with the repha prefix:

- র্ (r) + জ্ (j) + য (ya) gives the ligature rjya, with the repha prefix and ya phala suffix:

Gujarati Ja

Ja (જ) is the eighth consonant of the Gujarati abugida. It is possibly derived from a variant of 16th century Devanagari Ja ![]() with the top bar (shiro rekha) removed, and ultimately the Brahmi letter
with the top bar (shiro rekha) removed, and ultimately the Brahmi letter ![]() . When combined with certain vowels, the Gujarati Ja may assume unique forms, such as જા, જી, and જો.
. When combined with certain vowels, the Gujarati Ja may assume unique forms, such as જા, જી, and જો.
Gujarati-using Languages
The Gujarati script is used to write the Gujarati and Kutchi languages. In both languages, જ is pronounced as [jə] or [j] when appropriate. Like all Indic scripts, Gujarati uses vowel marks attached to the base consonant to override the inherent /ə/ vowel:
| Ja | Jā | Ji | Jī | Ju | Jū | Jr | Jl | Jr̄ | Jl̄ | Jĕ | Je | Jai | Jŏ | Jo | Jau | J |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||||
| Gujarati Ja syllables, with vowel marks in red. | ||||||||||||||||
Related letters
Za (જ઼) is the character Ja (જ) with a single dot underneath. It corresponds to the Devanagari character Za (ज़). It is also used in Gujarati transcriptions of Avestan (𐬰),[8][9][10] Urdu (ژ), English, and other languages to denote the voiced alveolar sibilant [z]. Zha (ૹ) is the character Ja (જ) with three dots underneath. It is used in Gujarati transcriptions of the Avestan letter zhe (𐬲) to denote the voiced palatal fricative [ʒ] and is analogous to the Devanagari character zha (ॹ).[8][9] Zha (ૹ) was added to the Unicode Standard as a single character ljust like the Devanagari character zha (ॹ) with Unicode 8.0 on 17 June 2015.[10][11] An example of a word in the Gujarati script the uses zha (ૹ) is ચીૹ્દી.[12]
Conjuncts with જ
Gujarati જ exhibits conjunct ligatures, much like its parent Devanagari Script. While most Gujarati conjuncts can only be formed by reducing the letter shape to create a "half form" that fits tightly to following letter, Ja does not have a half form. A few conjunct clusters can be represented by a true ligature, instead of a shape that can be broken into constituent independent letters, and vertically stacked conjuncts can also be found in Gujarati, although much less commonly than in Devanagari. Lacking a half form, X will normally use an explicit virama when forming conjuncts without a true ligature. True ligatures are quite rare in Indic scripts. The most common ligated conjuncts in Gujarati are in the form of a slight mutation to fit in context or as a consistent variant form appended to the adjacent characters. Those variants include Na and the Repha and Rakar forms of Ra.
- ર્ (r) + જ (ja) gives the ligature RJa:

- જ્ (j) + ર (ra) gives the ligature JRa:

- જ્ (j) + ઞ (ɲa) gives the ligature JÑa:
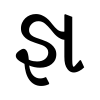
- ર્ (r) + જ (ja) ઞ (ɲa) gives the ligature RJÑa:
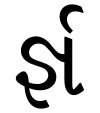
- જ (ja) + ઞ્ (ɲ) + ર (ra) gives the ligature JÑRa:

Gurmukhi script
Jajjaa [d͡ʒəd͡ʒːɑ] (ਜ) is the thirteenth letter of the Gurmukhi alphabet. Its name is [d͡ʒəd͡ʒːɑ] and is pronounced as /d͡ʒ/ when used in words. It is derived from the Laṇḍā letter ja, and ultimately from the Brahmi ja. Gurmukhi jajaa does not have a special pairin or addha (reduced) form for making conjuncts, and in modern Punjabi texts do not take a half form or halant to indicate the bare consonant /d͡ʒ/, although Gurmukhi Sanskrit texts may use an explicit halant.
Jajje vicc bindi
A dot added below Jajja (ਜ਼) denotes that it has to be pronounced as the voiced alveolar fricative /z/.
Telugu Ja


Ja (జ) is a consonant of the Telugu abugida. It ultimately arose from the Brahmi letter ![]() . It is closely related to the Kannada letter ಜ. Since it lacks the v-shaped headstroke common to most Telugu letters, జ remains unaltered by most vowel matras, and its subjoined form is simply a smaller version of the normal letter shape.
Telugu conjuncts are created by reducing trailing letters to a subjoined form that appears below the initial consonant of the conjunct. Many subjoined forms are created by dropping their headline, with many extending the end of the stroke of the main letter body to form an extended tail reaching up to the right of the preceding consonant. This subjoining of trailing letters to create conjuncts is in contrast to the leading half forms of Devanagari and Bengali letters. Ligature conjuncts are not a feature in Telugu, with the only non-standard construction being an alternate subjoined form of Ṣa (borrowed from Kannada) in the KṢa conjunct.
. It is closely related to the Kannada letter ಜ. Since it lacks the v-shaped headstroke common to most Telugu letters, జ remains unaltered by most vowel matras, and its subjoined form is simply a smaller version of the normal letter shape.
Telugu conjuncts are created by reducing trailing letters to a subjoined form that appears below the initial consonant of the conjunct. Many subjoined forms are created by dropping their headline, with many extending the end of the stroke of the main letter body to form an extended tail reaching up to the right of the preceding consonant. This subjoining of trailing letters to create conjuncts is in contrast to the leading half forms of Devanagari and Bengali letters. Ligature conjuncts are not a feature in Telugu, with the only non-standard construction being an alternate subjoined form of Ṣa (borrowed from Kannada) in the KṢa conjunct.
Malayalam Ja

