
4-Substituted-2,5-dimethoxyamphetamines (DOx) is a chemical class of substituted amphetamine derivatives featuring methoxy groups at the 2- and 5- positions of the phenyl ring, and a substituent such as alkyl or halogen at the 4- position of the phenyl ring.[1] Most compounds of this class are potent and long-lasting psychedelic drugs, and act as highly selective 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptor partial agonists. A few bulkier derivatives such as DOAM have similarly high binding affinity for 5-HT2 receptors but instead act as antagonists, and so do not produce psychedelic effects though they retain amphetamine-like stimulant effects.
DOx derivatives
The DOx family includes the following members:
| Structure | Name | Abbreviation | CAS number |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-amylamphetamine | DOAM | 63779-90-8 |
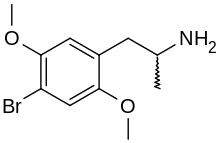 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-bromoamphetamine | DOB | 64638-07-9 (racemate) |
 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-butylamphetamine | DOBU | 63779-89-5 |
 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-chloroamphetamine | DOC | 123431-31-2 |
 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethoxyamphetamine | MEM | 16128-88-4 |
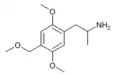 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(methoxymethyl)amphetamine | DOMOM [2] | 260810-10-4 |
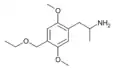 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(ethoxymethyl)amphetamine | DOMOE | 930836-81-0 |
 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethylamphetamine | DOET | 22004-32-6 |
 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethylthioamphetamine | Aleph-2 | 185562-00-9 |
 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-fluoroamphetamine | DOF | 125903-69-7 |
amphetamine.svg.png.webp) |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(2-fluoroethyl)amphetamine | DOEF | 121649-01-2 |
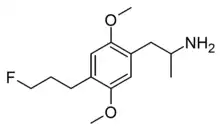 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(3-fluoropropyl)amphetamine | DOPF | |
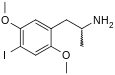 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine | DOI | 42203-78-1 |
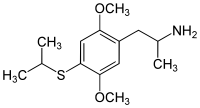 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-isopropylthioamphetamine | Aleph-4 | 123643-26-5 |
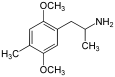 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine | DOM | 15588-95-1 |
 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-methylthioamphetamine | Aleph-1 | 61638-07-1 |
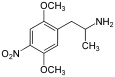 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-nitroamphetamine | DON | 67460-68-8 |
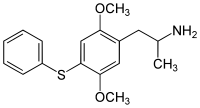 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-phenylthioamphetamine | Aleph-6 | 952006-44-9 |
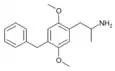 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-benzylamphetamine | DOBZ [3] | 125903-73-3 |
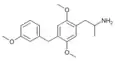 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(3-methoxybenzyl)amphetamine | DO3MeOBZ [4] | 930836-90-1 |
 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-[(tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methyl]amphetamine | DOTHFM | 930776-12-8 |
 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-propylamphetamine | DOPR | 63779-88-4 |
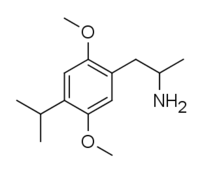 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-isopropylamphetamine | DOiP | 42306-96-7 |
 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-propylthioamphetamine | Aleph-7 | 207740-16-7 |
 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(difluoromethyl)amphetamine | DODFM | |
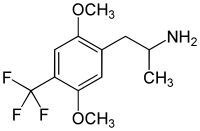 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-trifluoromethylamphetamine | DOTFM | 159277-07-3 |
 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)amphetamine | DOTFE [5] | |
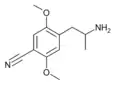 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-cyanoamphetamine | DOCN [6] | 125903-74-4 |
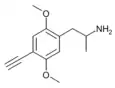 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethynylamphetamine | DOYN [7] | 633290-70-7 |
Related compounds
A number of additional compounds are known with alternative substitutions:
