 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
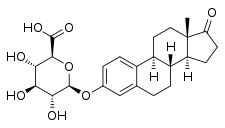
| IUPAC name
17-Oxoestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-3-yl β-D-glucopyranosiduronic acid | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S,3S,4S,5R,6S)-3,4,5-Trihydroxy-6-{[(3aS,3bR,9bS,11aS)-11a-methyl-1-oxo-2,3,3a,3b,4,5,9b,10,11,11a-decahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-7-yl]oxy}oxane-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Estrone 3-glucuronide; Estrone 3-D-glucuronide; Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3-ol-17-one 3-D-glucuronoside | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H30O8 | |
| Molar mass | 446.496 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
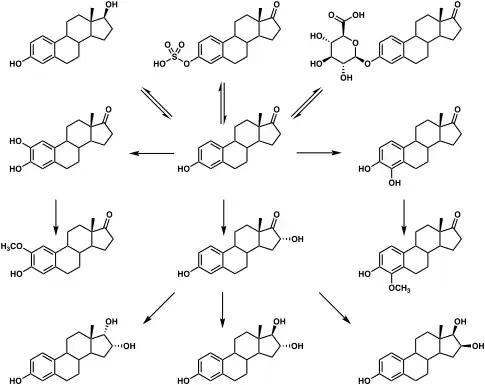
Estrone glucuronide, or estrone-3-D-glucuronide, is a conjugated metabolite of estrone.[1] It is formed from estrone in the liver by UDP-glucuronyltransferase via attachment of glucuronic acid and is eventually excreted in the urine by the kidneys.[1] It has much higher water solubility than does estrone.[1] Glucuronides are the most abundant estrogen conjugates and estrone glucuronide is the dominant metabolite of estradiol.[1]
When exogenous estradiol is administered orally, it is subject to extensive first-pass metabolism (95%) in the intestines and liver.[2][3] A single administered dose of estradiol is absorbed 15% as estrone, 25% as estrone sulfate, 25% as estradiol glucuronide, and 25% as estrone glucuronide.[2] Formation of estrogen glucuronide conjugates is particularly important with oral estradiol as the percentage of estrogen glucuronide conjugates in circulation is much higher with oral ingestion than with parenteral estradiol.[2] Estrone glucuronide can be reconverted back into estradiol, and a large circulating pool of estrogen glucuronide and sulfate conjugates serves as a long-lasting reservoir of estradiol that effectively extends its terminal half-life of oral estradiol.[2][3] In demonstration of the importance of first-pass metabolism and the estrogen conjugate reservoir in the pharmacokinetics of estradiol,[2] the terminal half-life of oral estradiol is 13 to 20 hours[4] whereas with intravenous injection its terminal half-life is only about 1 to 2 hours.[5]
| Estrogen | Other names | RBA (%)a | REP (%)b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER | ERα | ERβ | ||||
| Estradiol | E2 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Estradiol 3-sulfate | E2S; E2-3S | ? | 0.02 | 0.04 | ||
| Estradiol 3-glucuronide | E2-3G | ? | 0.02 | 0.09 | ||
| Estradiol 17β-glucuronide | E2-17G | ? | 0.002 | 0.0002 | ||
| Estradiol benzoate | EB; Estradiol 3-benzoate | 10 | 1.1 | 0.52 | ||
| Estradiol 17β-acetate | E2-17A | 31–45 | 24 | ? | ||
| Estradiol diacetate | EDA; Estradiol 3,17β-diacetate | ? | 0.79 | ? | ||
| Estradiol propionate | EP; Estradiol 17β-propionate | 19–26 | 2.6 | ? | ||
| Estradiol valerate | EV; Estradiol 17β-valerate | 2–11 | 0.04–21 | ? | ||
| Estradiol cypionate | EC; Estradiol 17β-cypionate | ?c | 4.0 | ? | ||
| Estradiol palmitate | Estradiol 17β-palmitate | 0 | ? | ? | ||
| Estradiol stearate | Estradiol 17β-stearate | 0 | ? | ? | ||
| Estrone | E1; 17-Ketoestradiol | 11 | 5.3–38 | 14 | ||
| Estrone sulfate | E1S; Estrone 3-sulfate | 2 | 0.004 | 0.002 | ||
| Estrone glucuronide | E1G; Estrone 3-glucuronide | ? | <0.001 | 0.0006 | ||
| Ethinylestradiol | EE; 17α-Ethynylestradiol | 100 | 17–150 | 129 | ||
| Mestranol | EE 3-methyl ether | 1 | 1.3–8.2 | 0.16 | ||
| Quinestrol | EE 3-cyclopentyl ether | ? | 0.37 | ? | ||
| Footnotes: a = Relative binding affinities (RBAs) were determined via in-vitro displacement of labeled estradiol from estrogen receptors (ERs) generally of rodent uterine cytosol. Estrogen esters are variably hydrolyzed into estrogens in these systems (shorter ester chain length -> greater rate of hydrolysis) and the ER RBAs of the esters decrease strongly when hydrolysis is prevented. b = Relative estrogenic potencies (REPs) were calculated from half-maximal effective concentrations (EC50) that were determined via in-vitro β‐galactosidase (β-gal) and green fluorescent protein (GFP) production assays in yeast expressing human ERα and human ERβ. Both mammalian cells and yeast have the capacity to hydrolyze estrogen esters. c = The affinities of estradiol cypionate for the ERs are similar to those of estradiol valerate and estradiol benzoate (figure). Sources: See template page. | ||||||
Metabolic pathways of estradiol in humans
|
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Human Metabolome Database: Showing metabocard for Estrone glucuronide (HMDB0004483)".
- 1 2 3 4 5 Oettel M, Schillinger E (6 December 2012). Estrogens and Antiestrogens II: Pharmacology and Clinical Application of Estrogens and Antiestrogen. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 268–. ISBN 978-3-642-60107-1.
- 1 2 Lauritzen C, Studd JW (22 June 2005). Current Management of the Menopause. CRC Press. pp. 364–. ISBN 978-0-203-48612-2.
- ↑ Stanczyk FZ, Archer DF, Bhavnani BR (June 2013). "Ethinyl estradiol and 17β-estradiol in combined oral contraceptives: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and risk assessment". Contraception. 87 (6): 706–27. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2012.12.011. PMID 23375353.
- ↑ Düsterberg B, Nishino Y (December 1982). "Pharmacokinetic and pharmacological features of oestradiol valerate". Maturitas. 4 (4): 315–24. doi:10.1016/0378-5122(82)90064-0. PMID 7169965.