Ja (ജ) is a consonant of the Malayalam abugida. It ultimately arose from the Brahmi letter ![]() , via the Grantha letter
, via the Grantha letter ![]() Ja. Like in other Indic scripts, Malayalam consonants have the inherent vowel "a", and take one of several modifying vowel signs to represent syllables with another vowel or no vowel at all.
Ja. Like in other Indic scripts, Malayalam consonants have the inherent vowel "a", and take one of several modifying vowel signs to represent syllables with another vowel or no vowel at all.
Conjuncts of ജ
As is common in Indic scripts, Malayalam joins letters together to form conjunct consonant clusters. There are several ways in which conjuncts are formed in Malayalam texts: using a post-base form of a trailing consonant placed under the initial consonant of a conjunct, a combined ligature of two or more consonants joined together, a conjoining form that appears as a combining mark on the rest of the conjunct, the use of an explicit candrakkala mark to suppress the inherent "a" vowel, or a special consonant form called a "chillu" letter, representing a bare consonant without the inherent "a" vowel. Texts written with the modern reformed Malayalam orthography, put̪iya lipi, may favor more regular conjunct forms than older texts in paḻaya lipi, due to changes undertaken in the 1970s by the Government of Kerala.
- ജ് (j) + ജ (ja) gives the ligature jja:

- ഞ് (ñ) + ജ (ja) gives the ligature ñja:

- ജ് (j) + ഞ (ña) gives the ligature jña:

Canadian Aboriginal Syllabics Ce
| Canadian Aboriginal Syllabics | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
ᒉ, ᒋ, ᒍ and ᒐ are the base characters "Ce", "Ci", "Co" and "Ca" in the Canadian Aboriginal Syllabics. The bare consonant ᒡ (C) is a small version of the A-series letter ᒐ, although the Western Cree letter ᐨ, derived from Pitman shorthand was the original bare consonant symbol for C. The character ᒉ is derived from a handwritten form of the Devanagari letter ज, without the headline or vertical stem, and the forms for different vowels are derived by mirroring.[13][14] Unlike most writing systems without legacy computer encodings, complex Canadian syllabic letters are represented in Unicode with pre-composed characters, rather than with base characters and diacritical marks.
| Variant | E-series | I-series | O-series | A-series | Other | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C + vowel | ᒉ | ᒋ | ᒍ | ᒐ | |||||||
| Ce | Ci | Co | Ca | ||||||||
| Small | - | ᣗ | ᒢ | ᒡ | ᐨ | ||||||
| - | Ojibway C | Sayisi Th | C | Cree C | |||||||
| C with long vowels | - | ᒌ | ᒎ | ᒏ | ᒑ | ᒊ | |||||
| - | Cī | Cō | Cree Cō | Cā | Cāi | ||||||
| C + W- vowels | ᒒ | ᒓ | ᒔ | ᒕ | ᒘ | ᒙ | ᒜ | ᒝ | |||
| Cwe | Cree Cwe | Cwi | Cree Cwi | Cwo | Cree Cwo | Cwa | Cree Cwa | ||||
| C + W- long vowels | - | ᒖ | ᒗ | ᒚ | ᒛ | ᒞ | ᒠ | ᒟ | - | ||
| - | Cwī | Cree Cwī | Cwō | Cree Cwō | Cwā | Naskapi Cwā | Cree Cwā | - | |||
Odia Ja


Ja (ଜ) is a consonant of the Odia abugida. It ultimately arose from the Brahmi letter ![]() , via the Siddhaṃ letter
, via the Siddhaṃ letter ![]() Ja. Like in other Indic scripts, Odia consonants have the inherent vowel "a", and take one of several modifying vowel signs to represent syllables with another vowel or no vowel at all.
Ja. Like in other Indic scripts, Odia consonants have the inherent vowel "a", and take one of several modifying vowel signs to represent syllables with another vowel or no vowel at all.
| Ja | Jā | Ji | Jī | Ju | Jū | Jr̥ | Jr̥̄ | Jl̥ | Jl̥̄ | Je | Jai | Jo | Jau | J |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ଜ | ଜା | ଜି | ଜୀ | ଜୁ | ଜୂ | ଜୃ | ଜୄ | ଜୢ | ଜୣ | ଜେ | ଜୈ | ଜୋ | ଜୌ | ଜ୍
Conjuncts of ଜAs is common in Indic scripts, Odia joins letters together to form conjunct consonant clusters. The most common conjunct formation is achieved by using a small subjoined form of trailing consonants. Most consonants' subjoined forms are identical to the full form, just reduced in size, although a few drop the curved headline or have a subjoined form not directly related to the full form of the consonant. The second type of conjunct formation is through pure ligatures, where the constituent consonants are written together in a single graphic form. This ligature may be recognizable as being a combination of two characters or it can have a conjunct ligature unrelated to its constituent characters.
|
Kaithi Ja
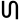