| Structure | Name | Abbreviation | CAS number |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
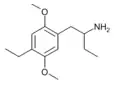
Dimoxamine ("Ariadne") | 4C-D | 52842-59-8 |
 |
1-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethylphenyl)butan-2-amine [8] | 4C-E | |
 |
1-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(n-propyl)phenyl)butan-2-amine | 4C-P | |
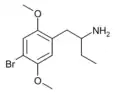 |
1-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)butan-2-amine | 4C-B | 69294-23-1 |
 |
1-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-chlorophenyl)butan-2-amine | 4C-C | 791010-74-7 |
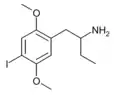 |
1-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)butan-2-amine | 4C-I | 758631-75-3 |
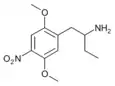 |
1-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-nitrophenyl)butan-2-amine | 4C-N | 775234-58-7 |
 |
1-[2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(ethylthio)phenyl]butan-2-amine | 4C-T-2 | 850007-13-5 |
.png.webp) |
Dimethoxymethamphetamine ("Beatrice") | N-methyl-DOM | 92206-37-6 |
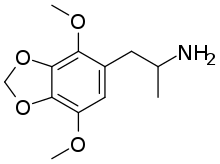 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine | DMMDA | 15183-13-8 |
 |
2,5-dimethoxy-3,4-dimethylamphetamine ("Ganesha") | 3-methyl-DOM | 207740-37-2 |
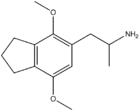 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-3,4-trimethylenylamphetamine | G-3 | |
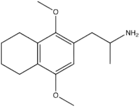 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-3,4-tetramethylenylamphetamine | G-4 | |
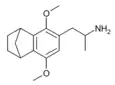 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-3,4-norbornylamphetamine | G-5 | |
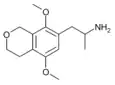 |
1-(5,8-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydro-1H-isochromen-7-yl)propan-2-amine [9] | G-O | 774538-38-4 |
 |
2,5-Dimethoxy-3,4-dichloroamphetamine | DODC | 1373918-65-0 |
 |
IDNNA | IDNNA | 67707-78-2 |
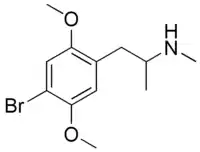 |
Methyl-DOB | N-methyl-DOB | 155638-80-5 |
 |
2,3,4,5-Tetramethoxyamphetamine | 2,3,4,5-Tetramethoxyamphetamine | 23693-26-7 |
 |
1-(4-Bromo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydrofuro[2,3-f][1]benzofuran-8-yl)propan-2-amine | DOB-FLY | 219986-75-1 |
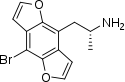 |
Bromo-DragonFLY | DOB-DFLY | 502759-67-3 |
 |
3-(4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)azetidine | Compound 1,[10] ZC-B | |
See also
References
- ↑ Daniel Trachsel; David Lehmann & Christoph Enzensperger (2013). Phenethylamine: Von der Struktur zur Funktion. Nachtschatten Verlag AG. ISBN 978-3-03788-700-4.
- ↑ Harms A, Ulmer E, Kovar K. Synthesis and 5-HT2A radioligand receptor binding assays of DOMCl and DOMOM, two novel 5-HT2A receptor ligands. Arch. Pharm., 16 Jun 2003, 336(3): 155–158. doi:10.1002/ardp.200390014
- ↑ Nelson DL, Lucaites VL, Wainscott DB, Glennon RA. Comparisons of hallucinogenic phenylisopropylamine binding affinities at cloned human 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptors. N-S. Arch. Pharmacol., 1 Jan 1999, 359(1): 1–6. doi:10.1007/PL00005315
- ↑ Hellberg M, Namil A, Feng Z, Ward J. Phenylethylamine Analogs and Their Use for Treating Glaucoma. Patent WO 2007/038372, 6 Apr 2007
- ↑ Trachsel D. Fluorine in psychedelic phenethylamines. Drug Test. Anal., 1 Jul 2012, 4(7-8): 577-590.doi:10.1002/dta.413
- ↑ Seggel MR, Yousif MY, Lyon RA, Titeler M, Roth BL, Suba EA, Glennon, RA. A structure-affinity study of the binding of 4-substituted analogues of 1-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminopropane at 5-HT2 serotonin receptors. J. Med. Chem., 1 Mar 1990, 33(3): 1032–1036. doi:10.1021/jm00165a023
- ↑ Trachsel D (August 2003). "Synthesis of Novel (Phenylalkyl) amines for the Investigation of Structure–Activity Relationships, Part 3: 4‐Ethynyl‐2,5‐dimethoxyphenethylamine (= 4‐Ethynyl‐2, 5‐dimethoxybenzeneethanamine; 2C‐YN)". Helvetica Chimica Acta. 86 (8): 2754–9. doi:10.1002/hlca.200390224.
- ↑ Shulgin AT. Treatment of senile geriatric patients to restore performance. Patent US 4034113
- ↑ Hellberg MR, Namil A. Benzopyran analogs and their use for the treatment of glaucoma. Patent US 7396856
- ↑ Kristensen J, et al. 5-HT2A Agonists for Use in Treatment of Depression. Patent US 2021/0137908