 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Glurenorm |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | High (Tmax = 2–3 hours) |
| Metabolism | Extensive hepatic |
| Onset of action | 1–1.5 hours |
| Excretion | Biliary (95%), renal (5%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.046.770 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
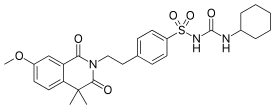
| Formula | C27H33N3O6S |
| Molar mass | 527.64 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Gliquidone (INN, sold under the trade name Glurenorm) is an anti-diabetic medication in the sulfonylurea class.[1] It is classified as a second-generation sulfonylurea. It is used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus type 2. It is marketed by the pharmaceutical company Boehringer Ingelheim (Germany).
Contraindications
- Allergy to sulfonylureas or sulfonamides
- Diabetes mellitus type 1
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Patients that underwent removal of the pancreas
- Acute porphyria
- Severe liver disease accompanying with liver insufficiency
- Several conditions (e.g., infectious diseases or major surgical intervention), when insulin administration is required
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding[2]
Pharmacokinetics
Gliquidone is fully metabolized by the liver. Its metabolites are excreted virtually completely with bile (even with long-term administration), thus allowing the use of medication in diabetic patients with kidney disease and diabetic nephropathy.[2]
References
- ↑ Malaisse WJ (2006). "Gliquidone contributes to improvement of type 2 diabetes mellitus management: a review of pharmacokinetic and clinical trial data". Drugs in R&D. 7 (6): 331–7. doi:10.2165/00126839-200607060-00002. PMID 17073516. S2CID 10155445.
- 1 2 "Glurenorm (gliquidone) 30 mg Tablets, for Oral Use. Full Prescribing Information". Russian State Register of Medicinal Products (in Russian). Boehringer Ingelheim. Archived from the original on 14 August 2016. Retrieved 12 July 2016.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.