Ja (𑂔) is a consonant of the Kaithi abugida. It ultimately arose from the Brahmi letter ![]() , via the Siddhaṃ letter
, via the Siddhaṃ letter ![]() Ja. Like in other Indic scripts, Kaithi consonants have the inherent vowel "a", and take one of several modifying vowel signs to represent syllables with another vowel or no vowel at all.
Ja. Like in other Indic scripts, Kaithi consonants have the inherent vowel "a", and take one of several modifying vowel signs to represent syllables with another vowel or no vowel at all.
| Ja | Jā | Ji | Jī | Ju | Jū | Je | Jai | Jo | Jau | J |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 𑂔 | 𑂔𑂰 | 𑂔𑂱 | 𑂔𑂲 | 𑂔𑂳 | 𑂔𑂴 | 𑂔𑂵 | 𑂔𑂶 | 𑂔𑂷 | 𑂔𑂸 | 𑂔𑂹 |
Conjuncts of 𑂔
As is common in Indic scripts, Kaithi joins letters together to form conjunct consonant clusters. The most common conjunct formation is achieved by using a half form of preceding consonants, although several consonants use an explicit virama. Most half forms are derived from the full form by removing the vertical stem. As is common in most Indic scripts, conjucts of ra are indicated with a repha or rakar mark attached to the rest of the consonant cluster. In addition, there are a few vertical conjuncts that can be found in Kaithi writing, but true ligatures are not used in the modern Kaithi script.
- 𑂔୍ (j) + 𑂩 (ra) gives the ligature jra:

- 𑂩୍ (r) + 𑂔 (ja) gives the ligature rja:

