 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
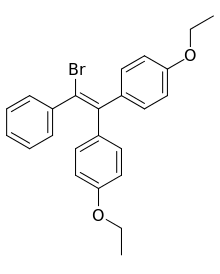
| Formula | C24H23BrO2 |
| Molar mass | 423.350 g·mol−1 |
Estrobin, also known as α,α-di(p-ethoxyphenyl)-β-phenylbromoethylene and commonly abbreviated as DBE, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the triphenylethylene group that was never marketed.[1][2] Chlorotrianisene, and subsequently clomifene and tamoxifen, were derived from it.[1][2] Estrobin, similarly to other triphenylethylenes, is very lipophilic and hence very long-lasting in its duration of action.[1][2] Similarly to chlorotrianisene, estrobin behaves a prodrug to a much more potent estrogen in the body.[2]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Jordan VC (1986). Estrogen/antiestrogen Action and Breast Cancer Therapy. Univ of Wisconsin Press. pp. 23–. ISBN 978-0-299-10480-1.
- 1 2 3 4 Welsh AL (April 1954). "Use of synthetic estrogenic substance chlorotrianisene (TACE) in treatment of acne". Archives of Dermatology. 69 (4): 418–27. doi:10.1001/archderm.1954.01540160020004. PMID 13147544.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.