 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.935 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
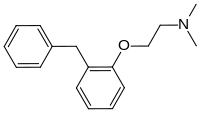
| Formula | C17H21NO |
| Molar mass | 255.361 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Phenyltoloxamine is an antihistamine with sedative and analgesic effects.[1][2] It is available in combination with other drugs such as paracetamol (acetominophen).[3]
Common use
Phenyltoloxamine is widely used in preparations as an enhancing agent for some analgesics and antitussives (acetaminophen, dihydrocodeine, codeine, hydrocodone). It is widely used in certain parts of the world as cough suppressant usually with codeine, and sometimes by itself or in addition to dextromethorphan as it, like diphenhydramine, possesses antitussive action of its own and is particularly useful in semi-productive coughs because of its moderate drying action.
Phenyltoloxamine is used in combination with paracetamol, aspirin and other salicylates and other drugs in proprietary preparations available over the counter for backache, muscle strains and similar conditions.
Adverse effects
Common adverse effects are those associated with most anticholinergics, with effects being more pronounced in children and the elderly.
Availability
Though it is rare in several Western countries, phenyltoloxamine is widely used on the global scale, particularly in the developing world.
In the past it was not a controlled substance. It was taken off the market but is available OTC again in the US by some pharmaceutical companies. Some preparations contain opiates such as codeine or hydrocodone and are controlled. When used in preparations with acetaminophen it is generally over the counter.
Phenyltoloxamine combinations are sold under wide variety of preparations, brand names and dosages around the world:
- Aceta-Gesic, Ed-Flex, Dologesic, Duraxin, Flextra-650, Novagesic, Pain-gesic, Phenylgesic - North America
- Codipront - Europe/South America
- Codivis - Israel
See also
References
- ↑ "Phenyltoloxamine". Drugbank.
- ↑ Cronk GA, Naumann DE (May 1955). "Phenyltoloxamine--dosage, toxicity, and clinical application". New York State Journal of Medicine. 55 (10): 1465–7. PMID 14370508.
- ↑ "Phenyltoloxamine-acetaminophen oral". WebMD.
| Benzimidazoles (*) | |
|---|---|
| Diarylmethanes |
|
| Ethylenediamines | |
| Tricyclics | |
| Others |
|
| For topical use | |
| Psychedelics (5-HT2A agonists) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dissociatives (NMDAR antagonists) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deliriants (mAChR antagonists) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H1 |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2 |
| ||||
| H3 |
| ||||
| H4 |
| ||||
| |||||
| mAChRsTooltip Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precursors (and prodrugs) | |||||
| |||||