Khmer Co
| ||||||||
Co (ជ) is a consonant of the Khmer abugida. It ultimately arose from the Brahmi letter ![]() , via the Pallava letter
, via the Pallava letter ![]() Va. Like in other Indic scripts, Khmer consonants have the inherent vowel "a", and take one of several modifying vowel signs to represent syllables with another vowel. Actually, the sounds of the vowels are modified by the consonant; see the article on the Khmer writing system for details.
Va. Like in other Indic scripts, Khmer consonants have the inherent vowel "a", and take one of several modifying vowel signs to represent syllables with another vowel. Actually, the sounds of the vowels are modified by the consonant; see the article on the Khmer writing system for details.
| Ja | Jā | Ji | Jī | Ju | Jū | Jr̥ | Jr̥̄ | Jl̥ | Jl̥̄ | Je | Jai | Jo | Jau | Jẏ | Jȳ | Jua | Joe | Jẏa | Jia | Jae | Jà | J |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ជ | ជា | ជិ | ជី | ជុ | ជូ | ជ្ឫ | ជ្ឬ | ជ្ឭ | ជ្ឮ | ជេ | ជៃ | ជោ | ជៅ | ជឹ | ជឺ | ជួ | ជើ | ជឿ | ជៀ | ជែ | ជៈ | ជ៑ |
Note: The vowels (other than vocalic liquids) are shown using the ALA-LC scheme.[15]
Pali and Sanskrit are written as abugidas with the lack of a vowel between consonants notated as consonants indicated by vertically stacking the consonants without their touching. For phonetically final consonants, the lack of a vowel is marked by virama.
The Khmer language works the same, except that a different method is used for the last consonant of a word. The final consonant in a consonant stack is indicated as having no implicit vowel by applying tôndôkhéad to it. By default, a consonant surmounted by robat is silent and lacks an inherent vowel. The yŭkôlpĭntŭ positively indicates the presence of a final implicit vowel, plus its automatic glottal stop. Otherwise, there is no final vowel, unless the word is of Pali or Sanskrit origin, in which case the spelling is ambiguous. Up until the start of the 20th century, the lack of a final vowel could be indicating by subscripting the consonant, as then done in Lao and in other non-Indic languages using the Tai Tham script.
Thai script
Cho chang (ช) and so so (ซ) are the tenth and eleventh letters of the Thai script. They fall under the low class of Thai consonants. Unlike many Indic scripts, Thai consonants do not form conjunct ligatures, and use the pinthu—an explicit virama with a dot shape—to indicate bare consonants.
Cho chang
In IPA, cho chang is pronounced as [tɕh] at the beginning of a syllable and are pronounced as [t̚] at the end of a syllable. The previous letter of the alphabet, cho ching (ฉ), is also named cho, however, it falls under the high class of Thai consonants. In the acrophony of the Thai script, chang (ช้าง) means 'elephant'. Cho chang corresponds to the Sanskrit character 'ज'.
So so
In IPA, so so is pronounced as [s] at the beginning of a syllable and are pronounced as [t̚] at the end of a syllable. In the acrophony of the Thai script, so (โซ่) means 'chain'. Old Thai had the voiced fricative sound /z/. When the Thai script was developed, cho chang was slightly modified to create distinct letter for /z/. In modern Thai, the voicing of /z/ became lost and thus is now pronounced as [s] at the beginning of a syllable.
Lao Script
So tam (ຊ) and Pali jha (ຌ) are the eighth and ninth consonants of the Pali alphabet in the Lao script. Unlike many Indic scripts, Lao consonants mostly do not form conjunct ligatures, and may use the Pali virama —an explicit virama with a dot shape—to indicate bare consonants.
So tam
In IPA, so tam was originally pronounced as [dʑ] at the beginning of a syllable. The next consonant in the Pali alphabet, jha, was oriɡinally nominally pronounced as [dʑɦ].
Pali jha
When the precursor of the Lao script was beinɡ developed, so tam was modified to create a consonant to represent the sound /z/ in the vernacular, and this was ordered after so tam in the alphabet. This also happened in the Tai Tham script, the script used for Pali texts. As a result of sound chanɡes, all three of so tam, its successor for the vernacular, and its successor in Pali came to be pronounced /s/, thouɡh so tam remained distinct in the reɡional centre, Chianɡ Mai. The two successors came to be confused, and so when the Pali-writinɡ capability of the Lao script was restored in the 1930s, the glyph chosen for Pali Jha was actually that proper to the vernacular successor. Meanwhile, the modified character had become redundant in the vernacular.
Javanese script
Tai Tham Script
Low Ca (ᨩ) is a consonant of the Tai Tham abugida. It ultimately arose from the Brahmi letter ![]() , via the Pallava letter
, via the Pallava letter ![]() Ja. The Tai Tham script was originally used to write Pali (the name 'Tham' is a local form of dharma), and faced the same limitations in writing Tai languages as Khmer had. The Thai solutions were adopted, with consonants being systematically modified by the addition of a tail to supply new consonants, mostly for fricatives. Low Ca was modified, yielding Low Sa. Both consonants are low consonants in the Tai alphabets. The two sounds, /dʑ/ and /z/, subsequently merɡed in Lao as /s/, and Low Sa is absent from the Lao variant of Tai Tham. The other Tai languages keep them separate, as /tɕ/ or /ts/ and /s/.
Ja. The Tai Tham script was originally used to write Pali (the name 'Tham' is a local form of dharma), and faced the same limitations in writing Tai languages as Khmer had. The Thai solutions were adopted, with consonants being systematically modified by the addition of a tail to supply new consonants, mostly for fricatives. Low Ca was modified, yielding Low Sa. Both consonants are low consonants in the Tai alphabets. The two sounds, /dʑ/ and /z/, subsequently merɡed in Lao as /s/, and Low Sa is absent from the Lao variant of Tai Tham. The other Tai languages keep them separate, as /tɕ/ or /ts/ and /s/.
There is considerable variation in the basic shape of this character; the two pieces typical of Northern Thai shapes join in Tai Khün, Tai Lü and Lao designs.
Low Ca
Like in other Indic scripts, Tai Tham consonants have the inherent vowel "a", and take one of several modifying vowel signs to represent syllables with another vowel.
| Syllable type | ja | jā | ji | jī | jư | jư̄ | ju | jū | jē | jǣ | jō |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closed or open | ᨩ | ᨩᩣ | ᨩᩥ | ᨩᩦ | ᨩᩧ | ᨩᩨ | ᨩᩩ | ᨩᩪ | ᨩᩮ | ᨩᩯ | ᨩᩮᩣ |
| jai | jaư | jau | jō̹i | ||||||||
| Open | ᨩᩱ | ᨩᩲ | ᨩᩮᩢᩣ | ᨩᩮᩫᩢᩣ | ᨩᩮᩫᩣ | ᨩᩳ | ᨩᩭ | ||||
| jo | ja | jō | jœ̄ | jō̹ | jo̹ | ||||||
| Open | ᨩᩰᩡ | ᨩᩡ | ᨩᩰ | ᨩᩮᩬᩥ | ᨩᩮᩦ | ᨩᩬᩴ | ᨩᩴ | ᨩᩬᩳ | ᨩᩳ | ᨩᩰᩬᩡ | ᨩᩰᩬ |
| Closed | ᨩᩫ | ᨩᩢ | ᨩᩰᩫ | ᨩᩮᩥ | ᨩᩮᩦ | ᨩᩬ | ᨩᩬᩢ | ||||
| jūa | jīa | jư̄a | |||||||||
| Open | ᨩ᩠ᩅᩫ | ᨩ᩠ᨿᩮ | ᨩᩮᩢ᩠ᨿ | ᨩᩮᩬᩥᩋ | ᨩᩮᩬᩨᩋ | ᨩᩮᩬᩨ | |||||
| Closed | ᨩ᩠ᩅ | ᨩ᩠ᨿ | ᨩᩮᩬᩥ | ᨩᩮᩬᩨ | |||||||
Notes:
- The transliteration scheme is an amalgamation of the ALA-LC schemes of Khmer[15], Pali[16] and Lao[17].
- Many of the matras include subscript wa (
 ), subscript ya (
), subscript ya (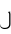 ), subscript a (
), subscript a ( ) or even the letter a (
) or even the letter a (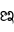 ) itself. Anusvara (
) itself. Anusvara ( ) and visarga (
) and visarga (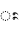 ) are also used.
) are also used. - In the relevant Tai languages, a short vowel in an open syllable includes an underlyinɡ ɡlottal stop.
Additional short vowels not shown above may be synthesised from the corresponding long vowel by appending visarga for open syllables (as shown for jo) or applying mai sat (![]() ) for closed syllables (as shown for jo̹). Unlike the other languages, Lao instead replaces an ī or ư̄ glyph by the corresponding short vowel.
) for closed syllables (as shown for jo̹). Unlike the other languages, Lao instead replaces an ī or ư̄ glyph by the corresponding short vowel.
The lack of a vowel between consonants notated as consonants is indicated by vertically stacking the consonants, generally without their touching. The Brahmi style of writing final consonants small and low developed, as vestigially seen in Khmer and Lao, into using subscripting to indicate that a consonant had no vowel of its own. In theory this leaves it ambiguous as to whether a consonant precedes or follows the vowel, but ambiguous cases are rare. Finally, if there is no room for the consonant below, it may be left as an 'independent' consonant or. in some cases, written superscript. Occasionally the visible virama (ra haam) is used, but this may signify that the consonant so marked is silent. The vowel /a/ will be made explicit if the final consonant is notated by a letter and is included in the same stack as the initial consonant or is written in a stack just consisting of that consonant.
In writing systems that make use of tall aa, as the initial letter of an akshara the letter is followed by round aa, as shown in the table of matras above, rather than tall aa.
Low Ca can serve as the initial consonant of a stack, and several examples can be seen above. It can also occur as the final element of a consonant stack in words of Indic origin, both in the clusters jja and ñja of Pali words and as the final consonant after apocope of the final vowel. The ligature ñja ![]() is not a simple vertical stack - see Ña (Indic)#Tai Tham Ña (forthcoming) for details.
is not a simple vertical stack - see Ña (Indic)#Tai Tham Ña (forthcoming) for details.
Low Sa
Like in other Indic scripts, Tai Tham consonants have the inherent vowel "a", and take one of several modifying vowel signs to represent syllables with another vowel.
| Syllable type | za | zā | zi | zī | zư | zư̄ | zu | zū | zē | zǣ | zō |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closed or open | ᨪ | ᨪᩣ | ᨪᩥ | ᨪᩦ | ᨪᩧ | ᨪᩨ | ᨪᩩ | ᨪᩪ | ᨪᩮ | ᨪᩯ | ᨪᩮᩣ |
| zai | zaư | zau | zō̹i | ||||||||
| Open | ᨪᩱ | ᨪᩲ | ᨪᩮᩢᩣ | ᨪᩮᩫᩣ | ᨪᩳ | ᨪᩭ | |||||
| zo | za | zō | zœ̄ | zō̹ | zo̹ | ||||||
| Open | ᨪᩰᩡ | ᨪᩡ | ᨪᩰ | ᨪᩮᩬᩥ | ᨪᩬᩴ | ᨪᩴ | ᨪᩬᩳ | ᨪᩳ | ᨪᩰᩬᩡ | ᨪᩰᩬ | |
| Closed | ᨪᩫ | ᨪᩢ | ᨪᩰᩫ | ᨪᩮᩥ | ᨪᩬ | ᨪᩬᩢ | |||||
| zūa | zīa | zư̄a | |||||||||
| Open | ᨪ᩠ᩅᩫ | ᨪ᩠ᨿᩮ | ᨪᩮᩬᩥᩋ | ᨪᩮᩬᩨᩋ | ᨪᩮᩬᩨ | ||||||
| Closed | ᨪ᩠ᩅ | ᨪ᩠ᨿ | ᨪᩮᩬᩥ | ᨪᩮᩬᩨ | |||||||
Notes:
- The transliteration scheme is an amalgamation of the ALA-LC schemes of Khmer[15], Pali[18] and Lao[19].
- Many of the matras include subscript wa (
 ), subscript ya (
), subscript ya ( ), subscript a (
), subscript a ( ) or even the letter a (
) or even the letter a ( ) itself. Anusvara (
) itself. Anusvara ( ) and visarga (
) and visarga ( ) are also used.
) are also used. - In the relevant Tai languages, a short vowel in an open syllable includes an underlyinɡ ɡlottal stop.
This form occurs only as the initial consonant of a syllable. This letter combined in aksharas with the dependent vowel Ā uses round aa, as shown in the table of matras above, rather than tall aa.
Comparison of Ja
The various Indic scripts are generally related to each other through adaptation and borrowing, and as such the glyphs for cognate letters, including Ja, are related as well.
| Comparison of Ja in different scripts |
|---|
|
Notes
|
Character encodings of Ja
Most Indic scripts are encoded in the Unicode Standard, and as such the letter Ja in those scripts can be represented in plain text with unique codepoint. Ja from several modern-use scripts can also be found in legacy encodings, such as ISCII.
| Preview | ஜ | జ | ଜ | ಜ | ജ | જ | ਜ | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | DEVANAGARI LETTER JA | BENGALI LETTER JA | TAMIL LETTER JA | TELUGU LETTER JA | ORIYA LETTER JA | KANNADA LETTER JA | MALAYALAM LETTER JA | GUJARATI LETTER JA | GURMUKHI LETTER JA | |||||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 2332 | U+091C | 2460 | U+099C | 2972 | U+0B9C | 3100 | U+0C1C | 2844 | U+0B1C | 3228 | U+0C9C | 3356 | U+0D1C | 2716 | U+0A9C | 2588 | U+0A1C |
| UTF-8 | 224 164 156 | E0 A4 9C | 224 166 156 | E0 A6 9C | 224 174 156 | E0 AE 9C | 224 176 156 | E0 B0 9C | 224 172 156 | E0 AC 9C | 224 178 156 | E0 B2 9C | 224 180 156 | E0 B4 9C | 224 170 156 | E0 AA 9C | 224 168 156 | E0 A8 9C |
| Numeric character reference | ज | ज | জ | জ | ஜ | ஜ | జ | జ | ଜ | ଜ | ಜ | ಜ | ജ | ജ | જ | જ | ਜ | ਜ |
| ISCII | 186 | BA | 186 | BA | 186 | BA | 186 | BA | 186 | BA | 186 | BA | 186 | BA | 186 | BA | 186 | BA |
| Preview | Ashoka Kushana Gupta | 𐨗 | 𑌜 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | BRAHMI LETTER JA | KHAROSHTHI LETTER JA | SIDDHAM LETTER JA | GRANTHA LETTER JA | ||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 69658 | U+1101A | 68119 | U+10A17 | 71061 | U+11595 | 70428 | U+1131C |
| UTF-8 | 240 145 128 154 | F0 91 80 9A | 240 144 168 151 | F0 90 A8 97 | 240 145 150 149 | F0 91 96 95 | 240 145 140 156 | F0 91 8C 9C |
| UTF-16 | 55300 56346 | D804 DC1A | 55298 56855 | D802 DE17 | 55301 56725 | D805 DD95 | 55300 57116 | D804 DF1C |
| Numeric character reference | 𑀚 | 𑀚 | 𐨗 | 𐨗 | 𑖕 | 𑖕 | 𑌜 | 𑌜 |
| Preview | ྗ | ꡆ | 𑨒 | 𑐖 | 𑰕 | 𑆘 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | TIBETAN LETTER JA | TIBETAN SUBJOINED LETTER JA | PHAGS-PA LETTER JA | ZANABAZAR SQUARE LETTER JA | NEWA LETTER JA | BHAIKSUKI LETTER JA | SHARADA LETTER JA | |||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 3911 | U+0F47 | 3991 | U+0F97 | 43078 | U+A846 | 72210 | U+11A12 | 70678 | U+11416 | 72725 | U+11C15 | 70040 | U+11198 |
| UTF-8 | 224 189 135 | E0 BD 87 | 224 190 151 | E0 BE 97 | 234 161 134 | EA A1 86 | 240 145 168 146 | F0 91 A8 92 | 240 145 144 150 | F0 91 90 96 | 240 145 176 149 | F0 91 B0 95 | 240 145 134 152 | F0 91 86 98 |
| UTF-16 | 3911 | 0F47 | 3991 | 0F97 | 43078 | A846 | 55302 56850 | D806 DE12 | 55301 56342 | D805 DC16 | 55303 56341 | D807 DC15 | 55300 56728 | D804 DD98 |
| Numeric character reference | ཇ | ཇ | ྗ | ྗ | ꡆ | ꡆ | 𑨒 | 𑨒 | 𑐖 | 𑐖 | 𑰕 | 𑰕 | 𑆘 | 𑆘 |
| Preview | ဇ | ᨩ | ᨪ | ᦋ | ᦌ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | MYANMAR LETTER JA | TAI THAM LETTER LOW CA | TAI THAM LETTER LOW SA | NEW TAI LUE LETTER LOW TSA | NEW TAI LUE LETTER LOW SA | |||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 4103 | U+1007 | 6697 | U+1A29 | 6698 | U+1A2A | 6539 | U+198B | 6540 | U+198C |
| UTF-8 | 225 128 135 | E1 80 87 | 225 168 169 | E1 A8 A9 | 225 168 170 | E1 A8 AA | 225 166 139 | E1 A6 8B | 225 166 140 | E1 A6 8C |
| Numeric character reference | ဇ | ဇ | ᨩ | ᨩ | ᨪ | ᨪ | ᦋ | ᦋ | ᦌ | ᦌ |
| Preview | ជ | ຊ | ຌ | ช | ซ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | KHMER LETTER CO | LAO LETTER SO TAM | LAO LETTER PALI JHA | THAI CHARACTER CHO CHANG | THAI CHARACTER SO SO | |||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 6023 | U+1787 | 3722 | U+0E8A | 3724 | U+0E8C | 3594 | U+0E0A | 3595 | U+0E0B |
| UTF-8 | 225 158 135 | E1 9E 87 | 224 186 138 | E0 BA 8A | 224 186 140 | E0 BA 8C | 224 184 138 | E0 B8 8A | 224 184 139 | E0 B8 8B |
| Numeric character reference | ជ | ជ | ຊ | ຊ | ຌ | ຌ | ช | ช | ซ | ซ |
| Preview | ජ | 𑄎 | ᥗ | 𑜊 | 𑤓 | ꢙ | ꨎ | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | SINHALA LETTER ALPAPRAANA JAYANNA | CHAKMA LETTER JAA | TAI LE LETTER THA | AHOM LETTER JA | DIVES AKURU LETTER JA | SAURASHTRA LETTER JA | CHAM LETTER JA | |||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 3490 | U+0DA2 | 69902 | U+1110E | 6487 | U+1957 | 71434 | U+1170A | 71955 | U+11913 | 43161 | U+A899 | 43534 | U+AA0E |
| UTF-8 | 224 182 162 | E0 B6 A2 | 240 145 132 142 | F0 91 84 8E | 225 165 151 | E1 A5 97 | 240 145 156 138 | F0 91 9C 8A | 240 145 164 147 | F0 91 A4 93 | 234 162 153 | EA A2 99 | 234 168 142 | EA A8 8E |
| UTF-16 | 3490 | 0DA2 | 55300 56590 | D804 DD0E | 6487 | 1957 | 55301 57098 | D805 DF0A | 55302 56595 | D806 DD13 | 43161 | A899 | 43534 | AA0E |
| Numeric character reference | ජ | ජ | 𑄎 | 𑄎 | ᥗ | ᥗ | 𑜊 | 𑜊 | 𑤓 | 𑤓 | ꢙ | ꢙ | ꨎ | ꨎ |
| Preview | 𑘕 | 𑦵 | 𑩣 | ꠎ | 𑶀 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | MODI LETTER JA | NANDINAGARI LETTER JA | SOYOMBO LETTER JA | SYLOTI NAGRI LETTER JO | GUNJALA GONDI LETTER JA | KAITHI LETTER JA | ||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 71189 | U+11615 | 72117 | U+119B5 | 72291 | U+11A63 | 43022 | U+A80E | 73088 | U+11D80 | 69780 | U+11094 |
| UTF-8 | 240 145 152 149 | F0 91 98 95 | 240 145 166 181 | F0 91 A6 B5 | 240 145 169 163 | F0 91 A9 A3 | 234 160 142 | EA A0 8E | 240 145 182 128 | F0 91 B6 80 | 240 145 130 148 | F0 91 82 94 |
| UTF-16 | 55301 56853 | D805 DE15 | 55302 56757 | D806 DDB5 | 55302 56931 | D806 DE63 | 43022 | A80E | 55303 56704 | D807 DD80 | 55300 56468 | D804 DC94 |
| Numeric character reference | 𑘕 | 𑘕 | 𑦵 | 𑦵 | 𑩣 | 𑩣 | ꠎ | ꠎ | 𑶀 | 𑶀 | 𑂔 | 𑂔 |
| Preview | 𑒖 | ᰈ | ᤈ | ꯖ | 𑱸 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | TIRHUTA LETTER JA | LEPCHA LETTER JA | LIMBU LETTER JA | MEETEI MAYEK LETTER JIL | MARCHEN LETTER JA | |||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 70806 | U+11496 | 7176 | U+1C08 | 6408 | U+1908 | 43990 | U+ABD6 | 72824 | U+11C78 |
| UTF-8 | 240 145 146 150 | F0 91 92 96 | 225 176 136 | E1 B0 88 | 225 164 136 | E1 A4 88 | 234 175 150 | EA AF 96 | 240 145 177 184 | F0 91 B1 B8 |
| UTF-16 | 55301 56470 | D805 DC96 | 7176 | 1C08 | 6408 | 1908 | 43990 | ABD6 | 55303 56440 | D807 DC78 |
| Numeric character reference | 𑒖 | 𑒖 | ᰈ | ᰈ | ᤈ | ᤈ | ꯖ | ꯖ | 𑱸 | 𑱸 |
| Preview | 𑚑 | 𑠑 | 𑈐 | 𑋂 | 𑅛 | 𑊌 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | TAKRI LETTER JA | DOGRA LETTER JA | KHOJKI LETTER JA | KHUDAWADI LETTER JA | MAHAJANI LETTER JA | MULTANI LETTER JA | ||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 71313 | U+11691 | 71697 | U+11811 | 70160 | U+11210 | 70338 | U+112C2 | 69979 | U+1115B | 70284 | U+1128C |
| UTF-8 | 240 145 154 145 | F0 91 9A 91 | 240 145 160 145 | F0 91 A0 91 | 240 145 136 144 | F0 91 88 90 | 240 145 139 130 | F0 91 8B 82 | 240 145 133 155 | F0 91 85 9B | 240 145 138 140 | F0 91 8A 8C |
| UTF-16 | 55301 56977 | D805 DE91 | 55302 56337 | D806 DC11 | 55300 56848 | D804 DE10 | 55300 57026 | D804 DEC2 | 55300 56667 | D804 DD5B | 55300 56972 | D804 DE8C |
| Numeric character reference | 𑚑 | 𑚑 | 𑠑 | 𑠑 | 𑈐 | 𑈐 | 𑋂 | 𑋂 | 𑅛 | 𑅛 | 𑊌 | 𑊌 |
| Preview | ᬚ | ᯐ | ᨍ | ꦗ | 𑻪 | ꤺ | ᮏ | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | BALINESE LETTER JA | BATAK LETTER JA | BUGINESE LETTER JA | JAVANESE LETTER JA | MAKASAR LETTER JA | REJANG LETTER JA | SUNDANESE LETTER JA | |||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 6938 | U+1B1A | 7120 | U+1BD0 | 6669 | U+1A0D | 43415 | U+A997 | 73450 | U+11EEA | 43322 | U+A93A | 7055 | U+1B8F |
| UTF-8 | 225 172 154 | E1 AC 9A | 225 175 144 | E1 AF 90 | 225 168 141 | E1 A8 8D | 234 166 151 | EA A6 97 | 240 145 187 170 | F0 91 BB AA | 234 164 186 | EA A4 BA | 225 174 143 | E1 AE 8F |
| UTF-16 | 6938 | 1B1A | 7120 | 1BD0 | 6669 | 1A0D | 43415 | A997 | 55303 57066 | D807 DEEA | 43322 | A93A | 7055 | 1B8F |
| Numeric character reference | ᬚ | ᬚ | ᯐ | ᯐ | ᨍ | ᨍ | ꦗ | ꦗ | 𑻪 | 𑻪 | ꤺ | ꤺ | ᮏ | ᮏ |
| Preview | 𑴓 | |
|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | MASARAM GONDI LETTER JA | |
| Encodings | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 72979 | U+11D13 |
| UTF-8 | 240 145 180 147 | F0 91 B4 93 |
| UTF-16 | 55303 56595 | D807 DD13 |
| Numeric character reference | 𑴓 | 𑴓 |
| Preview | ᒉ | ᒋ | ᒍ | ᒐ | ᒡ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | CANADIAN SYLLABICS CE | CANADIAN SYLLABICS CI | CANADIAN SYLLABICS CO | CANADIAN SYLLABICS CA | CANADIAN SYLLABICS C | |||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 5257 | U+1489 | 5259 | U+148B | 5261 | U+148D | 5264 | U+1490 | 5281 | U+14A1 |
| UTF-8 | 225 146 137 | E1 92 89 | 225 146 139 | E1 92 8B | 225 146 141 | E1 92 8D | 225 146 144 | E1 92 90 | 225 146 161 | E1 92 A1 |
| Numeric character reference | ᒉ | ᒉ | ᒋ | ᒋ | ᒍ | ᒍ | ᒐ | ᒐ | ᒡ | ᒡ |
- The full range of CE Canadian syllabic characters can be found at the codepoint ranges 1489-14A2, 150F, 158E-1594, 1670-1676, & 18D7.
References
- ↑ Ifrah, Georges (2000). The Universal History of Numbers. From Prehistory to the Invention of the Computer. New York: John Wiley & Sons. pp. 447–450. ISBN 0-471-39340-1.
- ↑ Evolutionary chart, Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bengal Vol 7, 1838
- ↑ Everson, Michael (30 March 2005). "Proposal to add four characters for Sindhi to the BMP of the UCS" (PDF). Unicode.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 July 2014. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- ↑ Lekhwani, Kanhaiyalal. 1987 (1909). An intensive course in Sindhi. Mysore: Central Institute of Indian Languages; [New York]: Hippocrene Books. OCLC 18986594
- ↑ "Proposal to encode 55 characters for Vedic Sanskrit in the BMP of the UCS" (PDF). Unicode.org. 18 October 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 June 2012. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- ↑ Pall, Peeter. "Microsoft Word - kblhi2" (PDF). Eesti Keele Instituudi kohanimeandmed. Eesti Keele Instituudi kohanimeandmed. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- ↑ "The Bengali Alphabet" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-09-28.
- 1 2 Rajan, Vinod (16 July 2013). "Proposal to encode Gujarati Letter ZHA" (PDF). Unicode.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 July 2014. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- 1 2 Rajan, Vinodh (15 April 2013). "Proposal to encode Gujarati Sign Triple Nukta" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 July 2014. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- 1 2 Rajan, Vinodh (26 April 2013). "Recommendations to UTC on Script Proposals" (PDF). Unicode.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 July 2014. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- ↑ West, Andrew (1 April 2015). "What's new in Unicode 8.0 ?". BabelStone. BabelStone. Archived from the original on 16 September 2016. Retrieved 2 November 2016.
- ↑ Kanga, Ervad Kavasji Edalji (1936). Kanga, Navroji Pestonji Kavasji (ed.). Khordeh Avestâ (PDF). Bombay: Nirnaya Sagar Press. p. 5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 October 2016 – via www.avesta.org.
- ↑ Andrew Dalby (2004:139) Dictionary of Languages
- ↑ Some General Aspects of the Syllabics Orthography, Chris Harvey 2003
- 1 2 3 ALA-LC Romanization Tables, Khmer, rev. 2012.
- ↑ Pali (in various scripts) romanization table (ALA-LC)
- ↑ [https://www.loc.gov/catdir/cpso/romanization/lao.pdf Lao romanization table (ALA-LC)
- ↑ Pali (in various scripts) romanization table (ALA-LC)
- ↑ [https://www.loc.gov/catdir/cpso/romanization/lao.pdf Lao romanization table (ALA-LC)
- Kurt Elfering: Die Mathematik des Aryabhata I. Text, Übersetzung aus dem Sanskrit und Kommentar. Wilhelm Fink Verlag, München, 1975, ISBN 3-7705-1326-6
- Georges Ifrah: The Universal History of Numbers. From Prehistory to the Invention of the Computer. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2000, ISBN 0-471-39340-1.
- B. L. van der Waerden: Erwachende Wissenschaft. Ägyptische, babylonische und griechische Mathematik. Birkhäuser-Verlag, Basel Stuttgart, 1966, ISBN 3-7643-0399-9
- Fleet, J. F. (January 1911). "Aryabhata's System of Expressing Numbers". Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland. 43: 109–126. doi:10.1017/S0035869X00040995. ISSN 0035-869X. JSTOR 25189823.
- Fleet, J. F. (1911). "Aryabhata's System of Expressing Numbers". The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland. Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland. 43: 109–126. doi:10.1017/S0035869X00040995. JSTOR 25189823.